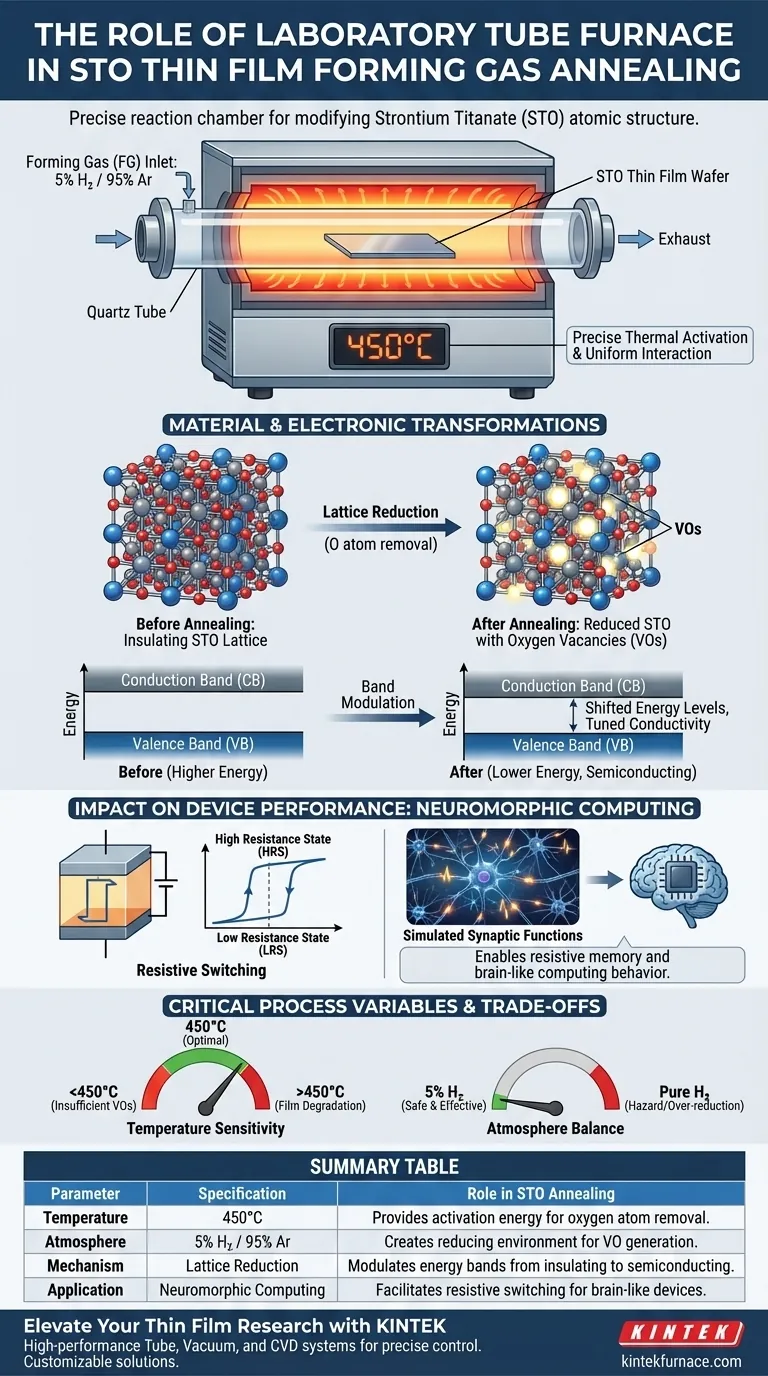
A laboratory tube furnace serves as the precise reaction chamber required to modify the atomic structure of Strontium Titanate (STO) thin films. It facilitates a specific annealing process at 450°C in a reducing environment, utilizing forming gas to intentionally alter the material's electronic properties.
Core Insight The tube furnace does not simply heat the material; it creates a controlled reducing atmosphere that removes oxygen atoms from the STO lattice. This generation of oxygen vacancies is the fundamental mechanism that unlocks the material's potential for use in advanced neuromorphic (brain-like) computing devices.

The Mechanism of Forming Gas Annealing
Creating the Reducing Environment
The primary role of the tube furnace is to maintain a specific atmospheric composition known as forming gas (FG). For STO thin films, this atmosphere consists of 5% Hydrogen (H2) balanced with Argon (Ar).
