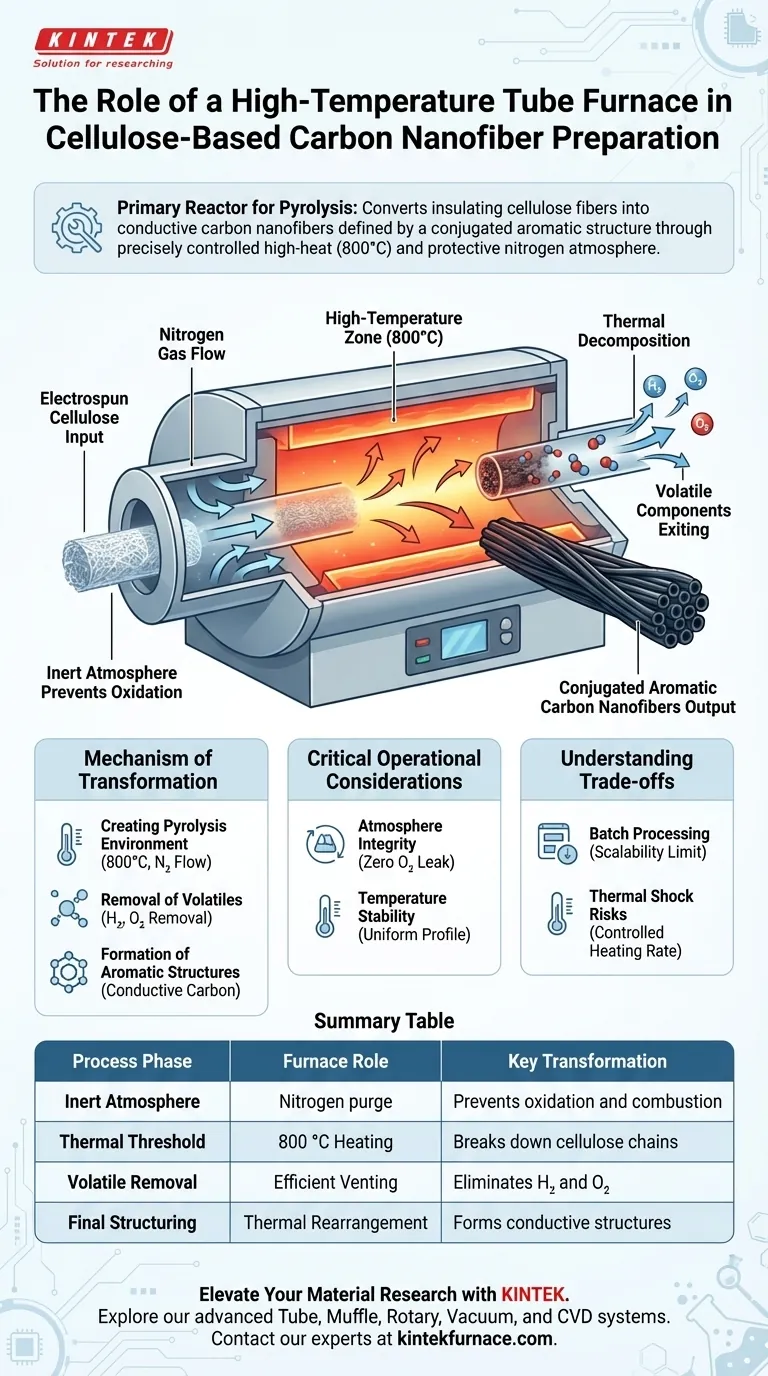
In the preparation of cellulose-based carbon nanofibers, the high-temperature tube furnace serves as the primary reactor for carbonization. It creates a stable, high-heat environment—specifically around 800 °C—while maintaining a protective nitrogen atmosphere. This precise setting is required to drive the pyrolysis of electrospun cellulose, stripping away volatile components to leave behind a pure carbon structure.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it facilitates a complex chemical transformation called pyrolysis. By strictly controlling the atmosphere and temperature, it converts insulating cellulose fibers into conductive carbon nanofibers defined by a conjugated aromatic structure.
