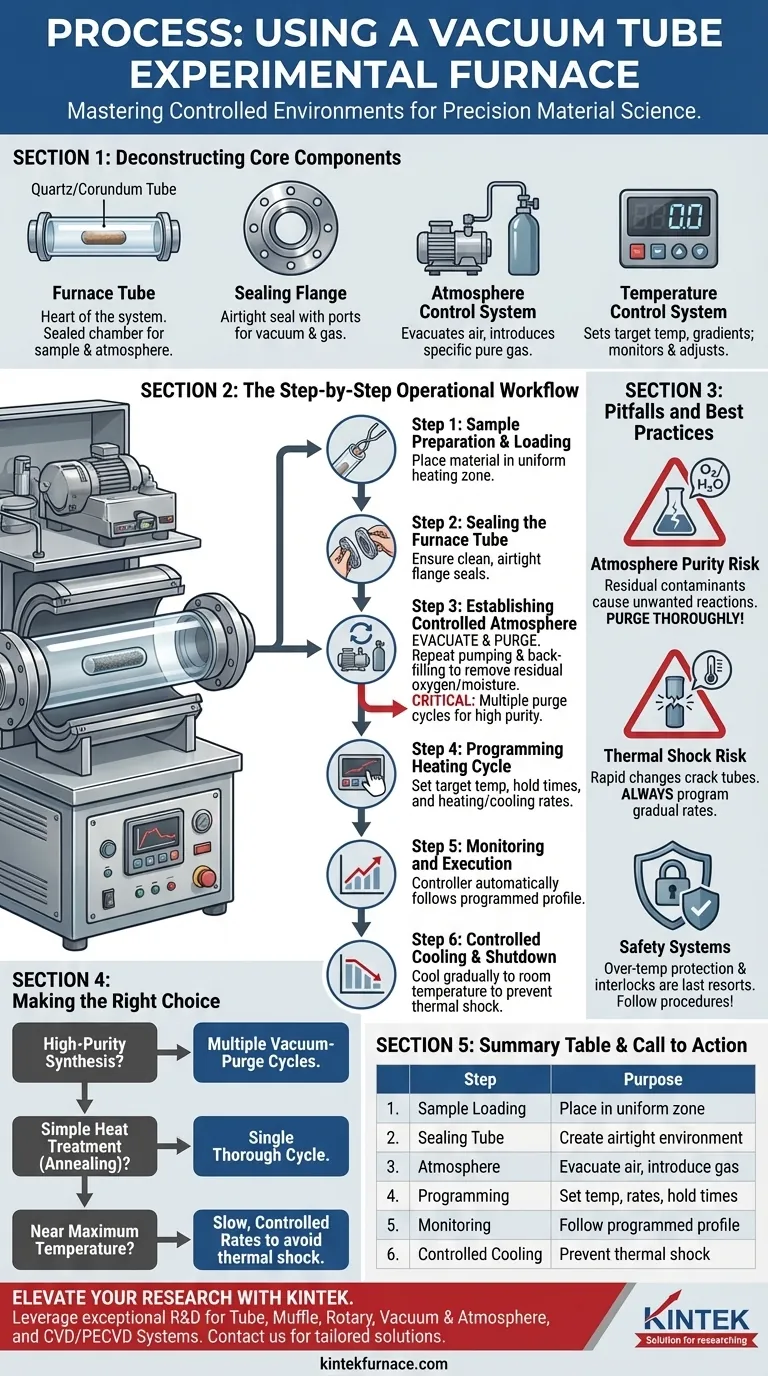
At its core, the process for using a vacuum tube furnace involves loading your material, sealing it within a tube, precisely controlling the atmospheric environment, and then executing a controlled heating and cooling cycle. The fundamental steps include placing the sample, sealing the tube with a flange, using a vacuum pump to remove air, optionally introducing a specific gas, and then running the pre-programmed temperature profile.
The successful operation of a vacuum tube furnace is less about the heating and more about the meticulous preparation of the internal atmosphere. Mastering the cycle of evacuating and purging the furnace tube is the single most critical factor for achieving a pure, controlled experimental environment.

