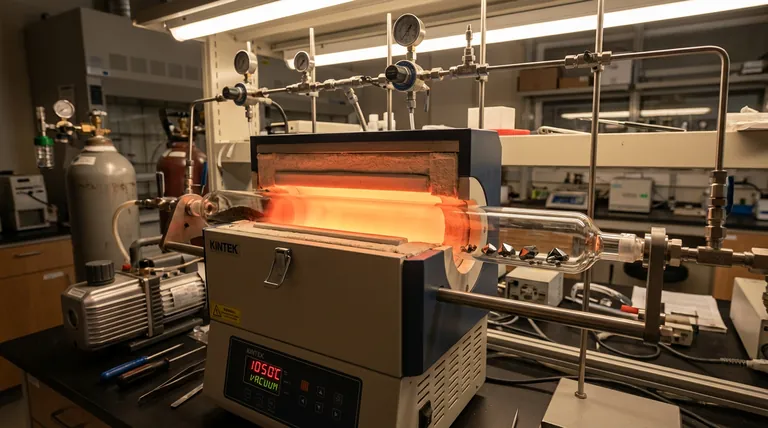
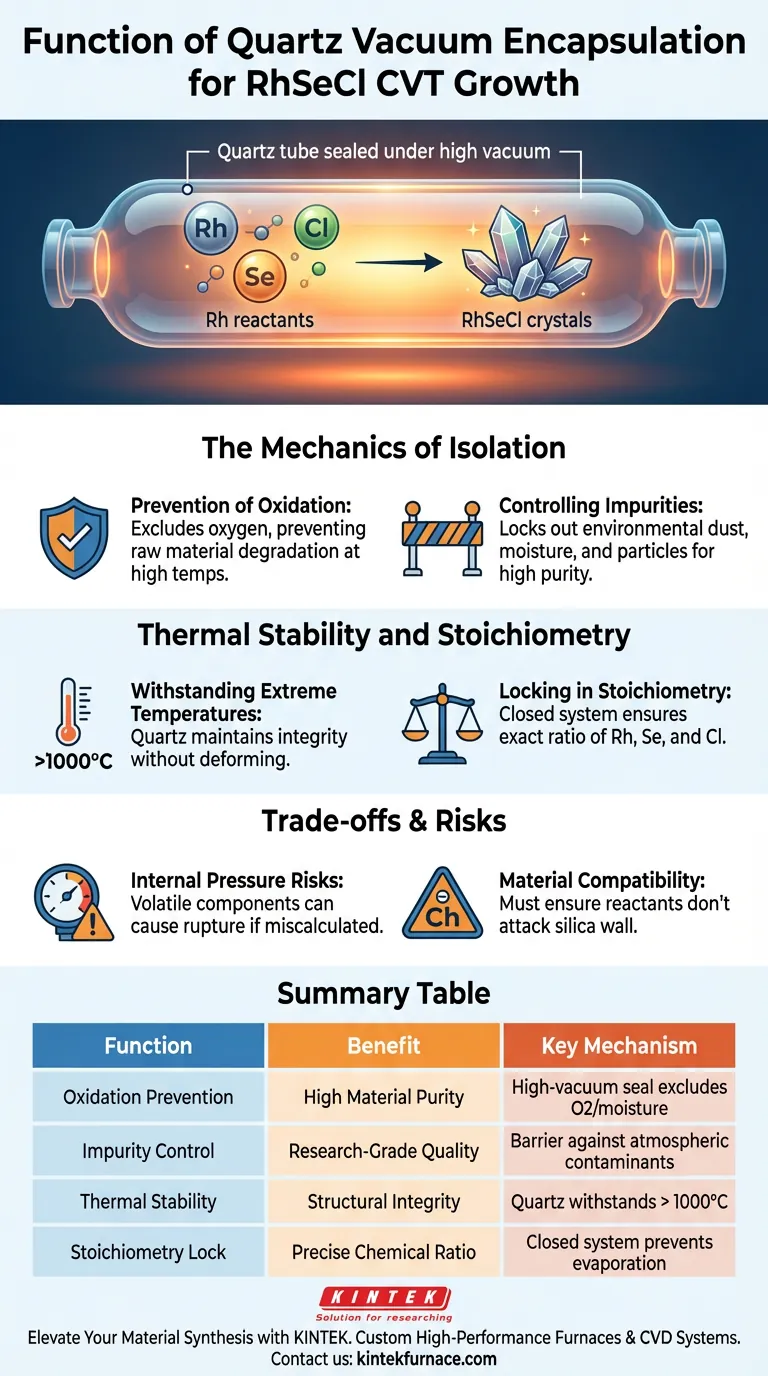
Quartz vacuum encapsulation functions as the critical isolation chamber for the Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) growth of RhSeCl. By sealing the reactants in a high-vacuum quartz tube, the process creates a pristine environment that strictly prevents raw materials from oxidizing or reacting with atmospheric impurities.
