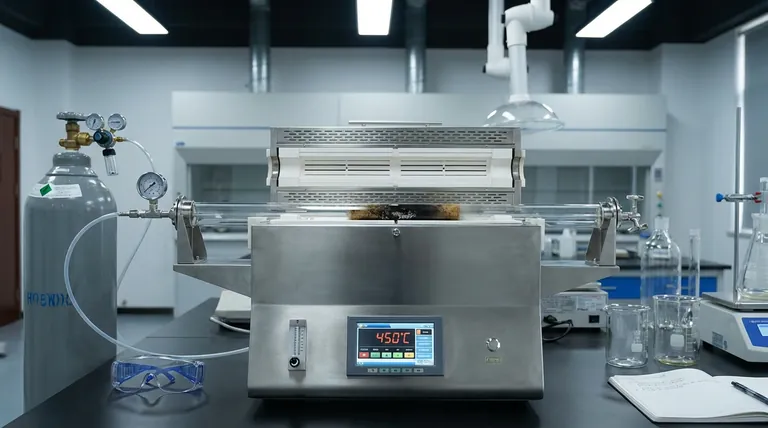
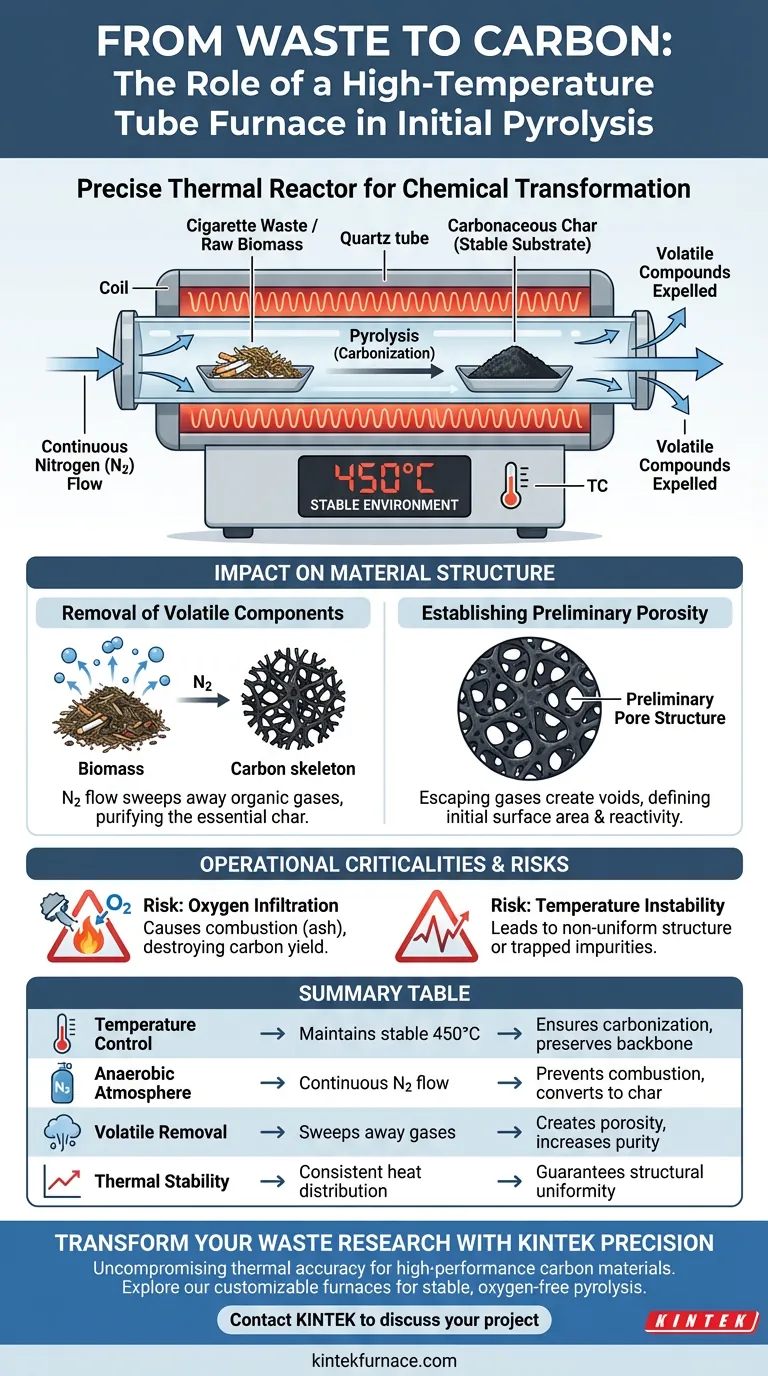
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the precise thermal reactor required to chemically transform cigarette waste into a stable carbon substrate. During the initial pyrolysis stage, it maintains a strictly controlled 450°C environment while circulating nitrogen to prevent combustion. This process drives off volatile compounds and converts the raw biomass into a carbonaceous char with a defined preliminary structure.
