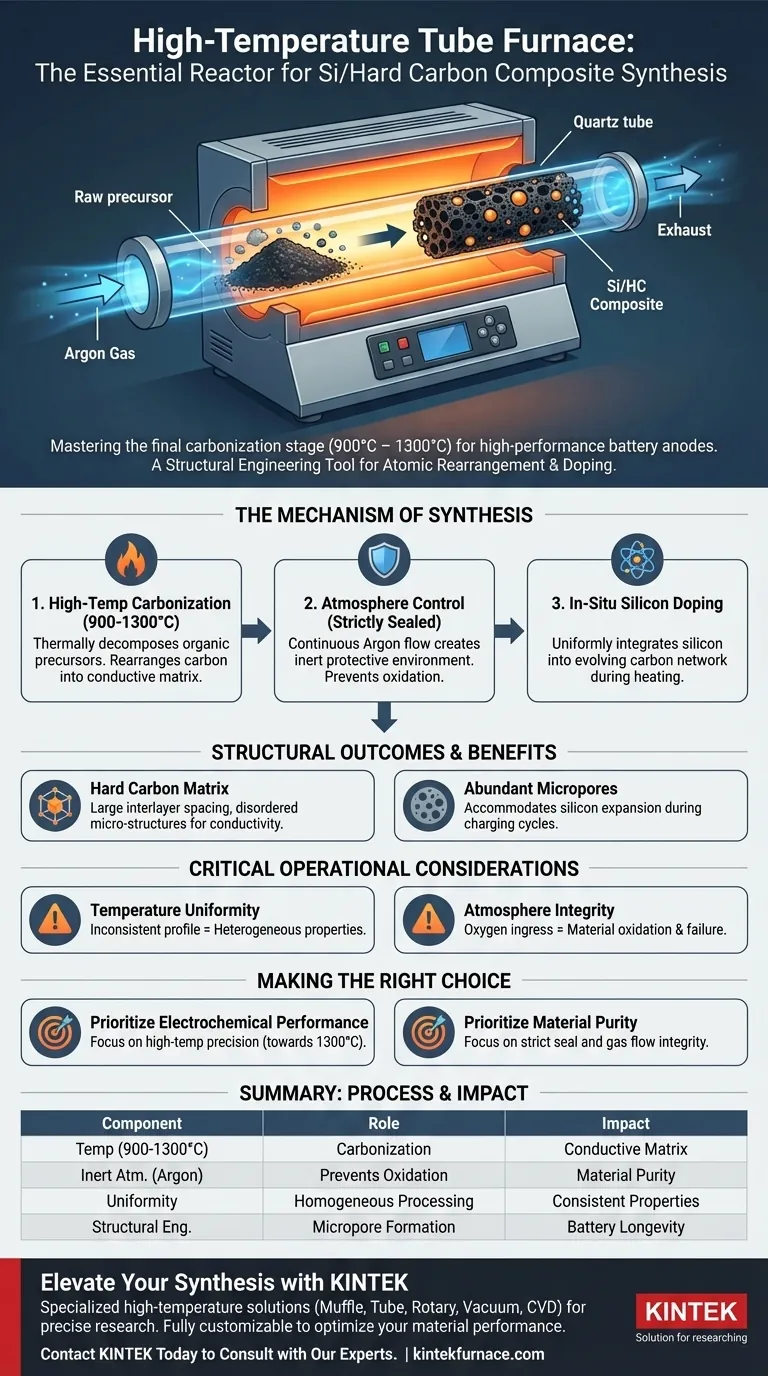
A high-temperature tube furnace functions as the essential reactor for the final carbonization stage of Silicon/Hard Carbon composite synthesis. Operating within a precise thermal range of 900 °C to 1300 °C, it provides a strictly sealed environment for treating precursor materials. By introducing a protective inert atmosphere (typically Argon), the furnace enables the chemical transformation required to integrate silicon into a stable carbon network without the risk of oxidation.
Core Insight: The tube furnace is not merely a heater; it is a structural engineering tool. Its primary value lies in its ability to facilitate the atomic rearrangement of carbon while simultaneously doping it with silicon, creating a composite material with the specific porosity and spacing required for high-performance energy storage.

