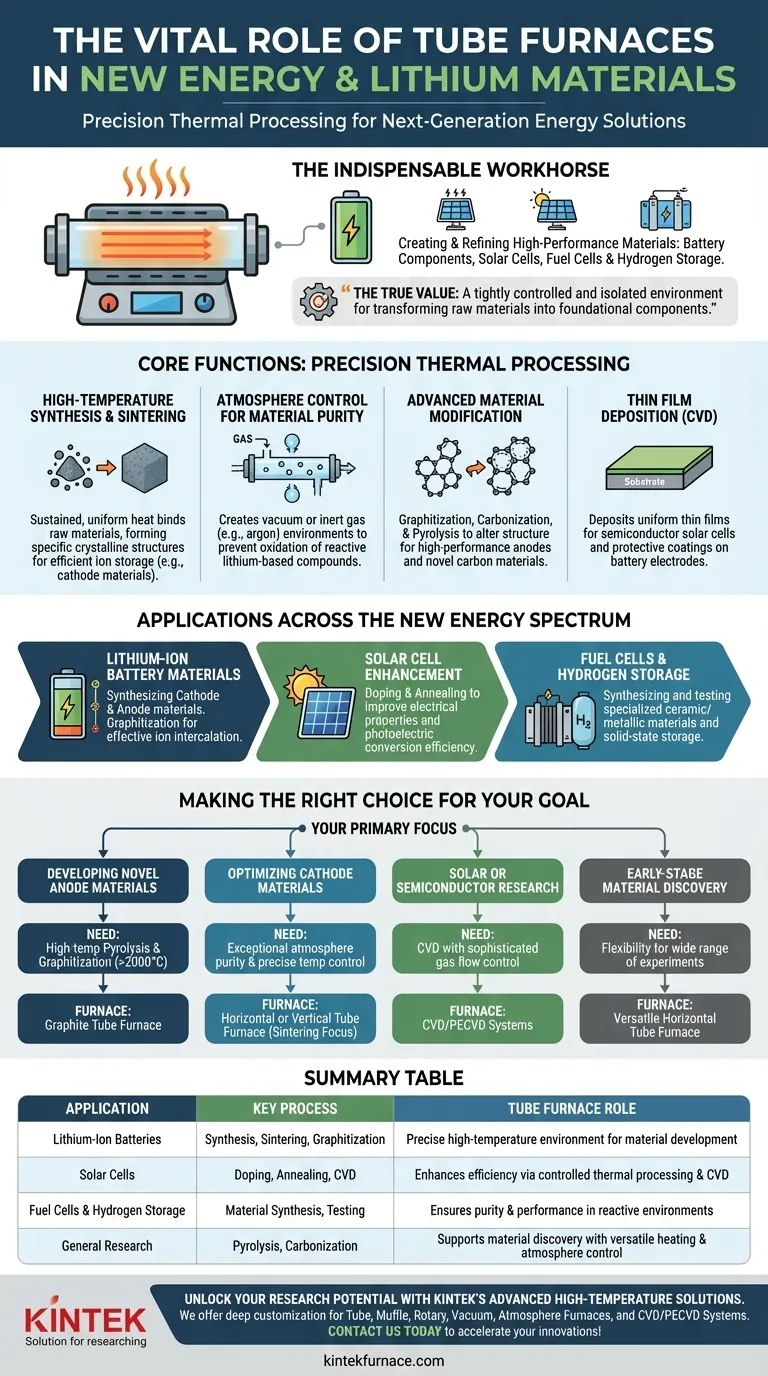
At their core, tube furnaces are the indispensable workhorses for creating and refining the high-performance materials that power the new energy industry. They are used for the critical thermal processing of next-generation lithium-ion battery components, enhancing the efficiency of solar cells, and developing materials for fuel cells and hydrogen storage. Their function is to provide an extremely precise and controllable high-temperature environment, which is non-negotiable for achieving the specific material properties required for advanced energy applications.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its capacity to create a tightly controlled and isolated environment. This precision is what allows researchers and manufacturers to transform raw materials into the foundational components of modern energy technology.

The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
A tube furnace's role extends far beyond simple heating. It is an instrument of transformation, enabling specific chemical and physical changes that are impossible to achieve under normal conditions.
High-Temperature Synthesis and Sintering
Many advanced materials, particularly the cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries, are created through solid-state reactions.
