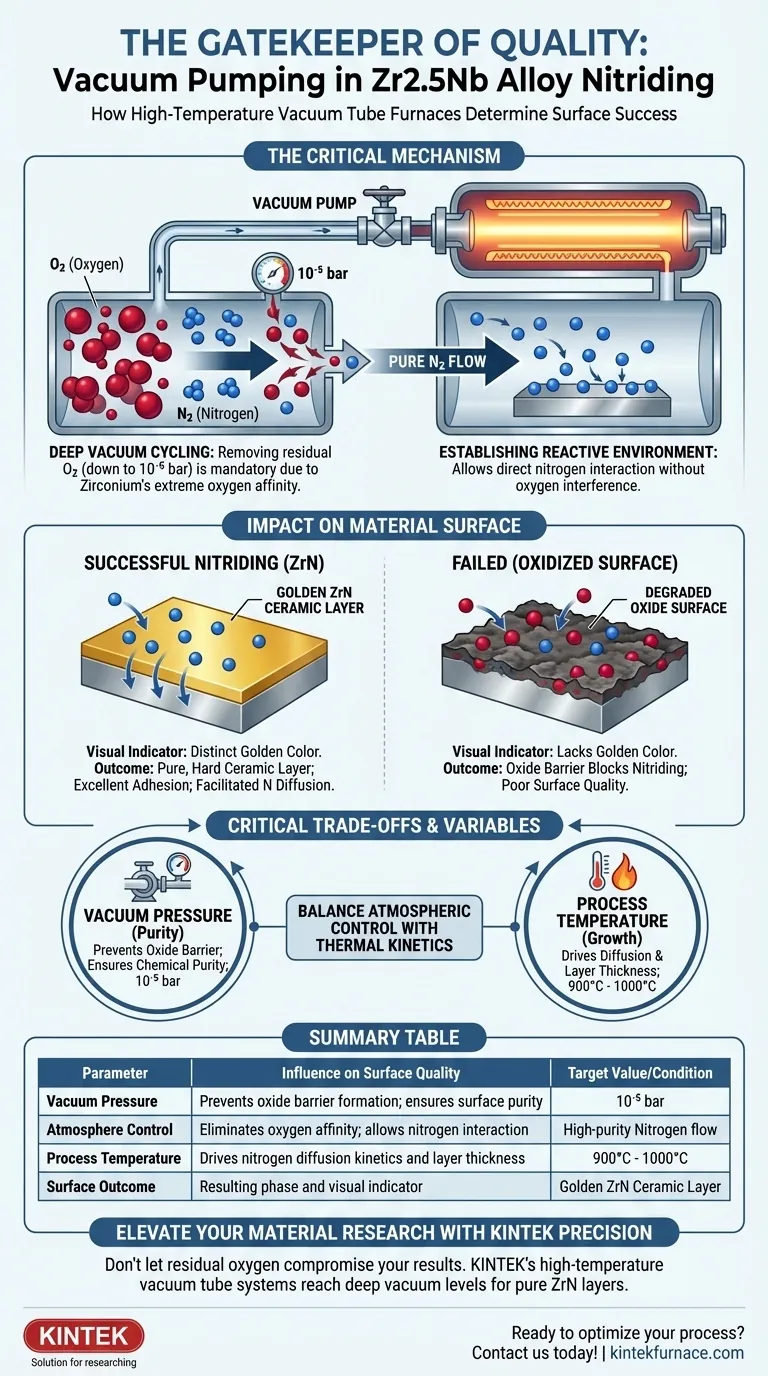
The vacuum pumping procedure is the critical gatekeeper that determines whether your Zr2.5Nb alloy forms a high-performance ceramic layer or a degraded oxide surface.
By utilizing multiple vacuum cycling steps to reach pressures as low as $10^{-5}$ bar, the furnace aggressively removes residual oxygen. This step is mandatory because zirconium has an extreme affinity for oxygen; without this deep vacuum, the alloy would oxidize immediately, preventing the formation of the desired golden zirconium nitride (ZrN) layer.
Core Takeaway Because Zirconium reacts with oxygen more readily than nitrogen, a standard purge is insufficient for high-quality nitriding. A high-vacuum environment combined with high-purity gas flow is the specific mechanism that prevents surface oxidation, allowing the formation of a pure, hard ceramic ZrN coating.

The Mechanism of Surface Protection
Overcoming Zirconium's Oxygen Affinity
Zirconium alloys, such as Zr2.5Nb, are highly reactive metals. They possess a natural chemical "hunger" for oxygen that surpasses their affinity for nitrogen.
