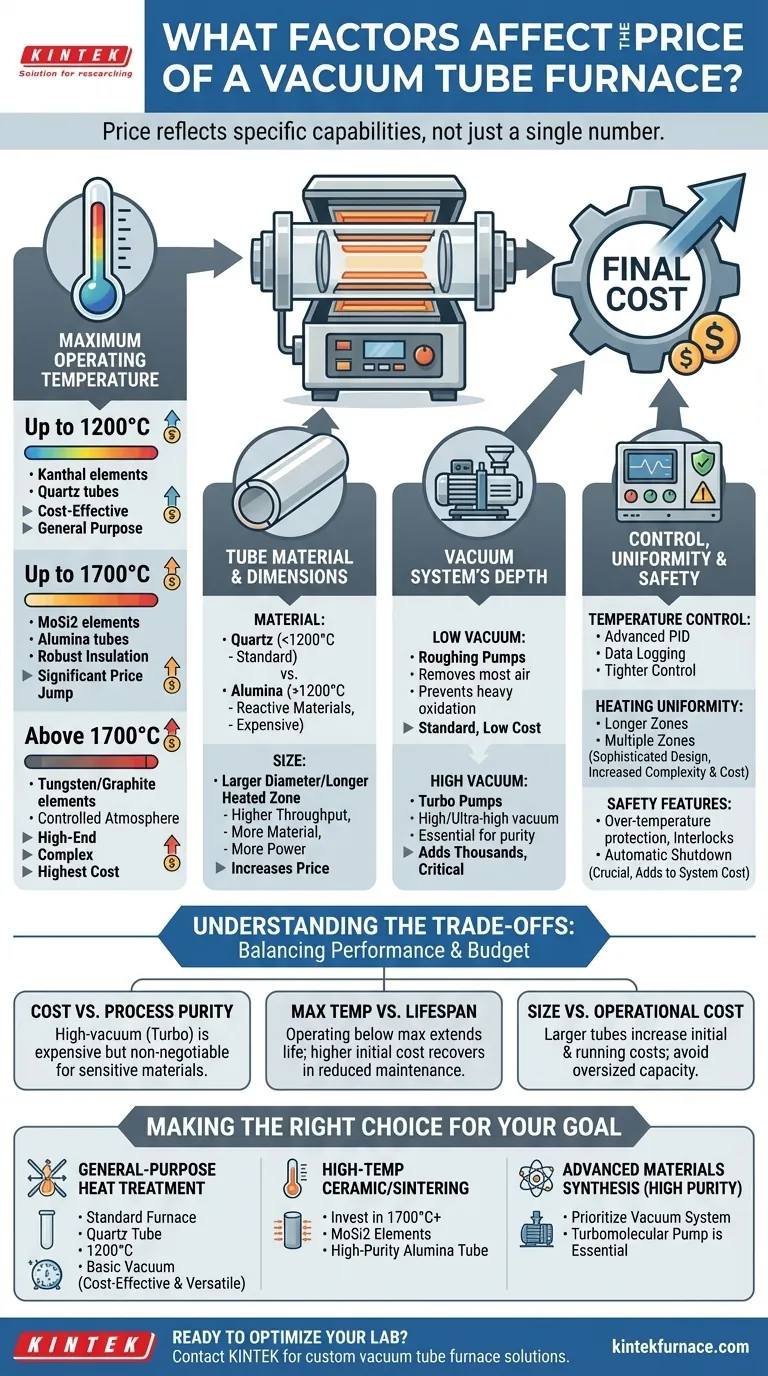
The price of a vacuum tube furnace is not a single number, but a direct reflection of its specific capabilities. The final cost is determined by a core set of factors, including its maximum operating temperature, the material and size of its process tube, the performance of its vacuum system, and the precision of its control systems. While basic models are available for a few thousand dollars, highly specialized systems for advanced research can easily exceed tens of thousands.
The key to a sound investment is understanding that each technical specification directly impacts cost. Your goal is not to find the cheapest furnace, but to precisely match the furnace's capabilities to your specific application, ensuring you pay only for the performance you truly need.
