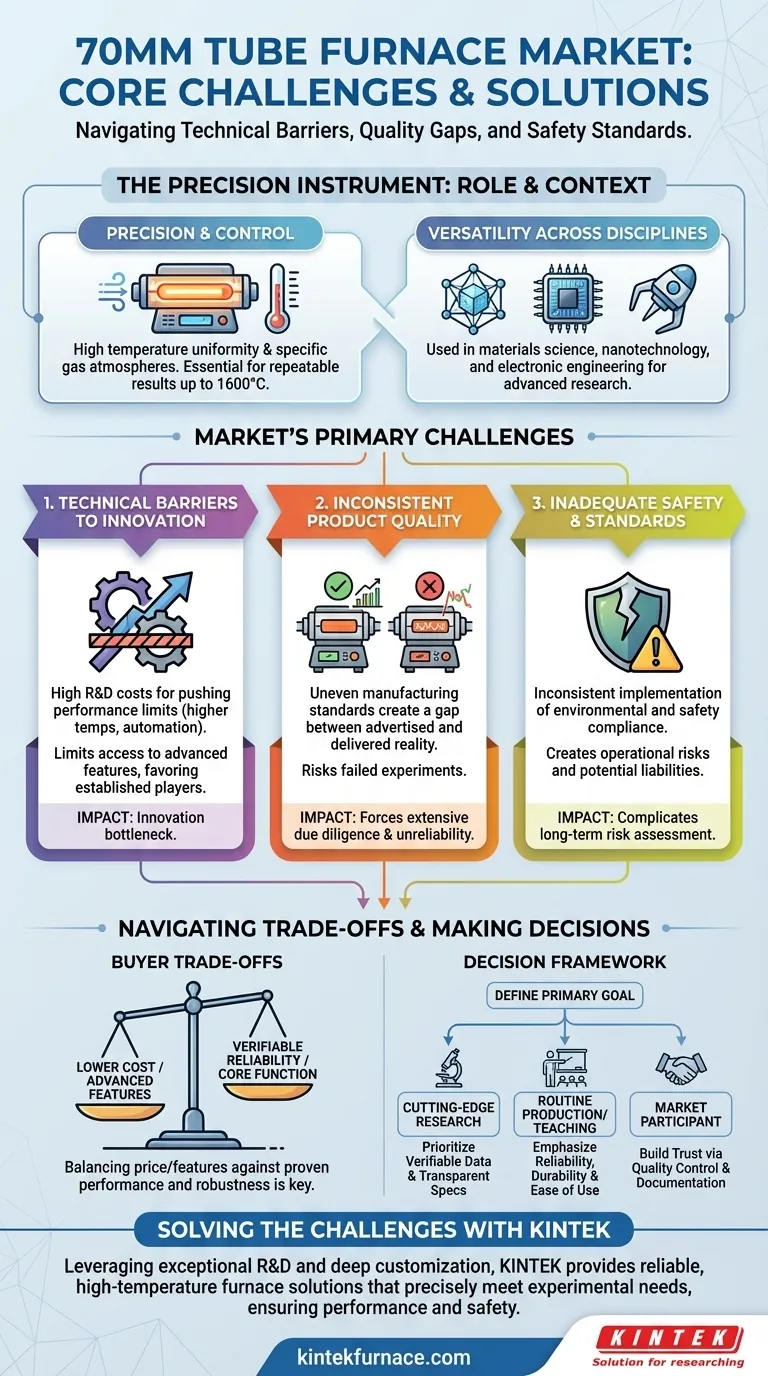
In short, the 70mm tube furnace market faces three primary challenges: significant technical barriers to innovation, inconsistent product quality across different manufacturers, and the inadequate implementation of environmental and safety standards. These issues create a landscape of uncertainty for both buyers and producers, demanding a greater focus on quality management and verifiable performance.
While the 70mm tube furnace is a crucial tool for advanced materials science and industrial processing, its market is fundamentally hampered by a gap between advertised potential and delivered reality. The path to realizing this potential lies in overcoming inconsistent manufacturing quality and a lack of standardized performance.

