In a tube furnace, heat is transferred to the material inside through a three-stage process. First, external heating elements generate heat that moves to the outer wall of the process tube via radiation and convection. Next, this heat travels through the solid wall of the tube by conduction. Finally, the heat is transferred from the hot inner wall of the tube to the sample itself through a combination of radiation, convection, and conduction.
The core principle to understand is that heat transfer in a tube furnace is not a single event, but a cascade of physical mechanisms. The efficiency and uniformity of heating your material depend entirely on which of these mechanisms—radiation, conduction, or convection—is dominant at each stage of the process.
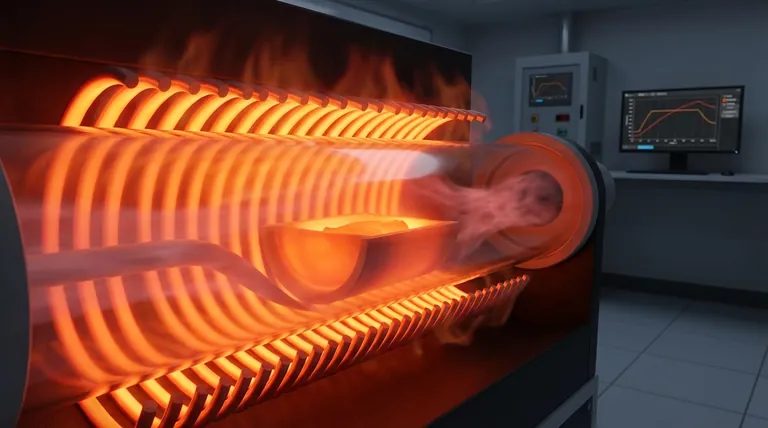
The Three-Stage Journey of Heat
To master your thermal process, you must visualize how heat travels from its source to your sample. It's a journey through different materials and spaces, with the method of transport changing along the way.
Stage 1: From Elements to the Tube Wall (Radiation & Convection)
The process begins with the heating elements, which are typically resistive coils or rods surrounding the work tube.
As electricity flows through these elements, their internal resistance generates intense heat. This energy is then transferred to the outer surface of the furnace tube primarily through thermal radiation—electromagnetic waves traveling through the space between the hot element and the cooler tube.
If there is air or another gas in the gap between the elements and the tube, convection also plays a role as the heated gas circulates and transfers energy to the tube wall.
Stage 2: Through the Tube Wall (Conduction)
Once the heat reaches the outer surface of the process tube (often made of quartz, alumina, or ceramic), it must pass through the solid material to the inside.
This transfer occurs via thermal conduction. The molecules on the outer wall vibrate more intensely and transfer that energy to adjacent molecules, creating a flow of heat through the tube's solid structure until it reaches the inner wall. The tube's material and thickness directly impact the speed of this process.
Stage 3: From the Tube to Your Sample (All Three Mechanisms)
This is the final and most complex stage. Once the inner wall of the tube is hot, it transfers heat to your sample using all three mechanisms, and their relative importance depends on your specific setup.
- Radiation: The hot inner surface of the tube radiates heat directly onto the surface of your sample. In a vacuum or when using a non-absorbing gas, this is often the most significant mode of heat transfer.
- Convection: If your process uses a flowing or static gas (like air, nitrogen, or argon), the gas heats up upon contact with the inner tube wall. This hot gas then circulates within the tube, transferring heat to all surfaces of the sample.
- Conduction: Where your sample is in direct physical contact with the bottom or sides of the tube, heat is transferred directly via conduction. This is efficient but typically only affects a small portion of the sample's surface area.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
The performance of your tube furnace is not fixed; it is dictated by the physics of your setup. Understanding these factors allows you to control the outcome of your process.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere (Vacuum vs. Gas)
In a vacuum, convection is eliminated. Heat transfer relies almost entirely on radiation from the tube wall to the sample. This can lead to slower heating rates and potential temperature gradients if the sample has a complex shape.
With a process gas, convection becomes a major contributor. A circulating or flowing gas helps distribute heat more evenly and can significantly speed up the heating process, leading to better temperature uniformity across the sample.
Furnace Design and Sample Form
The furnace's design has a profound impact. A rotary tube furnace, for instance, continuously tumbles the material. This ensures all parts of the sample are exposed to the hot tube wall (improving conduction) and the hot internal atmosphere (improving convection), resulting in exceptional heating uniformity, especially for powders or granules.
Similarly, multi-zone furnaces use separate heating circuits along the tube's length. This allows you to create a precise temperature profile, compensating for heat loss at the ends and ensuring the entire sample resides within a highly uniform temperature zone.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your operational strategy should be guided by your primary processing goal. Use these principles to optimize your results.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Use a process gas to encourage convection and consider a rotary tube furnace, especially for powders, to ensure all surfaces are heated evenly.
- If your primary focus is the fastest possible heating: Use a high-flow convective gas and ensure your sample has a large surface area exposed to radiation from the tube walls.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing in a vacuum: Recognize that radiation is your main tool. Position the sample to maximize its "view" of the hot tube walls and allow for longer soak times to ensure it heats through completely.
By understanding this sequence of heat transfer, you move from simply operating a furnace to precisely controlling a thermal environment.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Heat Transfer Mechanism | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1: Elements to Tube Wall | Radiation & Convection | Heating elements emit radiation; gas convection aids transfer to outer tube surface. |
| 2: Through Tube Wall | Conduction | Heat moves through solid tube material (e.g., quartz, alumina) to inner wall. |
| 3: Tube to Sample | Radiation, Convection, Conduction | Depends on setup: radiation dominates in vacuum; convection with gas; conduction if sample contacts tube. |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your heating uniformity and efficiency!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















