At its core, a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace offers four key advantages: exceptional temperature uniformity, high heat transfer efficiency, rapid reaction speeds, and highly flexible operational control. These features stem from its unique ability to suspend solid particles in an upward-flowing gas stream, forcing them to behave like a fluid and interact intensely with their environment.
The fundamental advantage of this technology is its ability to overcome the limitations of static heating. By fluidizing the material, the furnace creates an active, homogenous environment that dramatically enhances the efficiency and consistency of thermal processes for particulate solids.
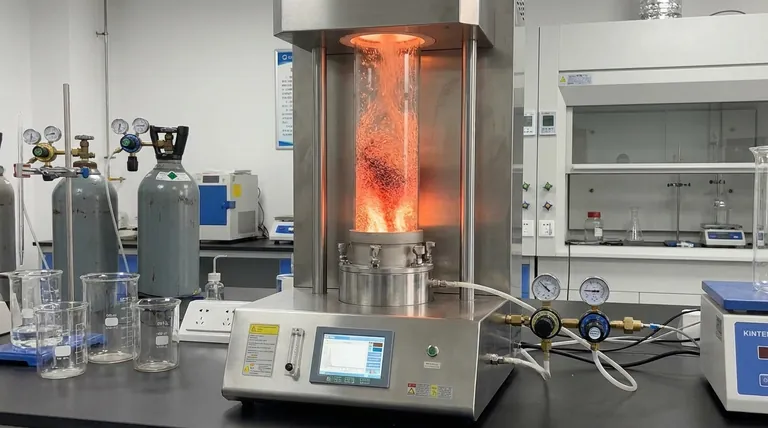

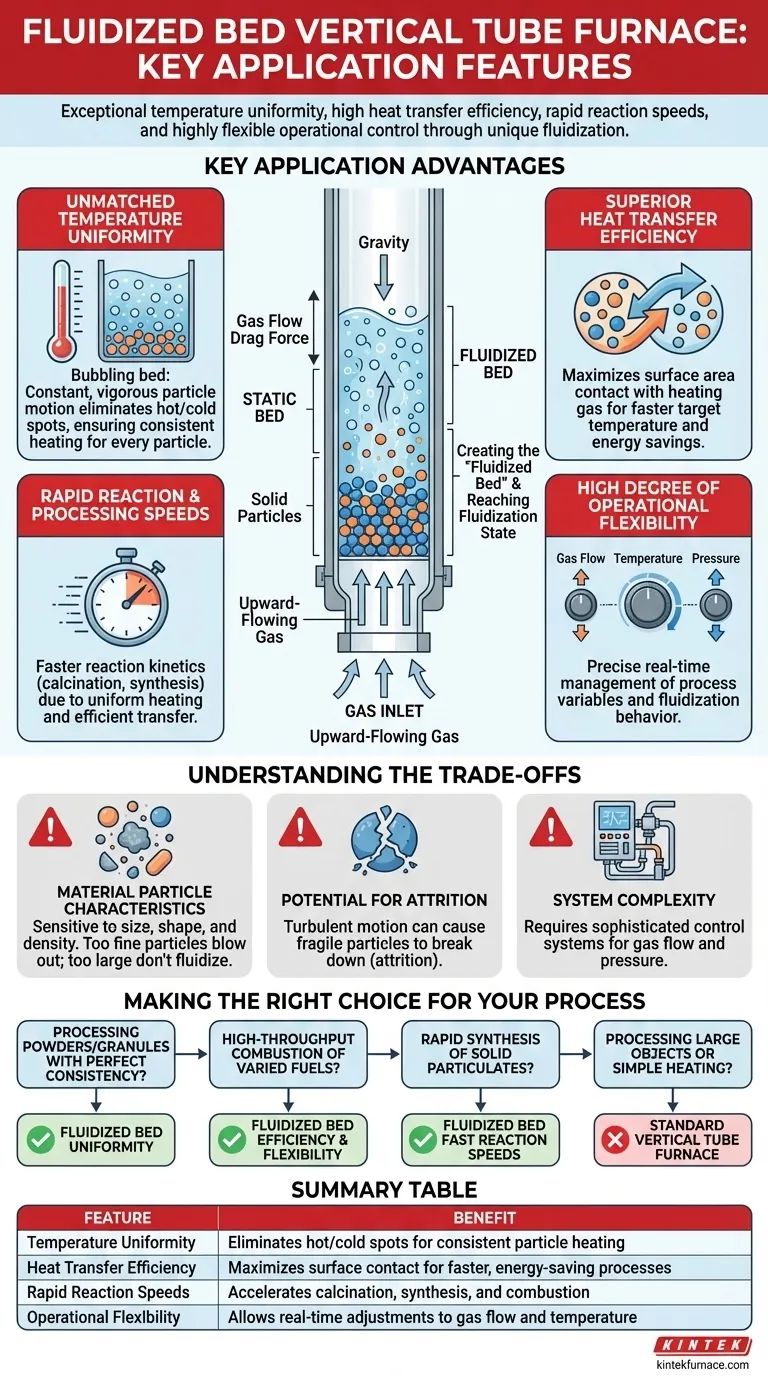
The Core Principle: How Fluidization Works
To understand the applications, you must first understand the mechanism. This furnace design combines the structure of a vertical tube with the dynamics of a fluidized bed.
