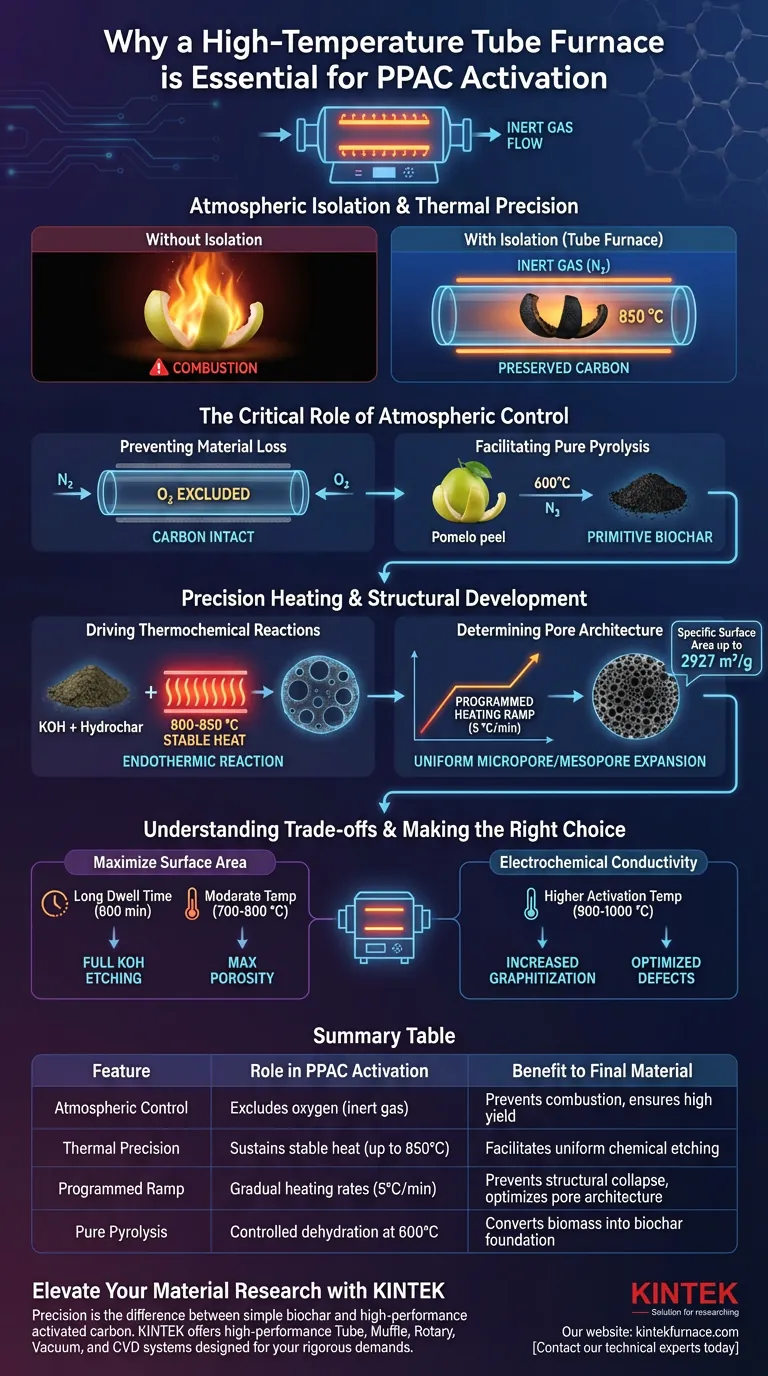
Atmospheric isolation and thermal precision are the non-negotiable requirements. A high-temperature tube furnace is essential for activating pomelo peel-based activated carbon (PPAC) because it provides a strictly controlled, oxygen-free environment while maintaining exact temperatures, typically around 850 °C. This specific setup prevents the carbon substrate from burning away via oxidation, ensuring that chemical reactions create deep porosity rather than destroying the material.
The tube furnace acts as a precision reactor that decouples high heat from combustion. By maintaining an inert atmosphere, it allows activating agents to physically etch the carbon matrix, generating the extreme specific surface area required for high-performance electrochemical applications.

The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
Preventing Material Loss
The primary function of the tube furnace is to create a sealed environment that excludes oxygen. At activation temperatures of 850 °C, carbon is highly reactive and would instantly combust if exposed to air.
