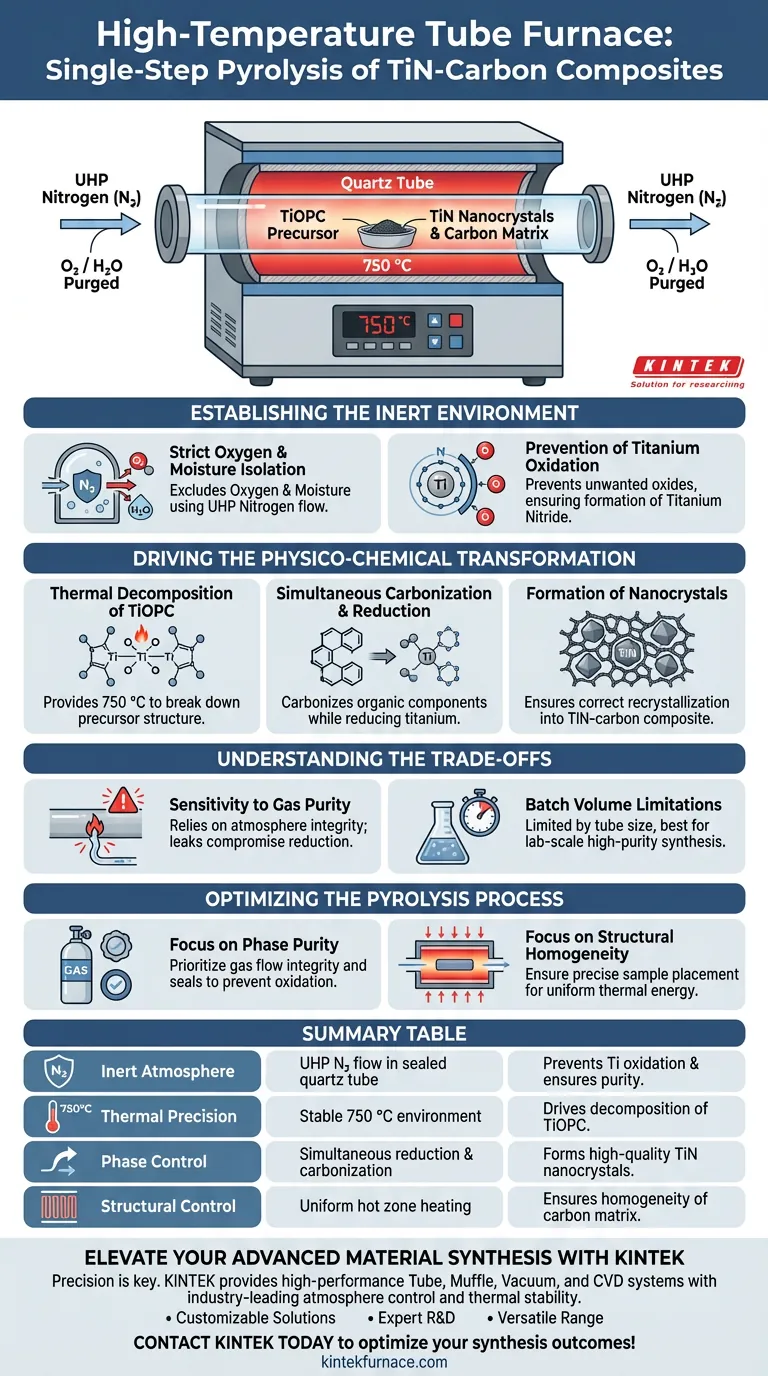
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel that enables the single-step pyrolysis of titanium nitride-carbon (TiN-carbon) composites. Its primary function is to maintain a precisely controlled thermal environment at 750 °C while simultaneously establishing a strict inert atmosphere using ultra-high purity (UHP) nitrogen. This dual capability allows for the thermal decomposition of titanyl phthalocyanine (TiOPC) without the interference of oxygen.
By isolating the reaction within a quartz tube flushed with UHP nitrogen, the furnace prevents the oxidation of titanium at high temperatures. This specific environment is non-negotiable for ensuring the precursor converts into titanium nitride nanocrystals rather than titanium oxides.

