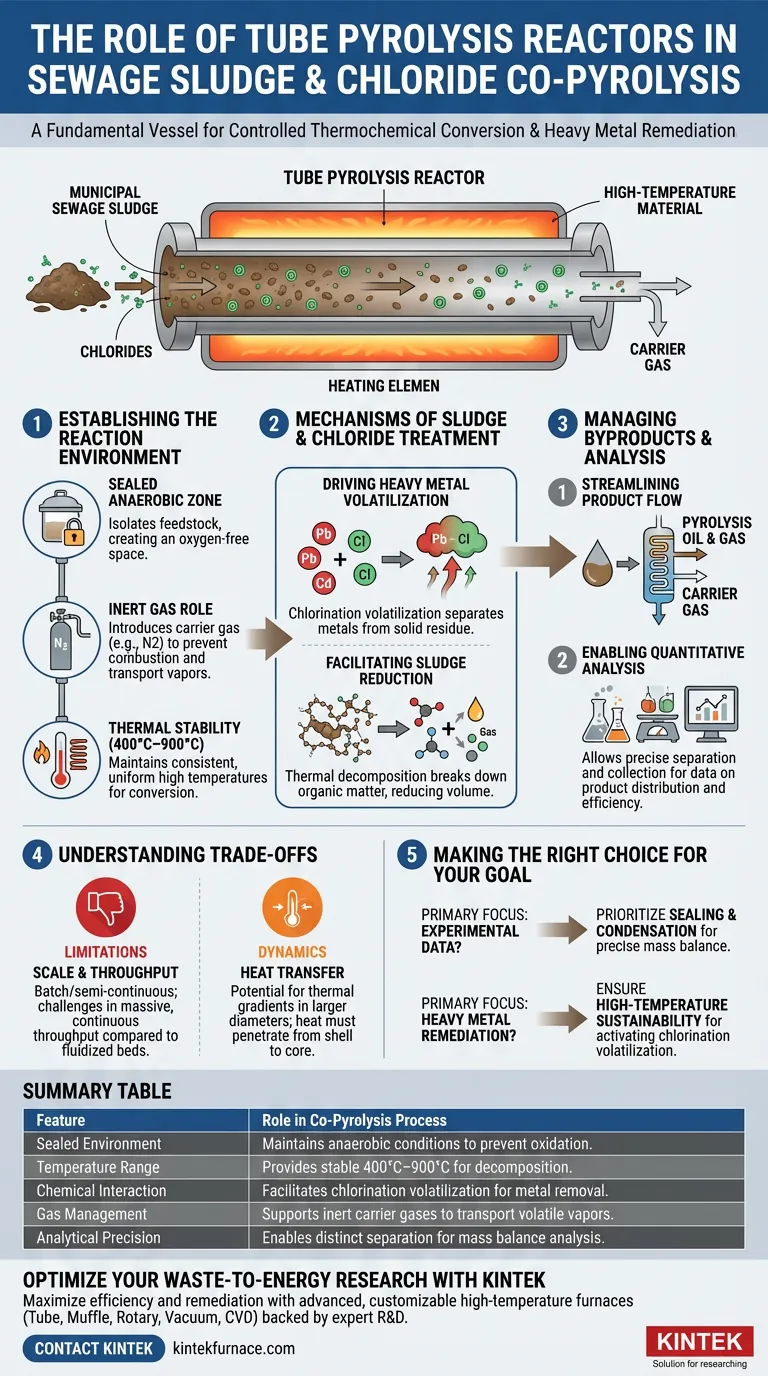
A tube pyrolysis reactor serves as the fundamental vessel for the controlled thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge. It creates a sealed, high-temperature environment that excludes oxygen, allowing for the precise heating required to decompose organic matter. Crucially, this specific reactor design facilitates the interaction between sludge and chlorides, enabling the effective removal of heavy metals through chlorination volatilization.
The tube pyrolysis reactor is not just a heating element; it is a stabilized process chamber. It balances the need for uniform high temperatures with a controlled atmosphere to drive simultaneous waste reduction and heavy metal separation.
Establishing the Reaction Environment
Creating a Sealed Anaerobic Zone
The primary function of the reactor is to isolate the feedstock from the external atmosphere. By using high-temperature resistant reaction tubes, the system provides a completely sealed space that supports anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions.
