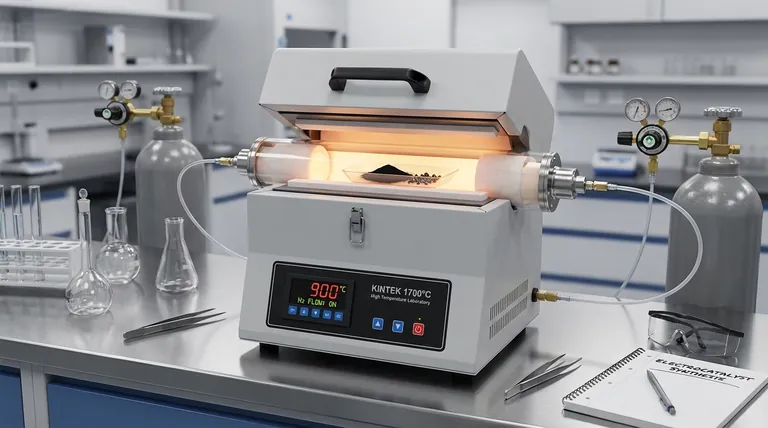
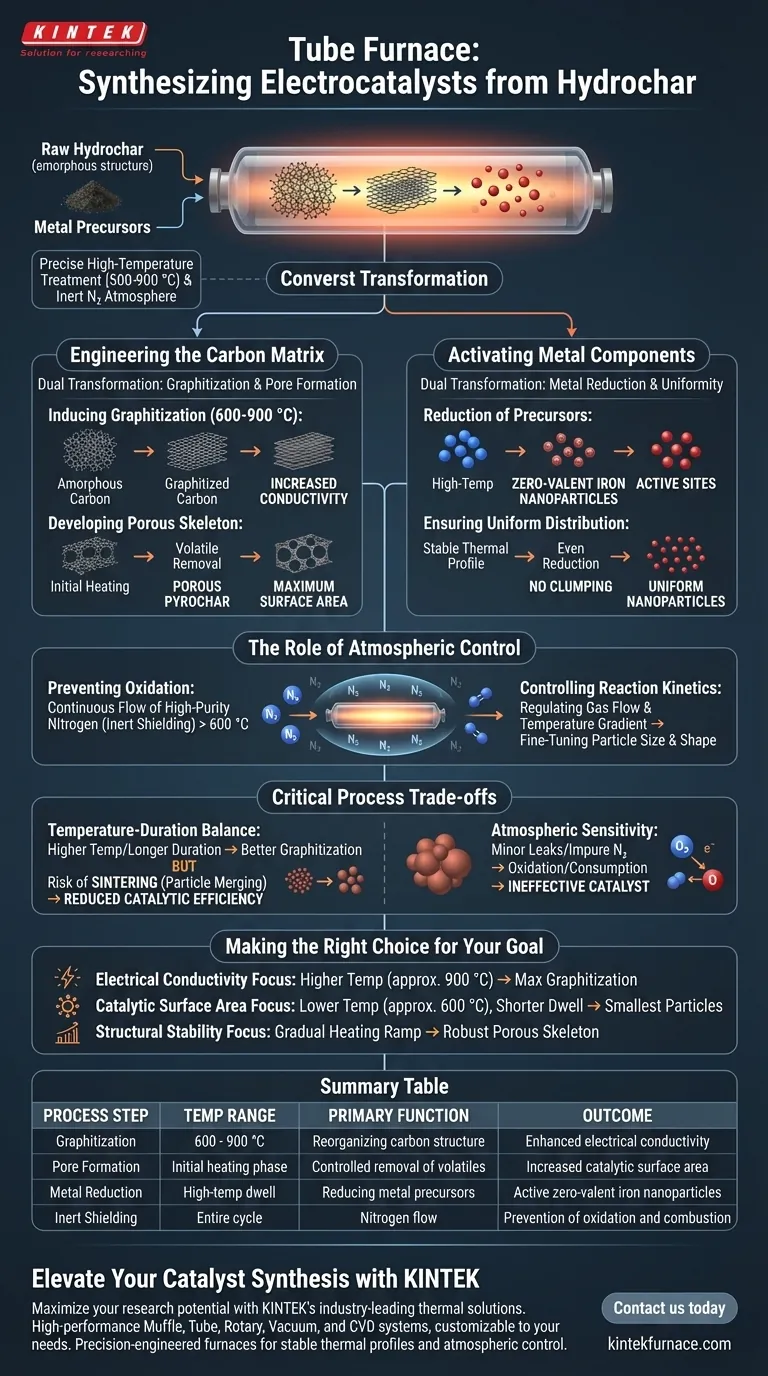
The tube furnace serves as the definitive reaction vessel for synthesis, converting raw hydrochar into functional electrocatalysts through precise high-temperature treatment. It creates a strictly controlled environment, typically between 600 and 900 °C, that drives the structural evolution of the material while preventing degradation through an inert nitrogen atmosphere.
The core function of the tube furnace is to facilitate a dual transformation: it graphitizes the amorphous carbon matrix to increase conductivity and simultaneously reduces iron precursors into uniformly distributed, active zero-valent iron nanoparticles.

