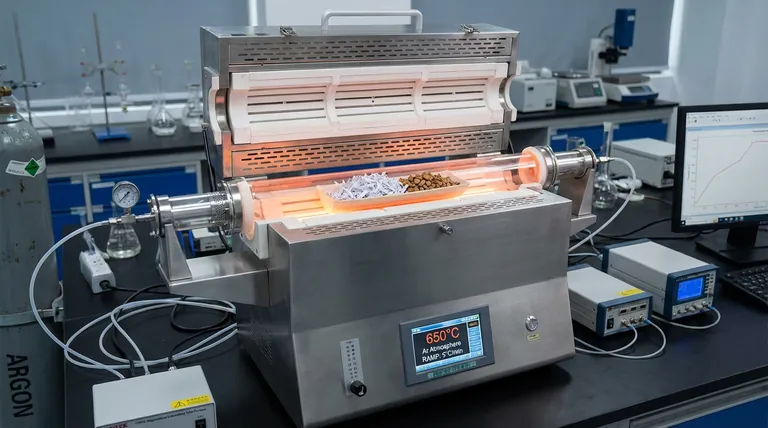
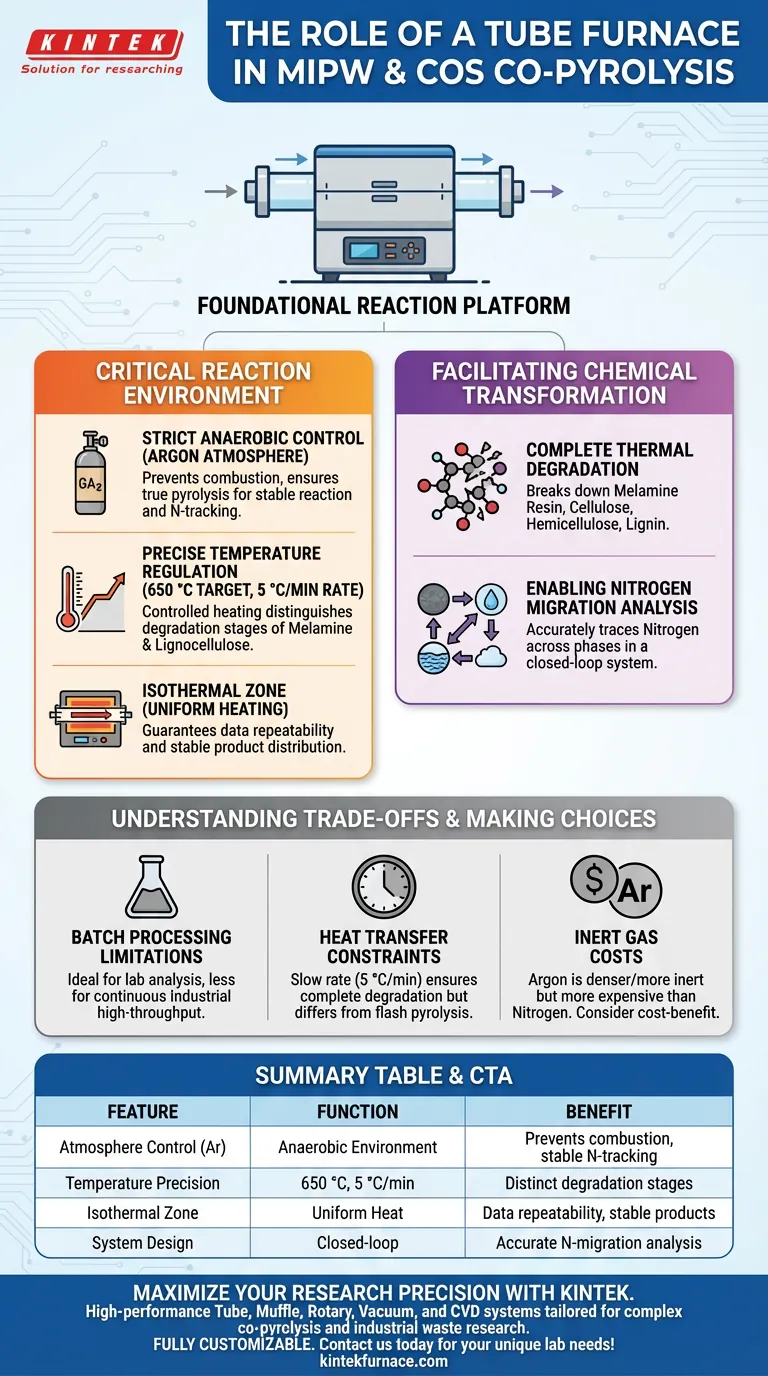
The tube furnace serves as the foundational reaction platform for the co-pyrolysis of Melamine Impregnated Paper Waste (MIPW) and Camellia Oleifera Shells (COS). It functions as a precision instrument that provides a strictly anaerobic environment and exact temperature regulation, ensuring the complete thermal degradation of complex components like melamine resin and lignocellulose.