The Role of the 70mm Tube Furnace
To understand the market's challenges, we must first appreciate the furnace's critical function. It is not just a heater; it is a precision instrument designed for creating and testing the materials of the future.
Precision in a Compact Form
A 70mm tube furnace offers a highly controlled environment. Its key attributes are temperature uniformity and the ability to maintain a specific gas atmosphere, which are essential for repeatable experiments and manufacturing processes.
These furnaces are designed to deliver rapid heating rates to temperatures as high as 1600°C, making them vital tools in laboratories and specialized production lines where space and precision are paramount.
Versatility Across Disciplines
The applications are extensive and demanding. In material science, they are used to study thermal stability and phase transitions. In nanotechnology and electronic engineering, they are used for synthesizing nanomaterials, growing thin films, and annealing semiconductors.
Deconstructing the Market's Core Challenges
The difficulties facing the market are not about a lack of demand, but about the execution and reliability of the supply. These challenges directly impact the trust and outcomes for end-users.
The Technical Barrier: The Push for Higher Performance
While current furnaces are capable, the market demands continuous innovation. Pushing for higher temperatures, better temperature uniformity, and more sophisticated automation and intelligence are significant technical hurdles.
Manufacturers must invest heavily in R&D to meet these demands, creating a barrier for smaller players and concentrating innovation among those with sufficient resources.
The Quality Dilemma: Uneven Product Standards
This is arguably the most significant challenge for a buyer. The market suffers from uneven product quality. One manufacturer's furnace may perform exactly to specification, while a similar-looking unit from another may fail to deliver consistent temperature uniformity or durability.
This inconsistency forces buyers to perform extensive due diligence, as advertised features like durability and ease of use cannot always be taken at face value.
The Compliance Gap: Inadequate Environmental and Safety Standards
Manufacturing and operating high-temperature equipment involves inherent risks and environmental considerations. The market faces a challenge in the inadequate or inconsistent implementation of standards.
This affects everything from operator safety to environmental compliance, creating potential liabilities for institutions and businesses. A lack of clear, enforced standards makes it difficult for buyers to assess the true long-term operational cost and risk of a unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs for Buyers
These market challenges create a difficult landscape for anyone looking to purchase or specify a 70mm tube furnace. Navigating it requires understanding the compromises you may be forced to make.
Cost vs. Verifiable Reliability
The most common trade-off is price versus proven performance. A lower-cost furnace may be tempting, but it carries a higher risk of failing to meet its own specifications for temperature uniformity or stability.
Investing in a unit from a reputable manufacturer with verifiable test data often mitigates the risk of failed experiments or production runs, justifying the higher initial cost.
Advanced Features vs. Core Function
The market trend toward "smart" and automated furnaces introduces another trade-off. While features like remote monitoring and programmable recipes are valuable, they can add complexity.
For some applications, a mechanically simpler but more robust furnace that excels at its core function—maintaining a stable, uniform temperature—is a more prudent choice than a feature-rich but potentially less reliable alternative.
How to Make an Informed Decision
Your choice should be dictated by your primary goal and your tolerance for risk. Use the following framework to guide your decision-making process.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge research: Prioritize manufacturers who provide comprehensive, verifiable performance data and transparent specifications, even if it comes at a premium price.
- If your primary focus is routine production or teaching: Emphasize reliability, durability, and ease of use over the absolute highest performance specs or complex automation features.
- If you are a manufacturer or market participant: Recognize that building trust through rigorous quality control and transparent documentation is the most effective strategy for long-term success.
Navigating these challenges requires a clear understanding of your specific needs, enabling you to select a tool that truly empowers your work.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Description | Impact on Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Barriers | High R&D costs for innovation in temperature control and automation | Limits access to advanced features, increases reliance on established manufacturers |
| Inconsistent Quality | Uneven product standards across manufacturers | Forces extensive due diligence, risks failed experiments or production |
| Environmental & Safety Gaps | Inadequate implementation of standards | Raises operational risks and liabilities, complicates long-term cost assessment |
Facing challenges with 70mm tube furnaces? KINTEK is here to help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable performance and enhanced safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can empower your lab with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















