In materials science, chemical vapor transport (CVT) is a highly effective method for synthesizing, purifying, and growing high-quality single crystals of solid materials. It works by converting a non-volatile solid into a volatile, gaseous compound using a "transport agent," moving it along a temperature gradient, and then reversing the reaction to re-deposit the pure solid elsewhere. A tube furnace is the essential piece of equipment that creates and controls this precise temperature gradient.
Chemical vapor transport isn't simply about heating; it's a strategic process that leverages a reversible chemical reaction and a controlled temperature gradient to move and purify solid materials. A tube furnace is the ideal instrument for establishing this precise thermal environment, making it the workhorse for CVT.
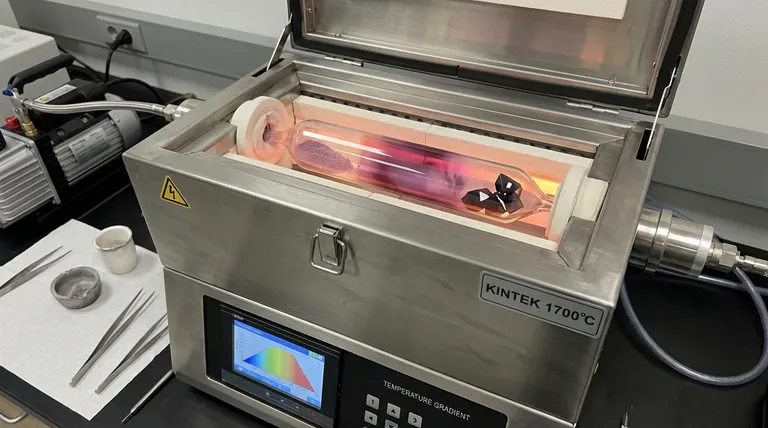

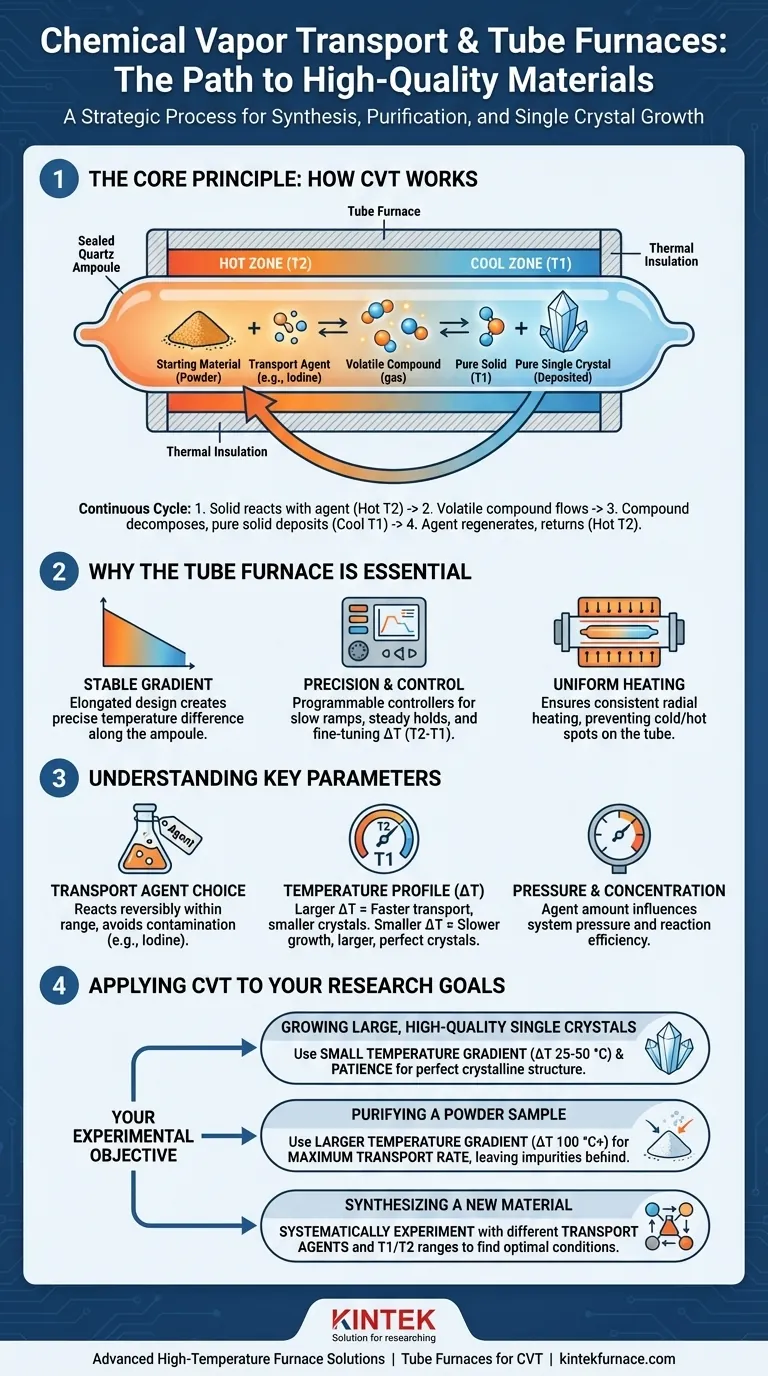
The Core Principle: How CVT Works
Chemical vapor transport operates within a sealed container, typically a quartz tube (ampoule), where all the magic happens. The process is a continuous, closed-loop cycle driven by temperature.