The primary value of this technique is its ability to maintain precise chemical stoichiometry at temperatures exceeding 1000 °C. It ensures a pure, stable reaction environment where volatile components are contained and protected from external variables.

The Mechanics of Isolation
Prevention of Oxidation
The most immediate function of encapsulation is the exclusion of oxygen. At the high temperatures required for CVT, raw materials like rhodium, selenium, and chlorine are highly reactive.
Without a high-vacuum seal, these elements would rapidly oxidize. This degradation would alter the chemical composition and ruin the crystal growth process before it begins.
Controlling Impurities
Beyond oxidation, the sealed vessel acts as a barrier against environmental contaminants. Dust, moisture, and other atmospheric particles are completely locked out.
This isolation is essential for semiconductor and research-grade materials, where even trace impurities can drastically alter the physical properties of the final RhSeCl crystals.
Thermal Stability and Stoichiometry
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures
The primary reference notes that this process frequently exceeds 1000 °C. Quartz is utilized specifically because it maintains structural integrity at these extreme thermal ranges.
Unlike standard glass or lower-grade ceramics, quartz does not soften or deform easily under these conditions. This ensures the physical geometry of the transport tunnel remains constant throughout the growth cycle.
Locking in Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the exact ratio of elements in a chemical compound. In an open system, volatile elements might evaporate unevenly, shifting this ratio.
Quartz encapsulation creates a closed system. Because nothing can escape the sealed tube, the ratio of Rh, Se, and Cl remains constant, ensuring the final crystal matches the intended chemical formula.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Internal Pressure Risks
While the vacuum prevents external contamination, the closed nature of the system creates internal risks. As the temperature rises, volatile components transition to the gas phase, increasing internal pressure.
If the precursor amounts are miscalculated or the temperature ramp is too aggressive, the pressure can exceed the quartz tube's tensile strength, leading to rupture or explosion.
Material Compatibility
Quartz is chemically inert to many substances, but not all. While suitable for RhSeCl, one must always verify that the transport agent or reactants do not chemically attack the silica wall at high temperatures, which would introduce silicon impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful CVT growth using this method, consider the following operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Crystal Purity: Ensure the quartz tube is thoroughly cleaned and evacuated to a high-vacuum standard before sealing to remove all residual contaminants.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Calculate the theoretical internal pressure of your reactants at peak temperature to ensure it remains well within the safe limits of the quartz tubing's wall thickness.
By leveraging the thermal stability and isolation capabilities of quartz, you guarantee the chemical fidelity necessary for high-quality RhSeCl synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | High Material Purity | High-vacuum seal excludes oxygen and moisture |
| Impurity Control | Research-Grade Quality | Barrier against atmospheric dust and contaminants |
| Thermal Stability | Structural Integrity | Quartz withstands temperatures exceeding 1000°C |
| Stoichiometry Lock | Precise Chemical Ratio | Closed system prevents evaporation of volatile components |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise crystal growth like RhSeCl CVT requires equipment that can withstand extreme thermal and vacuum demands. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are scaling production or conducting sensitive research, our high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and reliability your work deserves.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Kefeng Liu, Huiyang Gou. Optimized Synthesis and Characterization of Janus RhSeCl with Uniform Anionic Valences, Nonlinear Optical and Optoelectronic Properties. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505279
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the types of Tube Furnaces based on tube shape? Choose Between Solid and Split for Your Lab
- How is a tube furnace designed to operate at 1200°C? Precision Engineering for Extreme Heat
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the preparation of cellulose-based carbon nanofibers?
- What is the intended use of the 3-Zone tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What is the function of an industrial tube furnace during the secondary carbonization of biomass? Achieve Precision.
- Why are ceramic fiber blankets used in linear actuated tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Lab Safety
- What makes tubular furnaces versatile? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for NiWO4 calcination? Achieving High-Performance Cathode Materials



















