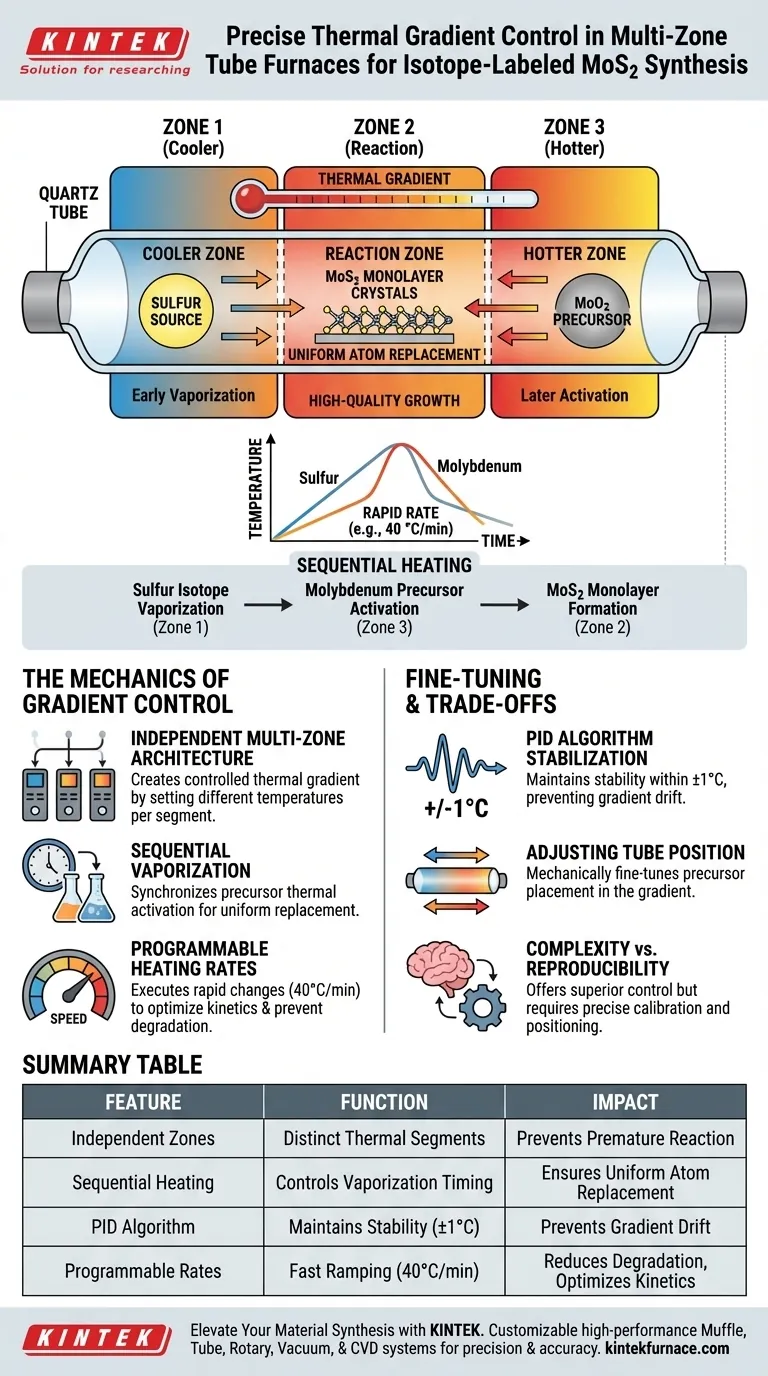
Precise temperature gradient control is achieved through the combination of independent zone heating and programmable thermal profiles. In a multi-zone tube furnace, specific heating rates—such as 40 °C per minute—are applied to distinct sections of the quartz tube. This allows the furnace to maintain different temperatures simultaneously, ensuring that the Molybdenum Dioxide (MoO2) precursor and Sulfur powder are processed at their exact, respective evaporation and reaction points.
Core Takeaway The success of isotope-labeled MoS2 synthesis relies on sequential heating. The multi-zone furnace acts as a timing mechanism, vaporizing the sulfur isotope source and the molybdenum source at different moments to ensure atoms replace active sites uniformly, creating high-quality monolayer crystals.

