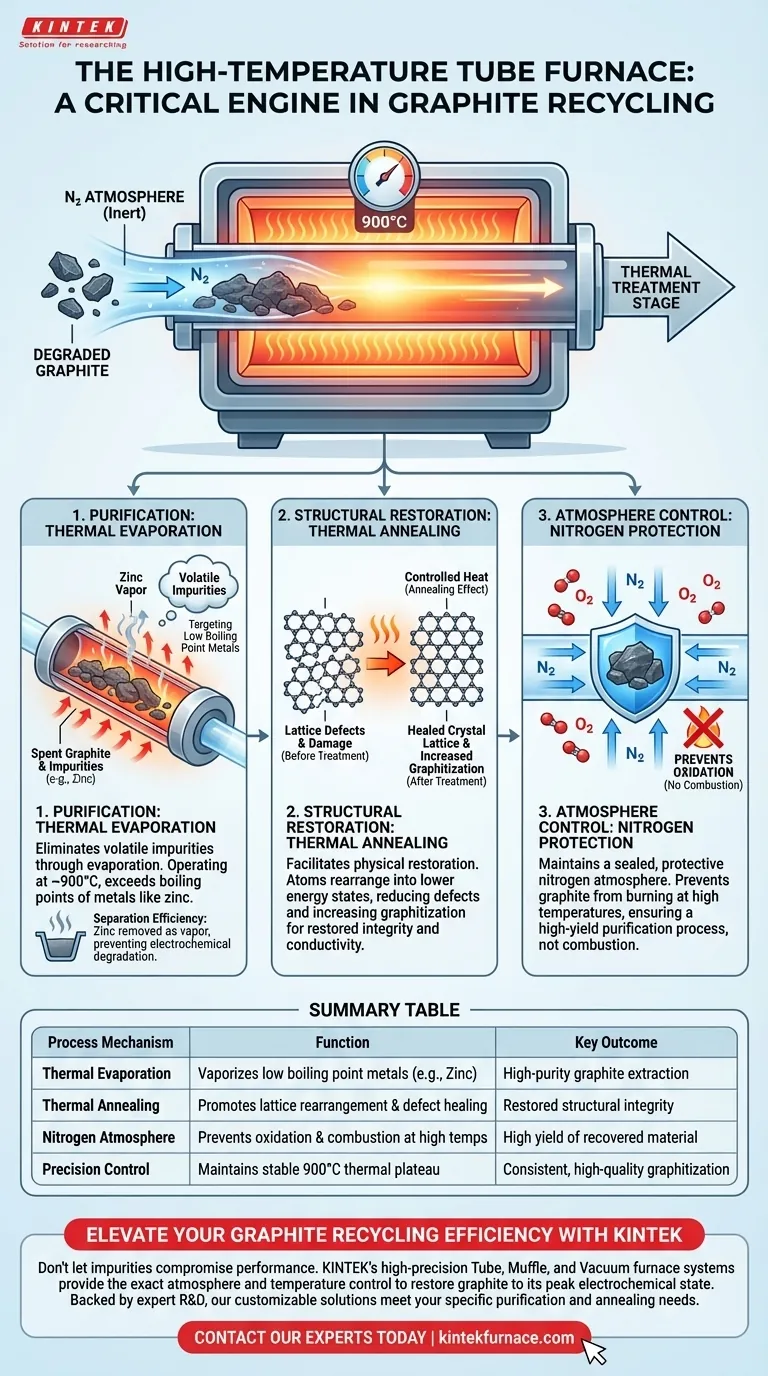
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical purification and structural restoration engine in graphite recycling. It functions by creating a strictly controlled nitrogen atmosphere capable of reaching precise temperatures, typically around 900°C. This thermal treatment eliminates volatile impurities through evaporation and repairs the material's internal crystal lattice to restore performance.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace does more than simply heat the material; it selectively isolates graphite. By leveraging specific boiling points to vaporize metal contaminants like zinc and inducing thermal annealing, it transforms degraded waste into high-quality, highly graphitized material ready for reuse.

Purification Through Thermal Evaporation
Targeting Low Boiling Point Metals
The primary mechanism for purification in this stage is thermal evaporation. The furnace operates at temperatures high enough to exceed the boiling points of specific metal impurities found in spent graphite.