Deconstructing the Core Components
To operate the furnace correctly, you must first understand the function of its key parts. Each component plays a distinct role in creating a controlled, high-temperature environment.
The Furnace Tube
The furnace tube, typically made of quartz or corundum, is the heart of the system. It acts as the sealed chamber that contains your experimental material and the controlled atmosphere.
The Sealing Flange
Stainless steel flanges are used to create an airtight seal at the ends of the furnace tube. These flanges are equipped with ports for connecting a vacuum pump and an air inlet for introducing specific gases.
The Atmosphere Control System
This system consists of a vacuum pump and a gas inlet. The pump evacuates unwanted air and contaminants, while the inlet allows for the introduction of a specific, pure gas or gas mixture to create the desired experimental atmosphere.
The Temperature Control System
This is the furnace's brain. It allows you to set target temperatures, define heating and cooling rates (gradients), and automatically monitor and adjust the heating elements throughout the experiment to ensure precision.
The Step-by-Step Operational Workflow
Following a systematic procedure is essential for safety and experimental repeatability. Each step builds upon the last to ensure the final environment is exactly as intended.
Step 1: Sample Preparation and Loading
Begin by placing your prepared experimental material inside the center of the quartz or corundum tube. Ensure it is positioned within the uniform heating zone of the furnace.
Step 2: Sealing the Furnace Tube
Carefully attach the stainless steel flanges to both ends of the tube. Ensure the seals are clean and properly seated to guarantee an airtight environment.
Step 3: Establishing the Controlled Atmosphere
This is the most critical phase. First, use the vacuum pump to evacuate the tube and remove the ambient air. Once a vacuum is achieved, introduce your desired experimental gas through the air inlet.
For experiments requiring high purity, it is strongly recommended to repeat this process of pumping a vacuum and back-filling with the desired atmosphere several times. This purging cycle drastically reduces residual oxygen and moisture.
Step 4: Programming and Initiating the Heating Cycle
Using the control system, program your target temperature, any necessary holding times, and the rates for both heating and cooling. Once set, you can start the heating process.
Step 5: Monitoring and Execution
The control system will now take over. It will continuously monitor the temperature and automatically adjust power to the heating elements to follow your programmed profile precisely.
Step 6: Controlled Cooling and Shutdown
After the experimental duration is complete, the controller will turn off the heating elements. The furnace must be allowed to cool down gradually to room temperature before you vent the tube and retrieve your sample.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Best Practices
Simply following the steps is not enough; understanding the "why" behind them prevents failed experiments and equipment damage.
The Critical Need for Atmosphere Purity
Failing to properly purge the tube is the most common mistake. Residual oxygen or moisture can cause unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures, compromising the integrity of your experiment and the quality of your results.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
Both quartz and corundum tubes are susceptible to cracking if subjected to rapid temperature changes. Always program gradual heating and cooling rates to avoid thermal shock and extend the life of your furnace tube.
Prioritizing Safety Systems
Modern furnaces are equipped with over-temperature protection and safety interlocks. Understand what these features do, but do not rely on them as a substitute for correct operational procedure. They are a last line of defense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your specific goal dictates how you should apply this process. Use the following guidelines to tailor the operation to your needs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: You must perform the vacuum-and-purge cycle multiple times to minimize contaminants.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment (annealing): A single, thorough vacuum-and-purge cycle may be sufficient if trace contaminants are not a concern.
- If your primary focus is working near maximum temperature: Pay close attention to the tube material's rating and use slow, controlled heating and cooling rates to prevent thermal shock.
Mastering this process transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a precision instrument for material science.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sample Preparation and Loading | Place material in uniform heating zone |
| 2 | Sealing the Furnace Tube | Create airtight environment with flanges |
| 3 | Establishing Controlled Atmosphere | Evacuate air and introduce specific gases |
| 4 | Programming Heating Cycle | Set temperature, rates, and hold times |
| 5 | Monitoring and Execution | Automatically follow programmed profile |
| 6 | Controlled Cooling and Shutdown | Cool gradually to prevent thermal shock |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