If even trace amounts of oxygen remain in the furnace chamber, the alloy will preferentially form zirconium oxide. This oxide acts as a barrier, effectively blocking the nitriding process and degrading the surface quality.
The Role of Deep Vacuum Cycling
To counteract this, high-temperature tube furnaces employ a rigorous vacuum cycling process. This is not a single evacuation, but often a series of cycles designed to scour the chamber atmosphere.
The target pressure drops to approximately $10^{-5}$ bar. At this level of vacuum, the volume of residual oxygen is reduced to a negligible quantity, creating a "clean slate" for the alloy surface.
Establishing the Reactive Environment
Once the deep vacuum is achieved, high-purity nitrogen is introduced to the chamber. Because the vacuum cycle has already removed the competing oxygen, the nitrogen atoms can interact directly with the zirconium surface without interference.
Impact on Material Characteristics
Achieving the ZrN Ceramic Layer
The primary indicator of a successful vacuum procedure is the formation of Zirconium Nitride (ZrN). When the vacuum successfully excludes oxygen, the nitrogen reacts to form a distinct ceramic layer.
This layer is characterized by a specific golden color. If the vacuum procedure is compromised, the surface will lack this signature appearance, indicating oxide contamination.
Facilitating Nitrogen Diffusion
The vacuum environment creates the initial conditions required for diffusion. By keeping the surface metallic and oxide-free, nitrogen atoms can penetrate the alloy lattice.
While the vacuum protects the surface, the subsequent heating (typically 900°C to 1000°C) drives the kinetics. The vacuum ensures that the diffusion occurring at these high temperatures involves nitrogen, not oxygen.
Critical Trade-offs and Process Variables
Vacuum vs. Temperature Roles
It is vital to distinguish between surface purity and layer properties. The vacuum procedure guarantees the chemical purity of the surface (avoiding oxidation).
However, the mechanical properties—such as layer thickness and hardness—are driven by temperature. The vacuum permits the reaction, but thermal energy drives the growth.
The Limits of Vacuum Cycling
While deep vacuum ($10^{-5}$ bar) is effective, it increases cycle time and energy consumption.
Furthermore, even a perfect vacuum cannot correct for low-purity gas inputs. If the nitrogen gas introduced after pumping contains moisture or oxygen, the benefits of the vacuum cycle are negated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the nitriding of Zr2.5Nb, you must balance atmospheric control with thermal kinetics.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and adhesion: Prioritize the vacuum cycling phase to ensure pressures reach $10^{-5}$ bar, ensuring the elimination of oxides before heating begins.
- If your primary focus is layer thickness and hardness: Focus on the thermal parameters, increasing temperatures toward 1000°C to maximize nitrogen diffusion and promote (111) crystal plane growth.
The vacuum provides the clean canvas, but precise thermal control paints the picture of a durable, high-performance alloy.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence on Surface Quality | Target Value/Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pressure | Prevents oxide barrier formation; ensures surface purity | $10^{-5}$ bar |
| Atmosphere Control | Eliminates oxygen affinity; allows nitrogen interaction | High-purity Nitrogen flow |
| Process Temperature | Drives nitrogen diffusion kinetics and layer thickness | 900°C - 1000°C |
| Surface Outcome | Resulting phase and visual indicator | Golden ZrN Ceramic Layer |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don’t let residual oxygen compromise your Zr2.5Nb nitriding results. KINTEK’s high-temperature vacuum tube systems are engineered to reach the deep vacuum levels necessary to prevent oxidation and ensure the growth of pure, hard ceramic ZrN layers.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your specific lab requirements. Whether you need precise thermal kinetics or superior atmospheric control, our equipment delivers the reliability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Longlong Zhang, Yong Luo. Thermal Nitridation Deoxygenation and Biotribological Properties of Zr2.5Nb. DOI: 10.1049/bsb2.70005
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace during the reduction phase of graphite flake surface treatment?
- How does a tube furnace differ from a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What role does a tube furnace play in Se/NC composite synthesis? Mastering the Melt-Diffusion Method
- What types of containers are used in vacuum tube furnaces? Choose Quartz or Corundum for Optimal Performance
- Why is calibration important for a horizontal electric furnace? Ensure Precise Temperature Control for Your Materials
- How does a Tube Resistance Furnace facilitate biomass pyrolysis? Achieve High-Purity Biochar Production
- What are the key application features of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity
- How does a Tube Furnace system facilitate the growth of nanoporous graphene? Achieve Precision CVD Results



