### The Sealed System
The process begins with the starting material—often a powder—placed inside a quartz ampoule along with a small amount of a transport agent. The ampoule is then evacuated to remove air and other contaminants and sealed under vacuum.
### The Transport Agent
The transport agent is the key. This is a chemical (commonly a halogen like iodine) that is gaseous at the operating temperature and reacts reversibly with the solid material you want to move.
### Establishing the Temperature Gradient
The sealed ampoule is placed inside a tube furnace, which is configured to create two distinct temperature zones: a hotter zone (T2) and a cooler zone (T1). The starting material is located in the hot zone.
### The Reversible Reaction in Action
At the hot end (T2), the solid material reacts with the transport agent gas to form a new, volatile gaseous compound.
Solid (at T2) + Agent (gas) ⇌ Volatile Compound (gas)
This gaseous compound then diffuses or flows from the hot zone toward the cooler zone (T1).
### Deposition and Regeneration
Once the volatile compound reaches the cooler zone (T1), the thermodynamic equilibrium shifts. The reverse reaction becomes favorable, and the compound decomposes, depositing the pure solid material and releasing the transport agent gas.
This newly deposited material is often in the form of high-purity single crystals. The freed transport agent gas is now ready to diffuse back to the hot zone to react with more starting material, continuing the cycle.
Why the Tube Furnace is Essential
The tube furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision instrument perfectly suited for the demands of CVT.
### Creating the Stable Gradient
The elongated, cylindrical shape of a tube furnace is ideal for establishing a stable and predictable temperature gradient along the length of the sealed ampoule. Multi-zone furnaces allow for precise, independent control over the T2 and T1 temperatures.
### Precision and Control
Modern tube furnaces offer programmable controllers that allow researchers to slowly ramp temperatures, hold them steady for days or weeks, and fine-tune the ΔT (the difference between T2 and T1). This control is critical for influencing the rate of transport and the quality of the resulting crystals.
### Uniform Heating
The furnace's design ensures uniform radial heating around the ampoule. This prevents unwanted cold or hot spots on the circumference of the tube, ensuring the transport process occurs consistently along its length.
Understanding the Key Parameters
Success with CVT depends on carefully controlling a few critical variables. This is where the process moves from a simple concept to a nuanced scientific technique.
### Choosing the Transport Agent
The agent must react reversibly with the source material within a practical temperature range. It should not form any undesirable, stable side-products that would contaminate the final crystal. Iodine is a classic agent used for transporting many metals and chalcogenides, like the tantalum disulfide (TaS₂) mentioned in literature.
### The Temperature Profile (T2 and T1)
The temperatures of the hot and cold zones are the primary drivers. The temperature difference (ΔT) dictates the speed of the transport. A larger ΔT generally leads to faster transport but can result in smaller or lower-quality crystals. A small ΔT yields slower growth but often produces larger, more perfect single crystals.
### Pressure and Concentration
The amount of transport agent added to the sealed ampoule determines the partial pressure within the system. This pressure directly influences the reaction equilibrium and, consequently, the efficiency and rate of the transport process.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your experimental objective will determine how you configure the CVT process.
- If your primary focus is growing large, high-quality single crystals: Use a small temperature gradient (e.g., ΔT of 25-50 °C) and be patient, as this slow growth rate promotes crystalline perfection.
- If your primary focus is purifying a powder sample: Use a larger temperature gradient (e.g., ΔT of 100 °C or more) to maximize the transport rate, leaving impurities behind in the hot zone.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing a new material: Systematically experiment with different transport agents and a wide range of T1 and T2 temperatures to discover the conditions under which the desired compound forms.
Mastering chemical vapor transport is about harnessing thermodynamics to precisely control the formation and purity of solid-state materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Reversible reaction in a sealed ampoule with a transport agent (e.g., iodine) to move and deposit solids via a temperature gradient. |
| Key Equipment | Tube furnace for creating and controlling precise temperature zones (hot T2 and cool T1). |
| Applications | Synthesis, purification, and growth of high-quality single crystals in materials science. |
| Critical Parameters | Transport agent choice, temperature gradient (ΔT), and pressure/concentration in the system. |
Ready to elevate your materials research with precise temperature control? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces ideal for chemical vapor transport. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—whether for crystal growth, purification, or synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