By establishing an oxygen-free, stable thermal environment, the tube furnace ensures the successful conversion of raw biomass into a preliminary carbon skeleton, preventing combustion and defining the material's initial structural properties.

The Mechanics of the Transformation
To understand the role of the furnace, it is necessary to look at how it controls the physical environment around the sample.
Precise Thermal Regulation
The furnace utilizes electric heating coils wrapped around a cylindrical chamber to generate heat. A thermocouple allows the system to monitor and adjust the temperature in real-time.
For cigarette waste specifically, the furnace maintains a stable 450°C. This specific temperature is sufficient to initiate chemical decomposition without destroying the carbon backbone of the material.
Creating an Anaerobic Atmosphere
Pyrolysis requires the absence of oxygen. The tube furnace is designed to support a continuous flow of nitrogen gas.
This gas flow purges oxygen from the cylindrical cavity. By creating these anaerobic conditions, the furnace ensures the waste material undergoes carbonization (turning into charcoal) rather than combustion (burning to ash).
Impact on Material Structure
The furnace does more than simply heat the material; it dictates the physical architecture of the final product.
Removal of Volatile Components
As the furnace holds the material at 450°C, volatile organic compounds within the cigarette waste act as gases and are expelled.
The continuous nitrogen flow helps sweep these released volatiles away from the sample. This purification step leaves behind the essential "char," or carbonaceous material.
Establishing Preliminary Porosity
The escape of these volatile components is not passive; it is structural. As gases exit the solid material, they create voids.
This process establishes a preliminary pore structure within the carbon-based substrate. This initial porosity is critical, as it determines the surface area and potential reactivity of the final carbon material.
Operational Criticalities and Risks
While the tube furnace is a robust tool, the process relies on maintaining a delicate balance of variables.
The Risk of Oxygen Infiltration
The most critical function of the furnace is seal integrity. If the nitrogen atmosphere is compromised, oxygen will enter the chamber.
At 450°C, the introduction of oxygen causes immediate combustion. This destroys the carbon yield and results in useless ash rather than the desired porous carbon substrate.
Temperature Stability Concerns
The furnace must maintain stability to ensure uniformity. Fluctuations below the target temperature may leave volatile impurities trapped in the matrix.
Conversely, temperature spikes could alter the pore structure unpredictably. The control system's ability to regulate the heating coils is vital for reproducible results.
Optimizing the Pyrolysis Process
To ensure the highest quality conversion of cigarette waste, you must focus on the specific parameters of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Prioritize the integrity of the nitrogen flow to ensure a completely oxygen-free environment, maximizing the conversion of biomass to carbonaceous char.
- If your primary focus is structural consistency: regularly calibrate the thermocouple to ensure the furnace maintains a rigid 450°C, guaranteeing uniform volatile removal and pore formation.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the architect of the material's initial carbon framework.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Pyrolysis | Impact on Carbon Material |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintains stable 450°C | Ensures carbonization without destroying the material backbone |
| Anaerobic Atmosphere | Continuous Nitrogen (N2) flow | Prevents combustion and ensures raw biomass converts to char |
| Volatile Removal | Sweeps away organic gases | Creates preliminary porosity and increases material purity |
| Thermal Stability | Consistent heat distribution | Guarantees structural uniformity and reproducible pore formation |
Transform Your Waste Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance carbon materials require uncompromising thermal accuracy. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all designed to provide the stable, oxygen-free environments essential for advanced pyrolysis and carbonization.
Whether you are converting biomass or optimizing laboratory high-temperature processes, our customizable furnaces ensure the structural consistency your research demands. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique project needs and see how our expertise can elevate your material outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Giovanni Zuccante, Carlo Santoro. Transforming Cigarette Wastes into Oxygen Reduction Reaction Electrocatalyst: Does Each Component Behave Differently? An Experimental Evaluation. DOI: 10.1002/celc.202300725
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of high temperature tube furnaces? Unlock Precision for Material Science
- How vacuum pumping affects Zr2.5Nb nitriding? Achieve pure ZrN surfaces in high-temp tube furnaces.
- How do tube furnaces provide precise and uniform heating? Unlock Consistent Thermal Processing
- What are the pros and cons of vertical tube furnaces? Precision vs. Capacity for Your Lab
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Why are multi zone tube furnaces particularly useful for nanomaterial research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Synthesis
- How does a manual laboratory jack contribute to process precision in split tube furnaces? Achieve Perfect Alignment
- What materials can be processed in tubular furnaces? Versatile Solutions for Metals, Ceramics, and More



