A tube furnace provides the sustained, uniform high temperatures needed to sinter powdered raw materials, binding them together and forming the specific crystalline structure required for efficient ion storage and transfer.
Atmosphere Control for Material Purity
Many materials used in new energy, especially lithium-based compounds, are highly reactive with oxygen and moisture at high temperatures.
Tube furnaces excel at creating a controlled atmosphere, whether it's a vacuum to remove contaminants or an inert gas (like argon) to prevent oxidation. This ensures the final material is pure and possesses the desired electrochemical properties.
Advanced Material Modification
Tube furnaces are used for specialized processes that fundamentally alter a material's structure.
Graphitization and carbonization are key processes for producing high-performance carbon-based anode materials. Pyrolysis, the thermal decomposition of materials in the absence of oxygen, is used in biomass-to-energy research and for creating novel carbon structures.
Thin Film Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where a furnace is used to deposit a thin, uniform film of material onto a substrate.
This technique is crucial in the semiconductor industry for fabricating solar cells and is being explored for creating protective coatings on battery electrodes to improve their lifespan and performance.
Applications Across the New Energy Spectrum
While prominent in battery development, the role of tube furnaces spans the entire new energy landscape, from generation to storage.
Lithium-Ion Battery Materials
This is the most significant application. Furnaces are used to synthesize both cathode materials (like NMC or LFP) and anode materials. The graphitization of carbon for anodes is a classic high-temperature furnace process designed to create a structure that can effectively intercalate lithium ions.
Solar Cell Enhancement
In the production of silicon-based solar cells, tube furnaces are used for critical steps like doping and annealing. These controlled heating processes introduce impurities to alter the silicon's electrical properties and repair crystal lattice damage, directly improving the cell's photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Storage
The development of fuel cells relies on specialized materials for electrolytes and electrodes. Tube furnaces provide the controlled environment needed to synthesize and test these new ceramic and metallic materials, as well as materials being researched for solid-state hydrogen storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The specific design is dictated by the process it needs to perform, highlighting the importance of choosing the right tool for the job.
Specialized Furnace Types
A horizontal tube furnace is a versatile standard for general-purpose annealing and sintering. A vertical tube furnace is better for processes like CVD or when samples must not touch the tube walls. A graphite tube furnace is specifically designed to reach the ultra-high temperatures required for graphitization.
The Challenge of Scale
A furnace used for fundamental research in a lab is vastly different from one used in industrial production. Scaling a process from grams to kilograms or tons requires overcoming significant engineering challenges related to maintaining temperature uniformity and atmosphere control in a much larger volume.
The Cost of Precision
Higher performance comes at a cost. A simple furnace for basic heat treatment is relatively inexpensive. However, a system capable of reaching very high temperatures (>1500°C), maintaining a high vacuum, and allowing for precise multi-gas flow control is a complex and significantly more expensive piece of equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the type of thermal processing required. Understanding your primary objective is key to leveraging the right technology.
- If your primary focus is developing novel anode materials: You need a furnace capable of high-temperature pyrolysis and graphitization, often exceeding 2000°C.
- If your primary focus is optimizing cathode materials: You need a furnace with exceptional atmosphere purity and precise temperature control for solid-state sintering reactions.
- If your primary focus is solar or semiconductor research: Your priority should be a furnace system configured for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) with sophisticated gas flow control.
- If your primary focus is early-stage material discovery: A versatile horizontal tube furnace with good temperature and atmosphere control offers the flexibility for a wide range of experiments.
Mastering controlled thermal processing is fundamental to inventing the materials that will define the future of energy.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Tube Furnace Role |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Synthesis, Sintering, Graphitization | Provides precise high-temperature environment for cathode/anode material development |
| Solar Cells | Doping, Annealing, CVD | Enhances efficiency through controlled thermal processing and thin film deposition |
| Fuel Cells & Hydrogen Storage | Material Synthesis, Testing | Ensures purity and performance in reactive environments |
| General Research | Pyrolysis, Carbonization | Supports material discovery with versatile heating and atmosphere control |
Unlock the full potential of your new energy and lithium materials research with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're scaling up for production or optimizing for precision. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can accelerate your innovations in battery technology, solar energy, and beyond!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