Precise Thermal Activation
The furnace provides a stable thermal environment at exactly 450°C. This temperature is critical because it provides the activation energy required for the hydrogen to interact with the STO film without destroying the underlying substrate or film integrity.
Controlled Interaction
By confining the gas flow and heat within the tube, the furnace ensures the interaction between the hydrogen and the thin film is uniform. This uniformity is essential for consistent device performance across the entire wafer or sample.
Material and Electronic Transformations
Generation of Oxygen Vacancies (VOs)
The combination of heat and the hydrogen-rich atmosphere induces the removal of oxygen atoms from the STO crystal lattice. This process, known as reduction, creates oxygen vacancies (VOs) within the material structure.
Modulating Energy Bands
These oxygen vacancies are not defects in the negative sense; they are functional engineering tools. They alter the material's energy band structure. Specifically, they shift the valence band maximum and the conduction band minimum to lower energy levels.
Tuning Conductivity
This shift in the energy bands effectively tunes the electrical conductivity of the STO. It transitions the material from a purely insulating state closer to a semiconducting state suitable for switching applications.
Impact on Device Performance
Enabling Resistive Switching
The structural and electronic changes facilitated by the furnace are directly responsible for the material's resistive switching performance. This ability to switch between high and low resistance states is the memory mechanism in modern non-volatile memory.
Simulating Synaptic Functions
Because the oxygen vacancies can move under an electric field, the device can mimic biological synapses. The annealing process allows the STO to exhibit simulated synaptic functions, making it a viable candidate for neuromorphic computing hardware.
Critical Process Variables and Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While some annealing processes (like those for silicon or barium titanate) operate at temperatures exceeding 1000°C, STO forming gas annealing requires a relatively lower temperature of 450°C. Deviating significantly from this temperature can result in insufficient vacancy formation (if too low) or potential film degradation (if too high).
Atmosphere Balance
The concentration of hydrogen is a critical variable. A standard 5% mixture is safer and effective for this specific reduction. Using pure hydrogen would present significant safety hazards and might over-reduce the material, stripping too much oxygen and collapsing the crystal structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your annealing process, align your furnace parameters with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Material Physics: Prioritize the precise control of the 5% H2/Ar flow rate to fine-tune the density of oxygen vacancies and the resulting band structure shift.
- If your primary focus is Device Application: Focus on thermal uniformity at 450°C to ensure consistent resistive switching behaviors across the entire neuromorphic device array.
The laboratory tube furnace is the bridge between raw material and functional device, turning a standard dielectric into a dynamic component for next-generation computing.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Role in STO Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 450°C | Provides activation energy for oxygen atom removal without film degradation. |
| Atmosphere | 5% H₂ / 95% Ar | Creates a reducing environment to generate functional oxygen vacancies (VOs). |
| Mechanism | Lattice Reduction | Modulates energy bands to shift the material from insulating to semiconducting. |
| Application | Neuromorphic Computing | Facilitates resistive switching behavior for brain-like memory devices. |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when engineering oxygen vacancies for next-generation neuromorphic devices. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the exact thermal uniformity and atmosphere control required for STO forming gas annealing.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our laboratory high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs. Don't leave your material transformations to chance—contact our technical specialists today to find the ideal furnace solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Fandi Chen, Dewei Chu. Enhancing Synaptic Plasticity in Strontium Titanate‐Based Sensory Processing Devices: A Study on Oxygen Vacancy Modulation and Performance in Artificial Neural Networks. DOI: 10.1002/aidi.202500028
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are ceramic fiber blankets used in linear actuated tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Lab Safety
- What are the advantages of a dual-zone tube furnace for Ti3C2Tx MXene? Master Precise Sulfurization Kinetics
- Why is an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace required for NC substrate preparation? Essential for carbonization.
- What is the role of a tube sintering furnace during the activation of carbon materials? Expert Guide to CO2 Activation
- What role do tube furnaces play in the new energy and lithium materials industry? Essential for Precision Thermal Processing
- What are some thermal processes that tube furnaces are used for? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment with Uniformity
- What role does a tube pyrolysis reactor play in sludge and chloride co-pyrolysis? Enhanced Heavy Metal Removal
- What factors affect the price of a vacuum tube furnace? Key Drivers and Smart Investment Tips



















