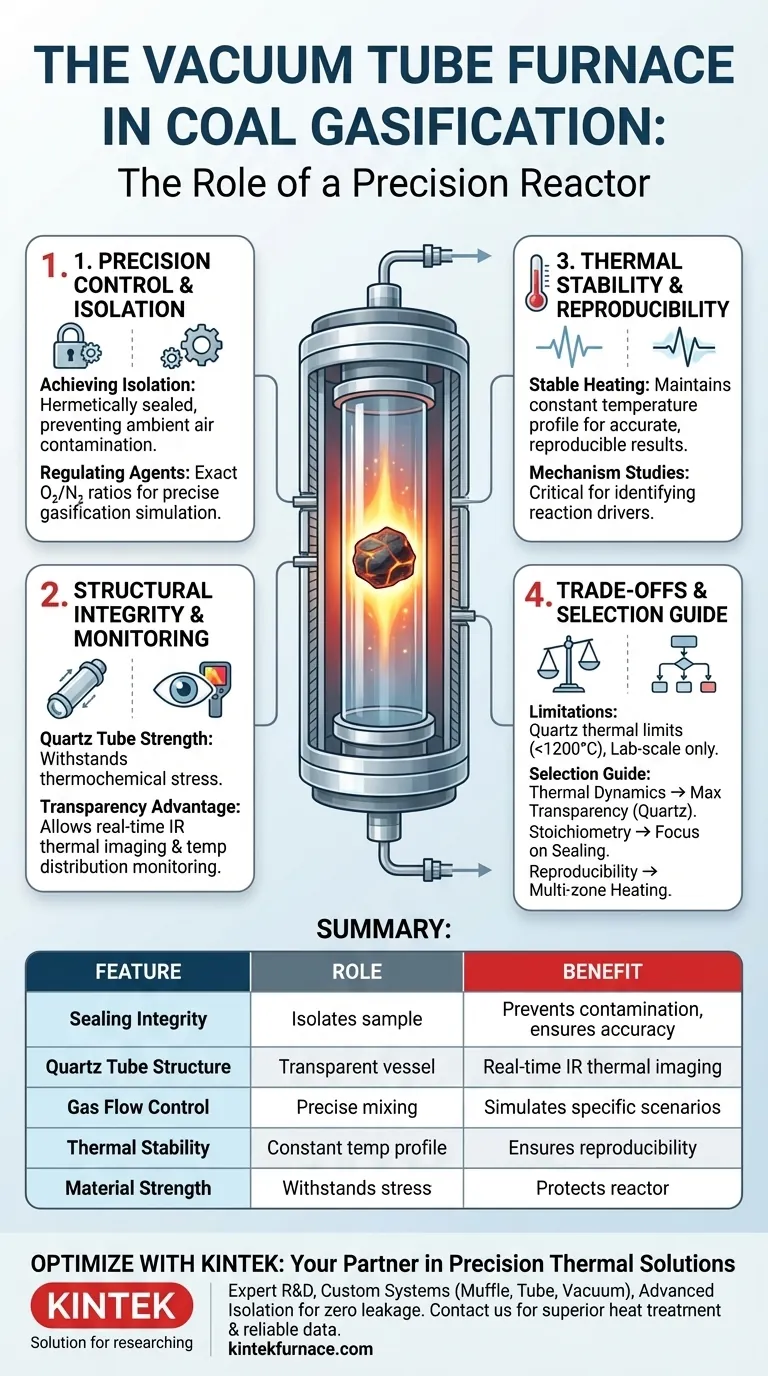
In the context of coal gasification research, the vacuum tube furnace serves as the primary reactor carrier. It provides a hermetically sealed, high-temperature environment that strictly isolates the reaction from external atmospheric interference, allowing researchers to introduce precise ratios of gasifying agents like oxygen and nitrogen to drive the chemical process.
The vacuum tube furnace functions as more than just a heat source; it is a precision containment vessel that safeguards reaction purity while offering a unique optical window for real-time thermal analysis.

Precision Control of the Reaction Environment
To understand the furnace's role, you must look beyond its ability to generate heat. Its primary function during gasification is environmental control.
Achieving Reaction Isolation
The furnace utilizes superior sealing performance to completely isolate the coal sample from the external lab environment. This prevents ambient air from entering the chamber, which would otherwise alter the stoichiometry of the reaction and skew data.