Creating the "Fluidized Bed"
A controlled stream of gas is introduced at the bottom of the vertical furnace tube. As this gas flows upward through a bed of solid particles (like powders, granules, or pellets), it exerts a drag force.
Reaching the Fluidization State
When the gas flow rate is high enough, this drag force counteracts gravity, causing the particles to become suspended and separated. In this state, the entire solid mass begins to bubble and flow, behaving much like a boiling liquid—this is the fluidized bed.
Key Application Advantages Explained
The fluidized state is not just a physical phenomenon; it is the source of the furnace's primary operational benefits.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Because the particles are in constant, vigorous motion, heat is distributed almost instantaneously throughout the entire bed. This eliminates hot or cold spots common in static furnaces, ensuring every particle experiences the exact same temperature profile.
Superior Heat Transfer Efficiency
The constant motion and separation of particles maximize the available surface area for contact with the heating gas. This direct, turbulent contact results in extremely high heat transfer efficiency, meaning the material reaches its target temperature much faster and with less wasted energy.
Rapid Reaction and Processing Speeds
The combination of uniform heating and efficient heat transfer allows for significantly faster reaction kinetics. Processes like calcination, synthesis, or combustion are completed in a fraction of the time required by conventional methods.
High Degree of Operational Flexibility
The system is highly responsive. Operators can precisely manage the process by adjusting key variables like gas flow rate, system temperature, and pressure. This allows for fine-tuning the fluidization behavior and reaction conditions on the fly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not universally applicable. Its effectiveness is dependent on the material and process.
Material Particle Characteristics
The process is highly sensitive to particle size, shape, and density. Materials that are too fine can be blown out of the furnace, while particles that are too large or heavy may not fluidize properly.
Potential for Attrition
The constant, turbulent motion can cause fragile particles to break down or wear away over time. This phenomenon, known as attrition, must be considered for materials that are sensitive to physical degradation.
System Complexity
Achieving and maintaining a stable fluidized bed requires more sophisticated control systems for gas flow and pressure compared to a simple static furnace. This can add to the initial cost and operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your material and the desired outcome of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules with perfect consistency: The unmatched temperature uniformity of a fluidized bed is your greatest asset.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput combustion of varied fuels (like biomass or coal): The technology's high efficiency and fuel flexibility make it an ideal choice for energy applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid synthesis or chemical reaction of solid particulates: The fast reaction speeds and excellent gas-solid contact will dramatically improve your process efficiency.
- If you are processing large, solid objects or require a simple, low-cost heating solution: A standard (non-fluidized) vertical tube furnace may be a more practical and economical option.
Ultimately, selecting a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace is a strategic choice for processes that demand the highest levels of thermal efficiency and uniformity for particulate materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent particle heating |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Maximizes surface contact for faster, energy-saving processes |
| Rapid Reaction Speeds | Accelerates calcination, synthesis, and combustion |
| Operational Flexibility | Allows real-time adjustments to gas flow and temperature |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with advanced fluidized bed solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior efficiency and uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