By utilizing an inert gas flow (typically Nitrogen), the furnace ensures the carbon remains intact. This protection is vital for preserving the yield of the material while allowing the chemical changes to occur within the carbon structure.
Facilitating Pure Pyrolysis
Before activation, the raw pomelo peel must undergo carbonization. The tube furnace facilitates this by heating the material to approximately 600 °C under nitrogen protection.
This environment drives the dehydration and decomposition of complex organic components. It converts the raw biomass into primitive biochar with an initial aromatic structure, which serves as the necessary foundation for subsequent chemical activation.
Precision Heating and Structural Development
Driving Thermochemical Reactions
The activation process relies on a reaction between the carbonized hydrochar and chemical agents, such as Potassium Hydroxide (KOH). This reaction is endothermic and requires sustained, stable heat to proceed.
The tube furnace provides the thermal stability needed to maintain the reaction chamber at roughly 800 °C to 850 °C. This energy input allows the KOH to effectively "digest" parts of the carbon framework, creating a vast network of pores.
Determining Pore Architecture
The specific surface area of the final material—which can reach values as high as 2927 m²/g—is directly dictated by the precision of the heating profile.
Tube furnaces allow for programmed heating rates (e.g., 5 °C/min). This gradual, controlled rise in temperature ensures uniform heating, which is critical for expanding micropore and mesopore structures evenly throughout the material without causing structural collapse.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Process Parameters
While tube furnaces offer precision, the quality of the output is highly sensitive to the programmed parameters. Deviation in temperature can drastically alter the material's properties; for instance, varying the temperature between 800 °C, 900 °C, and 1000 °C changes the degree of graphitization and defect ratios.
Complexity of Optimization
Unlike simpler heating methods, using a high-temperature tube furnace requires balancing multiple variables, such as gas flow rates, heating ramps, and dwell times (often up to 600 minutes). Improper calibration of these factors can lead to conduction loss or insufficient pore development, rendering the material less effective for electrochemical use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific settings you employ with your tube furnace should depend on the final application of the activated carbon.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Surface Area: Prioritize long dwell times (e.g., 600 minutes) at moderate temperatures (700 °C - 800 °C) to allow the activator (KOH) to fully etch micropores into the framework.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Conductivity: Target higher activation temperatures (900 °C - 1000 °C) to increase the degree of graphitization and optimize the ratio of defects in the carbon fibers.
Ultimatelty, the high-temperature tube furnace is not just a heat source; it is the instrument that allows you to sculpt the atomic structure of the carbon for specific high-tech applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in PPAC Activation | Benefit to Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Excludes oxygen via inert gas flow | Prevents material combustion and ensures high yield |
| Thermal Precision | Sustains stable heat (up to 850°C) | Facilitates uniform chemical etching by activating agents |
| Programmed Ramp | Gradual heating rates (e.g., 5°C/min) | Prevents structural collapse; optimizes pore architecture |
| Pure Pyrolysis | Controlled dehydration at 600°C | Converts biomass into biochar foundation for activation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between simple biochar and high-performance activated carbon. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of carbon activation and electrochemical research.
Whether you are optimizing pore architecture or scaling up production, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmospheric integrity your project requires.
Ready to sculpt your atomic structures with precision? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Kiran Kumar Reddy Reddygunta, Aruna Ivaturi. Sheet-like ZnCo<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> microspheres and pomelo peel waste-derived activated carbon for high performance solid state asymmetric supercapacitors. DOI: 10.1039/d4se00182f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of quartz vacuum encapsulation in RhSeCl CVT? Mastering Pure Crystal Growth
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in the carbonization of nitrogen-doped carbon? Optimize Your Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace equipped with a nitrogen environment necessary for biochar? Achieve Precise Pyrolysis Control
- How does a Horizontal Tubular Furnace contribute to the physical activation of sawdust-derived activated carbon?
- Why is environmental control in a high-temperature tube furnace necessary during NVP/C synthesis? Key to Success
- What is the purpose of a two-zone tube furnace for nanoparticle selenization? Achieve Precision Vapor Control
- What function does a vacuum tube furnace perform during t-BTO thin film annealing? Achieve Precision Crystallization
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the synthesis of electrocatalysts from hydrochar? Precision Thermal Engineering



