The Removal of Zinc
According to established protocols, the furnace is often set to maintain 900°C for one hour. At this specific thermal plateau, impurities such as zinc—which has a relatively low boiling point—transition into a vapor phase.
Separation Efficiency
Once vaporized, these metallic impurities are effectively separated from the solid graphite matrix. This allows for the efficient removal of contaminants that would otherwise degrade the electrochemical performance of the recycled material.
Structural Restoration and Annealing
The Annealing Effect
Beyond chemical purification, the tube furnace facilitates a physical restoration process known as thermal annealing. The high thermal energy input allows atoms within the material to vibrate and move, settling into lower energy states.
Reducing Lattice Defects
Spent graphite often suffers from structural damage and defects in its crystal lattice. The controlled heat promotes the rearrangement of the internal graphite structure, effectively "healing" these defects.
Increasing Graphitization
This structural reorganization results in a higher degree of graphitization. By aligning the carbon layers more perfectly, the material regains the structural integrity and conductivity required for high-performance applications.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
Preventing Oxidation
A critical function of the tube furnace is the maintenance of a protective nitrogen atmosphere. Graphite is susceptible to oxidation (burning) at high temperatures if exposed to oxygen.
Ensuring Inert Processing
The tube furnace design allows for a sealed environment where oxygen is displaced by nitrogen. This ensures that the thermal treatment acts strictly as a purification and annealing step, rather than a combustion process that would destroy the valuable graphite yield.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specificity of Impurity Removal
This method relies heavily on the boiling point differentials between graphite and its impurities. While highly effective for volatile metals like zinc, this specific thermal step may not be sufficient for refractory metals with boiling points higher than the operating temperature of 900°C.
Energy Intensity
Maintaining a temperature of 900°C for extended periods represents a significant energy cost. The process must be balanced against the value of the recovered material to ensure economic viability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your recycling line, consider how the furnace settings align with your specific input material:
- If your primary focus is Purity: Ensure your operating temperature specifically exceeds the boiling point of your target contaminants (e.g., >907°C for Zinc) while maintaining a strict inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Prioritize the duration of the dwell time (annealing phase) to allow sufficient time for lattice rearrangement and defect reduction.
The high-temperature tube furnace is not merely a heating element; it is a precision instrument that dictates the final purity and structural quality of your recycled graphite.
Summary Table:
| Process Mechanism | Function in Graphite Recycling | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Vaporizes low boiling point metals (e.g., Zinc) | High-purity graphite extraction |
| Thermal Annealing | Promotes lattice rearrangement and defect healing | Restored structural integrity |
| Nitrogen Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and combustion at high temps | High yield of recovered material |
| Precision Control | Maintains stable 900°C thermal plateau | Consistent, high-quality graphitization |
Elevate Your Graphite Recycling Efficiency with KINTEK
Don't let impurities compromise the performance of your recycled materials. KINTEK’s high-precision Tube, Muffle, and Vacuum furnace systems provide the exact atmosphere and temperature control required to restore graphite to its peak electrochemical state.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific purification and annealing requirements. Whether you are targeting refractory metals or optimizing lattice structure, KINTEK offers the thermal solutions your research and production demand.
Ready to optimize your thermal treatment process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory or industrial needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Hojung Yun, Jitti Kasemchainan. Achieving Waste-Valorized Anode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries by Surface Engineering of Recycled Graphite from Spent Zn–C Batteries. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5c04658
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between a lab tubular furnace and a box furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the process for using a vacuum tube experimental furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- What are the technical functions of an industrial tube furnace for ZIF-8 carbonization? Master Precise Pyrolysis
- How does a quartz tube furnace facilitate diamond water vapor annealing? Enhance Interface Stability at 500 °C
- What are the differences between solid and split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What critical environmental controls does a tubular furnace provide for CMS membranes? Optimize Pore Engineering
- How does a vacuum tube furnace serve as the core equipment in the consolidation of Ti-xCr-2Ge alloys?
- How is heat transferred to the material inside the tube furnace? Master the Three-Stage Process for Precise Heating



