The Role of Inert Gases
To prevent unwanted combustion or oxidation, the reactor structure facilitates the continuous introduction of inert protective gases. This "carrier gas" maintains the inert atmosphere required for pyrolysis and helps transport volatile vapors out of the heating zone.
Ensuring Thermal Stability
For co-pyrolysis to work effectively, temperatures must remain stable. The reactor is designed to maintain consistent high temperatures—typically ranging from 400°C to 900°C—ensuring that the thermal energy required for chemical conversion is applied uniformly to the sludge and chloride mixture.
Mechanisms of Sludge and Chloride Treatment
Driving Heavy Metal Volatilization
The inclusion of chlorides in the process is intended to treat heavy metals found in sewage sludge. The tube reactor provides the necessary thermal environment for "chlorination volatilization," a reaction where heavy metals react with chlorides to become volatile salts that can be separated from the solid residue.
Facilitating Sludge Reduction
Beyond heavy metals, the reactor functions as a volume reduction tool. The high-temperature environment triggers the thermal decomposition of the sludge's organic components, breaking down complex polymers into simpler compounds.
Managing Byproducts and Analysis
Streamlining Product Flow
The structural design of the reactor, particularly in horizontal configurations, optimizes the flow of byproducts. It guides the mixture of pyrolysis oil and gas, along with the carrier gas, out of the heated zone and into downstream condensation systems.
Enabling Quantitative Analysis
For experimental or process validation contexts, this reactor type is invaluable. It allows for the distinct separation and collection of solid residues, oils, and gases, ensuring the integrity of data regarding product distribution and conversion efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Scale and Throughput Limitations
While excellent for controlled environments and data gathering, tube reactors are often batch or semi-continuous systems. They may face challenges in processing the massive, continuous throughput required for full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants compared to fluidized bed reactors.
Heat Transfer Dynamics
Although the design aims for uniform heat, the physical nature of a tube means heat must penetrate from the shell to the core. In larger diameter tubes, this can occasionally lead to thermal gradients where the material in the center heats more slowly than material near the walls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a tube pyrolysis reactor in your application, consider your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is experimental data and analysis: Prioritize the reactor's sealing capabilities and condensation system integration to ensure precise mass balance calculations and product characterization.
- If your primary focus is heavy metal remediation: Ensure the reactor can sustain the specific high-temperature thresholds required to activate the chlorination volatilization process for the specific metals present in your sludge.
Ultimately, the tube pyrolysis reactor provides the essential stability required to turn hazardous sewage sludge into manageable byproducts.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Co-Pyrolysis Process |
|---|---|
| Sealed Environment | Maintains anaerobic conditions to prevent oxidation and combustion. |
| Temperature Range | Provides stable 400°C–900°C heat for thermochemical decomposition. |
| Chemical Interaction | Facilitates chlorination volatilization to remove heavy metals from sludge. |
| Gas Management | Supports inert carrier gases to transport volatile vapors to condensation. |
| Analytical Precision | Enables distinct separation of solid, oil, and gas for mass balance analysis. |
Optimize Your Waste-to-Energy Research with KINTEK
Maximize the efficiency of your co-pyrolysis and heavy metal remediation processes with high-performance equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique laboratory or pilot-scale needs.
Whether you are refining chlorination volatilization or scaling sludge reduction, our precision-engineered high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmosphere control your research demands.
Ready to upgrade your lab’s thermal processing capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Mahboub Saffari, Rezvan Mashayekhi. The fate and mobility of chromium, arsenic and zinc in municipal sewage sludge during the co-pyrolysis process with organic and inorganic chlorides. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-87169-3
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the diversification of vacuum tube furnaces impact the market? Unlock Specialized Solutions for Advanced Materials
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace used for CVD in catalyst synthesis? Achieve Precise Nano-Material Growth
- Why is thermal uniformity important in a drop tube furnace? Ensure Reliable Results and Consistent Processes
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why is vacuum control critical when using a horizontal tube furnace for the 550 °C annealing of a-SiC:H films?
- What are the industrial design advantages of using a tube furnace for ex-situ reduction of catalysts? Optimize Efficiency
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace with an Argon atmosphere required for the carbonization of biomass? Key Insights
- In which industries and research domains are vertical tube furnaces commonly used? Essential for Precision Thermal Processing



