The Mechanism of Synthesis
High-Temperature Carbonization
The central role of the furnace is to drive the carbonization process. The equipment must sustain temperatures between 900 °C and 1300 °C to thermally decompose organic precursors. This intense heat triggers the rearrangement of the carbon structure, transforming raw materials into a conductive matrix.
Atmosphere Control
Success depends on the furnace's ability to maintain a strictly sealed environment. The tube furnace allows for the continuous flow of Argon gas, creating an inert protective atmosphere. This prevents the carbon and silicon materials from reacting with oxygen, which would degrade the material and ruin the synthesis.
In-Situ Silicon Doping
The thermal environment facilitates in-situ doping. During the heating process, silicon components are effectively incorporated into the evolving carbon network. The furnace ensures this integration happens uniformly, enhancing the final electrochemical performance of the composite.
Structural Outcomes
Formation of the Hard Carbon Matrix
The specific thermal treatment provided by the furnace results in a unique hard carbon structure. Unlike graphite, this matrix is characterized by large interlayer spacing and abundant disordered micro-structures.
Creation of Micropores
The process generates abundant micropores within the material. These physical characteristics are critical for battery applications, as they provide the necessary volume to accommodate the expansion of silicon during charging cycles.
Critical Operational Considerations
Temperature Uniformity
While the furnace targets a specific temperature (e.g., 1100 °C), the thermal profile along the tube length matters. Inconsistent heating can lead to heterogeneous material properties, where some portions of the sample are fully carbonized and others remain under-processed.
Atmosphere Integrity
The "strictly sealed" nature of the furnace is a potential point of failure. Any breach in the vacuum or gas lines that allows oxygen ingress will result in material oxidation. This compromises the fixation of doping elements and destroys the conductivity of the carbon framework.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Silicon/Hard Carbon composites, focus on these operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: Prioritize the precision of the upper temperature range (towards 1300 °C) to maximize carbon rearrangement and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Focus strictly on the integrity of the gas flow system and seals to ensure a zero-oxygen environment throughout the entire heating and cooling cycle.
Mastering the atmosphere and thermal profile of the tube furnace is the single most important factor in transitioning from raw precursors to a functional battery anode.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in Synthesis | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (900-1300°C) | High-Temperature Carbonization | Creates conductive matrix and atomic rearrangement. |
| Inert Atmosphere (Argon) | Prevents Oxidation | Ensures material purity and prevents degradation. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Homogeneous Processing | Guarantees consistent material properties and conductivity. |
| Structural Engineering | Micropore Formation | Accommodates silicon expansion for battery longevity. |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a failed batch and a high-performance battery anode. KINTEK provides the specialized high-temperature solutions necessary for the complex synthesis of Silicon/Hard Carbon composites.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you require precise thermal profiles for carbonization or strict atmosphere integrity for in-situ doping, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your material performance? Contact KINTEK today to consult with our experts and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Rajib Samanta, Sudip Barman. Correlating the Sodium Storage Mechanism and Enhancing the Initial Coulombic Efficiency of Biomass‐Derived Hard Carbon in Sodium‐Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/batt.202500295
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the pre-treatment of activated carbon catalysts? Precision Modification
- How does annealing in a laboratory tube furnace affect In2Se3 quality? Achieve Phase Stabilization & Purity
- What is the technical significance of using a dual-temperature zone tube furnace for CoTe2 tellurization?
- What is chemical vapor transport and how is it related to tube furnaces? Master CVT for High-Quality Crystal Growth
- Why is quartz tube vacuum sealing technology utilized during the synthesis of [Pd@Bi10][AlCl4]4 cluster compounds?
- How does a high vacuum tube furnace contribute to the carbonization process? Engineered Hard Carbon Synthesis
- What are the advantages of tube furnaces for certain applications? Unlock Precise Atmosphere and Temperature Control
- How do tube furnaces contribute to transport reactions and crystal production? Master High-Purity Synthesis with Precision Control



