By maintaining a controlled Argon atmosphere and a specific heating rate, the tube furnace creates the ideal conditions for studying how nitrogen migrates across solid, liquid, and gaseous phases during the breakdown of industrial and agricultural waste.

Creating the Critical Reaction Environment
Strict Anaerobic Control
The primary function of the tube furnace is to prevent combustion by excluding oxygen. By utilizing an Argon atmosphere, the furnace ensures that the feedstock undergoes true pyrolysis rather than burning.
This oxygen-free environment is essential for the stability of the reaction. It allows for the precise separation of chemical bonds within the waste materials without the interference of oxidation.
Precise Temperature Regulation
For MIPW and COS co-pyrolysis, the furnace is tasked with reaching a target temperature of 650 °C.
It achieves this through a controlled heating rate of 5 °C/min. This slow, steady ramp-up is critical for distinguishing the degradation stages of different components.
The Isothermal Zone
Beyond just reaching a temperature, the tube furnace creates a constant temperature isothermal zone.
This zone ensures that the sample is heated uniformly. Uniform heating is the key to maintaining the repeatability of experimental data and ensuring a stable distribution of products.
Facilitating Chemical Transformation
Complete Thermal Degradation
The furnace provides the energy required to break down the diverse chemical structures found in the feedstock.
This includes the cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin from the Camellia Oleifera Shells. Simultaneously, it degrades the melamine resin found in the impregnated paper waste.
Enabling Nitrogen Migration Analysis
A unique role of the tube furnace in this specific context is serving as a platform to track nitrogen.
Because the system is closed and controlled, researchers can accurately trace how nitrogen moves from the solid feedstock into the resulting char, bio-oil, and gas phases. This is vital for understanding the environmental impact and potential utility of the end products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch Processing Limitations
While excellent for precision, tube furnaces are typically batch reactors.
They process fixed amounts of material at a time. This makes them ideal for laboratory analysis and establishing baseline data, but less suitable for continuous, high-throughput industrial production compared to fluidized bed reactors.
Heat Transfer Constraints
The heating rate of 5 °C/min is relatively slow.
While this ensures complete degradation and high resolution of data, it does not mimic "flash pyrolysis" conditions where heating happens in seconds. Consequently, the product distribution (char vs. oil) may differ from fast pyrolysis systems.
Inert Gas Costs
The primary requirement for an Argon atmosphere adds to the operational cost.
While Argon is denser and often provides a more strictly inert blanket than Nitrogen, it is also more expensive. For large-scale operations, the cost-benefit analysis of the chosen inert gas is a necessary consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tube furnace in your co-pyrolysis projects, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Prioritize the furnace's ability to maintain a strictly anaerobic Argon environment to track nitrogen migration with high precision.
- If your primary focus is process scaling: Use the tube furnace to establish the baseline degradation temperatures (e.g., 650 °C) before transitioning to continuous flow reactors.
The tube furnace is the definitive tool for transforming raw experimental data into a clear understanding of thermochemical conversion.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in MIPW/COS Co-pyrolysis | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Argon-purged anaerobic environment | Prevents combustion; ensures true pyrolysis and stable nitrogen tracking. |
| Temperature Precision | Targeted 650 °C with 5 °C/min heating rate | Allows for distinct degradation stages of melamine and lignocellulose. |
| Isothermal Zone | Uniform heat distribution across samples | Guarantees data repeatability and stable bio-char/gas product distribution. |
| System Design | Closed-loop reaction platform | Facilitates accurate analysis of nitrogen migration across solid, liquid, and gas phases. |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Are you looking to achieve flawless thermal degradation and precise nitrogen migration analysis? Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for complex co-pyrolysis and industrial waste research. Our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific heating rates and atmospheric requirements.
Take the next step in your thermochemical conversion projects—Contact us today to discuss your unique laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhuo Zhen, Tingzhou Lei. Study on Nitrogen Migration during Co-Pyrolysis of Melamine-Impregnated Paper Waste and Camellia Oleifera Shell. DOI: 10.3390/su16031197
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What core functions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide? Master TiN-Carbon Composite Pyrolysis
- How does a tube heating system achieve adsorbent regeneration? Master CO2 Cyclic Stability with Precision
- How does a vacuum tube type experimental electric furnace work? Master Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What task is performed by industrial high-temperature tube or atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Carbon Aerogel Synthesis
- How does the temperature control system work in a multi gradient experimental tube furnace? Master Precise Heat Profiles for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using industrial aluminum profiles for tube furnaces? Achieve Modular Lab Efficiency
- What are the typical applications for tube furnaces? Master Precise Thermal Processing
- What role does the gas management system play in a 70mm tube furnace? Essential for Precise Atmosphere Control



