Establishing the Inert Environment
Strict Oxygen and Moisture Isolation
The most significant role of the tube furnace in this process is exclusion. By flowing UHP nitrogen through the sealed quartz tube, the system effectively purges oxygen and moisture from the reaction zone.
Prevention of Titanium Oxidation
Titanium is highly reactive with oxygen at elevated temperatures. Without the furnace's ability to maintain a pristine inert atmosphere, the titanium would oxidize, resulting in unwanted byproducts. The furnace ensures the chemical pathway leads specifically to titanium nitride.
Driving the Physico-Chemical Transformation
Thermal Decomposition of TiOPC
The furnace provides the consistent thermal energy required to break down the titanyl phthalocyanine (TiOPC) precursor. At 750 °C, the furnace triggers the decomposition of the metal-organic compound's structure.
Simultaneous Carbonization and Reduction
The tube furnace facilitates a complex, single-step reaction where two processes happen at once. As the organic components of the precursor are carbonized into a porous matrix, the titanium species are reduced.
Formation of Nanocrystals
This controlled thermal environment ensures that the reduced metal species recrystallize correctly. The result is the formation of titanium nitride nanocrystals embedded within the newly formed carbon framework.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Purity
The success of this process relies entirely on the integrity of the atmosphere provided by the furnace. Even minor leaks or insufficient nitrogen purity will compromise the reduction process, leading to impurities in the final composite.
Batch Volume Limitations
Tube furnaces are generally limited by the diameter and length of the quartz tube. While they provide exceptional control for laboratory-scale synthesis and high-purity results, they are typically batch-process devices that may face throughput challenges compared to continuous industrial kilns.
Optimizing the Pyrolysis Process
To achieve the best results in synthesizing TiN-carbon composites, consider the following operational focuses:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Prioritize the integrity of the gas flow system; ensure UHP nitrogen is used and the quartz tube seals are flawless to prevent any oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Structural Homogeneity: Focus on the precise placement of the sample within the furnace's "hot zone" to ensure the entire batch receives uniform thermal energy at 750 °C.
Success in this synthesis depends not just on heating the material, but on strictly controlling the atmosphere to dictate the chemical destiny of the titanium.
Summary Table:
| Core Function | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | UHP Nitrogen flow in a sealed quartz tube | Prevents titanium oxidation & ensures purity |
| Thermal Precision | Stable 750 °C environment | Drives decomposition of TiOPC precursors |
| Phase Control | Simultaneous reduction & carbonization | Forms high-quality TiN nanocrystals |
| Structural Control | Uniform hot zone heating | Ensures homogeneity of the carbon matrix |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a pure nanocrystal and an oxidized byproduct. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems engineered to meet the most rigorous research demands. Our furnaces offer the industry-leading atmosphere control and thermal stability required for complex processes like TiN-carbon pyrolysis.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored tube dimensions and gas handling for your specific lab needs.
- Expert R&D: Backed by manufacturing excellence to ensure structural homogeneity.
- Versatile Range: From rotary to high-temperature lab furnaces, we support every stage of your project.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique requirements and discover how our expert heating solutions can optimize your synthesis outcomes!
Visual Guide
References
- Helia M. Morales, Jasón G. Parsons. Synthesis and Characterization of Titanium Nitride–Carbon Composites and Their Use in Lithium-Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/nano14070624
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is precise heating rate control in a high-temperature tube furnace critical for HyDR? Master Reduction Kinetics
- What critical conditions does a high-precision tube furnace provide? Optimize Catalyst Reduction & Particle Control
- What factors influence the heating process in a tube furnace? Master Temperature Control and Efficiency
- How does a Tube Resistance Furnace facilitate biomass pyrolysis? Achieve High-Purity Biochar Production
- What are the key features of a vacuum tube furnace? Master High-Temp Processing with Precision Control
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the sintering process of modified graphite felt? Precision Control
- What are the advantages of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Unlock Superior Heat Treatment Efficiency
- How does an alumina-lined vertical tube furnace provide a stable environment for corrosion experiments? Get Expert Data



