Engineering the Carbon Matrix
To create an effective electrocatalyst, the underlying support structure—the hydrochar—must be chemically and physically altered.
Inducing Graphitization
The furnace provides the thermal energy required to reorganize the carbon structure. By sustaining temperatures between 600 and 900 °C, the amorphous carbon in the hydrochar undergoes graphitization.
This process increases the material's electrical conductivity, a critical requirement for efficient electron transfer during electrocatalytic reactions.
Developing the Porous Skeleton
During the initial stages of heating, the precise control offered by the tube furnace allows for the systematic removal of volatiles.
This results in the formation of a porous skeletal structure, often referred to as pyrochar. This porosity is essential for maximizing the surface area available for catalytic activity.
Activating the Metal Components
Beyond the carbon support, the tube furnace is responsible for activating the metal species that drive the chemical reaction.
Reduction of Precursors
The high-temperature environment facilitates the chemical reduction of metal compounds mixed with the hydrochar.
Specifically, it reduces iron precursors into zero-valent iron nanoparticles. These nanoparticles act as the active sites where the electrocatalytic reactions occur.
Ensuring Uniform Distribution
The furnace's ability to maintain a stable thermal profile ensures that this reduction happens evenly throughout the material.
This prevents the metal from clumping significantly, resulting in uniformly distributed nanoparticles. Uniformity is vital for consistent performance and maximizing the usage of the metal load.
The Role of Atmospheric Control
Temperature is only half the equation; the chemical environment inside the tube is equally critical.
Preventing Oxidation
At temperatures above 600 °C, carbon and zero-valent metals would instantly burn up if exposed to air.
The tube furnace mitigates this by maintaining a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen. This inert atmosphere shields the material, ensuring that the thermal energy induces structural evolution rather than combustion.
Controlling Reaction Kinetics
By regulating the flow of carrier gas and the temperature gradient, the furnace influences the size and shape of the resulting particles.
This allows researchers to fine-tune the synthesis, ensuring the final catalyst meets specific geometric and physical requirements.
Critical Process Trade-offs
While the tube furnace enables synthesis, improper management of the thermal profile can lead to suboptimal results.
The Temperature-Duration Balance
There is a delicate trade-off between the degree of graphitization and particle size.
Higher temperatures or longer durations improve conductivity (graphitization) but risk sintering the nanoparticles. If the particles merge and grow too large, the total active surface area drops, reducing catalytic efficiency.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
The system relies entirely on the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
Even minor leaks or impure nitrogen sources can introduce oxygen, leading to the partial oxidation of the zero-valent iron or the consumption of the carbon matrix, rendering the catalyst ineffective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific settings you use on the tube furnace should be dictated by the performance metric you value most.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize higher temperatures (closer to 900 °C) to maximize the graphitization of the carbon matrix, accepting a potential slight increase in particle size.
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Surface Area: Utilize the lower end of the temperature spectrum (closer to 600 °C) and shorter dwell times to preserve the smallest possible nanoparticle size and prevent sintering.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Ensure a gradual heating ramp to allow for the controlled release of volatiles, creating a robust porous skeleton without collapsing the pores.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision instrument that dictates the balance between conductivity and catalytic activity in your final material.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Temperature Range | Primary Function | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphitization | 600 - 900 °C | Reorganizing carbon structure | Enhanced electrical conductivity |
| Pore Formation | Initial heating phase | Controlled removal of volatiles | Increased catalytic surface area |
| Metal Reduction | High-temp dwell | Reducing metal precursors | Active zero-valent iron nanoparticles |
| Inert Shielding | Entire cycle | Nitrogen flow | Prevention of oxidation and combustion |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Maximize your research potential with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are optimizing graphitization for conductivity or minimizing sintering for surface area, our precision-engineered furnaces provide the stable thermal profiles and atmospheric control essential for advanced material science.
Ready to refine your synthesis process? Contact us today to discuss how our customizable high-temperature systems can drive your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Lilian Moumaneix, Tanja Kallio. Zero‐Valent Iron Nanoparticles Supported on Si/N Codoped Carbon Materials: From Biomass to Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts and Supercapacitors. DOI: 10.1002/aesr.202500092
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the accuracy of microplastic thermal decomposition? Ensure Pyrolysis Precision
- What core processing environment does a vacuum tube furnace provide for pyrolytic carbon lattices? Expert Guide
- What is the significance of using a vacuum-sealed fused silica tube in Bi2Te3 synthesis? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in graphite recycling? Restoring Purity and Structure
- What are the technical advantages of using an Entrained Flow Reactor (EFR)? Achieve Industrial Scale Char Simulation
- What role does a vacuum-controlled tube furnace play in Ti2AlN treatment? Master the Hexagonal MAX Phase Transition
- What factors should be considered when choosing a tube furnace for a lab? Ensure Precision and Safety in Your Experiments
- What is the function of a tube furnace in pRF preparation? Optimize Carbonization & Conductivity



