Regulating Gasifying Agents
Once isolated, the furnace acts as a mixing chamber for specific gases. It ensures that agents such as oxygen and nitrogen react internally at exact, user-defined ratios. This precision allows researchers to simulate specific gasification scenarios with high fidelity.
Structural Integrity and Monitoring Capabilities
The physical construction of the furnace plays a critical role in facilitating data collection during the harsh gasification process.
Withstanding Thermochemical Stress
The reactor typically employs a high-strength quartz tube structure. This material is engineered to withstand the intense thermal and chemical stresses generated during coal gasification without degrading or contaminating the sample.
The Transparency Advantage
Unlike opaque ceramic reactors, the quartz tube structure offers a transparent window into the process. This transparency is vital for using infrared thermal imagers. It allows researchers to monitor the real-time temperature distribution within the coal, providing data that standard thermocouples cannot capture.
The Role of Thermal Stability
While the primary reference highlights isolation and visibility, the furnace also plays a crucial role in maintaining the reaction's consistency.
Ensuring Reproducibility
Advanced tube furnaces provide a stable heating environment essential for chemical reaction research. By maintaining a constant temperature profile, the furnace ensures that experimental results are accurate and reproducible.
Facilitating Mechanism Studies
This stability is critical when studying the underlying mechanisms of new compound synthesis or coal breakdown. Without precise temperature control, identifying the specific drivers of a reaction becomes impossible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the vacuum tube furnace is a powerful tool for gasification research, it is important to recognize its operational boundaries.
Material Limitations
The reliance on a quartz tube for transparency introduces thermal limits. While high-strength, quartz cannot withstand the same extreme temperatures as opaque alumina tubes, potentially limiting experiments requiring ultra-high temperatures (typically above 1200°C).
Scale Constraints
This type of reactor is primarily designed for laboratory-scale experiments and mechanism studies. It is not suitable for high-volume industrial gasification, meaning data gathered here must be carefully extrapolated when applying it to mass production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
When selecting or configuring a vacuum tube furnace for coal gasification, your specific research goals should dictate your setup.
- If your primary focus is thermal dynamics and mapping: Prioritize a high-quality quartz tube setup to maximize transparency for infrared thermal imaging.
- If your primary focus is chemical stoichiometry: Focus on the sealing integrity of the flanges to ensure zero leakage of your oxygen and nitrogen mixtures.
- If your primary focus is reaction reproducibility: Ensure the furnace offers multi-zone heating control to maintain a uniform temperature profile across the entire sample length.
Success in gasification experiments relies on treating the furnace not just as a heater, but as a controlled analytical environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Coal Gasification | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Integrity | Isolates sample from external atmosphere | Prevents contamination and ensures stoichiometric accuracy |
| Quartz Tube Structure | Provides a high-strength, transparent vessel | Allows real-time infrared thermal imaging and monitoring |
| Gas Flow Control | Facilitates precise mixing of oxygen/nitrogen | Enables simulation of specific industrial gasification scenarios |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains a constant temperature profile | Ensures experimental reproducibility and accurate mechanism study |
| Material Strength | Withstands thermochemical stress | Protects the reactor from degradation during harsh chemical reactions |
Optimize Your Coal Gasification Research with KINTEK
Ready to elevate your laboratory analysis with precision-engineered thermal solutions? KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of coal research and chemical synthesis.
Why Choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are built for accuracy and durability.
- Fully Customizable: Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, we tailor every unit to your unique research needs.
- Advanced Isolation: Superior sealing technology ensures zero leakage for precise gasifying agent control.
Take the next step in achieving superior heat treatment and reliable data. Contact our technical experts today to discuss how our vacuum tube furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and experimental reproducibility.
Visual Guide
References
- Lele Feng, Jiaxuan Sun. H2 production in underground coal gasification with pretreatment by non-focusing microwave. DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1586267
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What challenges does the 70mm tube furnace market face? Overcome Technical, Quality, and Safety Hurdles
- What common processes are enabled by tube furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing for Your Lab
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in transforming photopolymerized parts into fully aromatic polyimide?
- What role does a tube furnace play in the co-pyrolysis of MIPW and COS? Unlock Precise Thermal Waste Transformation
- What conditions does a continuous flow fixed-bed quartz reactor provide? Master CO Oxidation Testing with Cobalt Oxide
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Silicon/Hard Carbon synthesis? Master Battery Anode Production
- What are the key features and advantages of tube furnaces? Precision Control for High-Temp Materials Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in STO thin film annealing? Unlock Neuromorphic Potential



