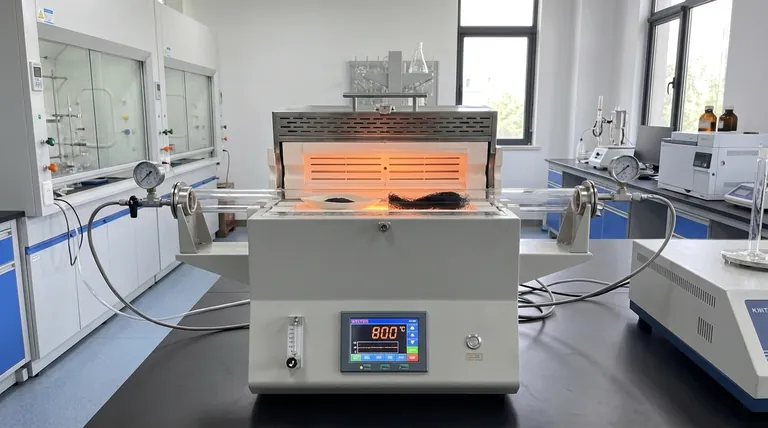

The Mechanism of Transformation
To understand the furnace's role, you must look beyond simple heating. It acts as a vessel for chemical restructuring.
Creating the Pyrolysis Environment
The furnace establishes a consistent temperature, typically 800 °C, which is the thermal threshold required to break down the cellulose polymer chain.
Crucially, this occurs under a continuous flow of nitrogen gas. This inert atmosphere prevents the material from burning (oxidizing) and ensures the reaction remains strictly pyrolytic.
Removal of Volatile Components
As the temperature rises within the tube, the cellulose undergoes thermal decomposition.
The heat forces non-carbon elements—primarily hydrogen and oxygen—to vaporize and exit the material. The furnace's design allows these volatiles to be efficiently vented away from the sample.
Formation of Aromatic Structures
The ultimate goal of using the furnace is the atomic rearrangement of the remaining material.
The high thermal energy drives the residual carbon atoms to reorganize into a conjugated aromatic structure. This specific structural evolution is what grants the final nanofibers their high electrical conductivity and mechanical stability.
Critical Operational Considerations
While the furnace is the enabler, the quality of the output depends on how the equipment is managed.
Atmosphere Integrity
The most critical function of the tube furnace is isolating the reaction from the outside air.
Even a minor leak of oxygen at 800 °C will destroy the sample, turning the cellulose into ash rather than carbon fiber. The nitrogen flow must be constant and pure.
Temperature Stability
The furnace must provide a uniform thermal profile along the length of the heating zone.
Fluctuations in temperature can lead to uneven carbonization, resulting in fibers with inconsistent conductivity or weak structural points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using a high-temperature tube furnace for this process involves specific limitations that must be managed.
Batch Processing Constraints
Tube furnaces are typically batch-processing tools. This limits the scalability of production compared to continuous industrial methods, making it ideal for research but a bottleneck for high-volume manufacturing.
Thermal Shock Risks
The heating rate must be carefully controlled.
Ramping the temperature up too quickly can cause rapid outgassing, which may physically rupture the nanofiber structure before it has time to stabilize. Conversely, heating too slowly can be inefficient and alter the final pore structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the tube furnace in your specific application, consider the following priorities:
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Ensure your furnace can reliably maintain temperatures of at least 800 °C to guarantee the full formation of conjugated aromatic structures.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Prioritize a furnace with precise programmable heating rates to prevent thermal shock during the volatile removal phase.
The tube furnace is the bridge that transforms organic cellulose into functional, high-performance carbon material through controlled thermal evolution.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Role | Key Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Nitrogen purge | Prevents oxidation and combustion |
| Thermal Threshold | 800 °C Heating | Breaks down cellulose polymer chains |
| Volatile Removal | Efficient Venting | Eliminates hydrogen and oxygen molecules |
| Final Structuring | Thermal Rearrangement | Forms conductive conjugated aromatic structures |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when transforming cellulose into high-performance carbon nanofibers. KINTEK provides the advanced thermal technology required to master pyrolysis, ensuring consistent atmosphere integrity and temperature stability for your lab.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs.
Ready to achieve superior conductivity and structural integrity? Contact our technical experts today to find your ideal furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Jingjing Liu, Lu Gan. Metal-Free Cellulose Carbon Nanofiber Supported Graphitic Carbon Nitride for High-Efficient BPA Degradation by Photcatalytic Peroxymonosulfate Activation. DOI: 10.3390/catal15080788
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is heat transferred to the material inside a tube furnace? Master the 3-Stage Process for Precise Thermal Control
- What safety features are included in tube furnaces? Essential Protection for High-Temperature Labs
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in flash annealing Mg/SiOx? Precision for Advanced Anode Synthesis
- What role does a vacuum tube furnace play as a reactor during the coal gasification reaction stage?
- How is solid-gas phase conversion achieved in a tube furnace? Master Fe-CoP/CW Catalyst Phosphatization
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in chromite reduction? Master Precision Solid-State Processing
- What is the recommended procedure for atmosphere control in a vacuum tube furnace? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processes
- What are common applications of Tube Furnaces? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment



