The Mechanics of Gradient Control
Independent Multi-Zone Architecture
A multi-zone furnace is divided into physically distinct heating segments. By setting different temperatures for each segment, the system creates a controlled thermal gradient across the length of the tube. This allows the Sulfur source (placed in a cooler zone) and the MoO2 source (placed in a hotter zone) to exist in the same chamber without reacting prematurely.
Sequential Vaporization
The primary goal of this gradient is to facilitate sequential heating. The furnace controls the timing so that the sulfur isotope vaporizes and travels to the reaction site exactly when the molybdenum source is thermally activated. This synchronization ensures that sulfur atoms sufficiently replace active sites in the molybdenum source.
Programmable Heating Rates
Industrial-grade furnaces utilize advanced software to execute rapid temperature changes, such as a rate of 40 °C per minute. This speed prevents the precursors from degrading during a long ramp-up phase and ensures the reaction occurs closer to thermodynamic equilibrium.
Fine-Tuning the Thermal Environment
Adjusting Tube Position
Beyond electronic controls, the physical placement of the quartz tube within the furnace chamber is a critical variable. By shifting the tube relative to the heating elements, operators can mechanically fine-tune exactly where the precursors sit within the thermal gradient.
PID Algorithm Stabilization
To maintain these gradients over time, modern furnaces use PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers. These systems automatically adjust power output to correct deviations, maintaining temperature stability within ±1°C and ensuring the gradient does not drift during the synthesis process.
Minimizing Intra-Zone Variation
While the goal is a gradient between zones, the temperature within each specific zone must remain uniform. Adjustable heating elements arranged around the tube prevent hot spots, ensuring that the "reaction zone" provides consistent thermal energy to the forming monolayer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity vs. Reproducibility
Utilizing multiple zones increases the complexity of the setup. While it offers superior control over reaction kinetics, it requires precise calibration; a slight mismatch in the heating ramp between zones can lead to incomplete sulfurization or uneven crystal growth.
Positioning Sensitivity
Relying on physical tube positioning for gradient control introduces a manual variable. While effective for fine-tuning, it can be difficult to replicate perfectly between different experiments compared to purely software-driven zone control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving high-quality isotope-labeled monolayers requires balancing equipment capabilities with experimental design.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Prioritize a furnace with high-precision PID control (±1°C) to ensure the reaction temperature remains stable during the critical growth phase.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Timing: Utilize independent multi-zone controls to program distinct ramp rates, ensuring the sulfur vapor arrives exactly when the molybdenum precursor is active.
Success depends on synchronizing the thermal activation of your precursors through precise spatial and temporal programming.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Gradient Control | Impact on MoS2 Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Independent Heating Zones | Creates distinct thermal segments | Prevents premature precursor reaction |
| Sequential Heating | Controls vaporization timing | Ensures uniform atom replacement in active sites |
| PID Algorithm | Maintains stability within ±1°C | Prevents gradient drift during crystal growth |
| Programmable Rates | Fast ramping (e.g., 40°C/min) | Reduces precursor degradation and optimizes kinetics |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of high-quality isotope-labeled monolayers. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Whether you need independent multi-zone control for complex thermal gradients or rapid heating rates for specialized chemical vapor deposition, our furnaces deliver the stability and accuracy your research demands. Empower your lab with the tools for breakthrough results.
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Vaibhav Varade, Jana Vejpravová. Sulfur isotope engineering in heterostructures of transition metal dichalcogenides. DOI: 10.1039/d4na00897a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the high-temperature heat treatment of vermiculite? Precision Control Expert
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in cigarette waste pyrolysis? Optimize Carbon Material Conversion
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace essential for PPAC activation? Precision Thermal Control for Superior Porosity
- What is an alumina tube furnace? Essential for High-Temp, Contamination-Free Material Processing
- What are the common features of the heating chamber in a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What environmental parameters must high-temperature furnaces maintain for YIG thin film annealing? Expert Guide
- How does a horizontal tube furnace ensure experimental safety and accuracy during the thermal dehydrogenation of Ca(AlH4)2?



