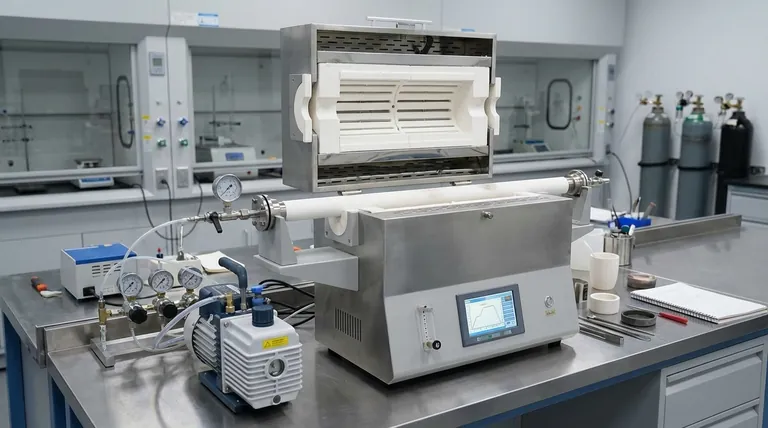

Deconstructing the Core Cost Drivers
A vacuum tube furnace is a system of interconnected components. The cost escalates as each component is upgraded to handle more extreme conditions.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The single largest driver of cost is often the maximum temperature. Furnaces are typically grouped into temperature classes, and crossing into a higher class involves a significant price jump.
- Up to 1200°C: These furnaces commonly use Kanthal (FeCrAl) heating elements and can use inexpensive quartz tubes, making them the most cost-effective option for general-purpose applications.
- Up to 1700°C: Reaching these temperatures requires more expensive Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements and high-purity alumina tubes. The insulation and power systems must also be more robust.
- Above 1700°C: This is the high-end tier. Furnaces may use tungsten or graphite elements, requiring carefully controlled inert or vacuum atmospheres to prevent the elements from oxidizing. This adds complexity and significant cost.
Tube Material and Dimensions
The process tube is the heart of the furnace, containing your sample and the process atmosphere. Its material and size are critical cost factors.
- Material: Quartz is standard for work below 1200°C. For higher temperatures or if your process involves materials that react with quartz (like alkalis), you must use a more expensive alumina tube.
- Size: A larger tube diameter or a longer heated zone allows for bigger samples or higher throughput. However, this requires a physically larger furnace, more powerful heating elements, and more raw material for the tube, all of which increase the price.
The Vacuum System's Depth
The term "vacuum" can mean very different things, and the level of vacuum you require directly influences the price.
- Low Vacuum (Roughing Pumps): A simple mechanical rotary vane pump can remove most of the air, which is sufficient for preventing heavy oxidation. This is a standard, relatively low-cost setup.
- High Vacuum (Turbo Pumps): To achieve a high or ultra-high vacuum environment for sensitive materials, a two-stage system is needed, pairing a roughing pump with a turbomolecular pump. This system, along with the necessary gauges and controllers, can add thousands of dollars to the furnace cost but is essential for preventing trace contamination.
Control, Uniformity, and Safety
The precision of the furnace's operation is another key factor.
- Temperature Control: All modern furnaces use a PID controller for stability, but higher-end systems offer more programming steps, data logging, and tighter control.
- Heating Uniformity: A basic furnace may have a short, uniform temperature zone in the center. Achieving a longer uniform zone for larger samples or crystal growth often requires a more sophisticated furnace design or even multiple, independently controlled heating zones, increasing complexity and cost.
- Safety Features: Features like over-temperature protection, vacuum interlocks, and automatic shutdown systems are crucial for safe operation but add to the overall system cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance requirements with budget constraints. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is the most common purchasing mistake.
Cost vs. Process Purity
A high-vacuum system with a turbo pump is significantly more expensive. However, for applications like thin-film deposition or synthesizing air-sensitive 2D materials, it is non-negotiable. Attempting such work in a low-vacuum system will lead to contaminated samples and failed experiments, making the cheaper furnace a wasted investment.
Maximum Temperature vs. Lifespan
Consistently operating a furnace at its absolute maximum rated temperature dramatically shortens the life of its heating elements and process tube. A more robust long-term strategy is to select a furnace with a maximum temperature at least 100-200°C higher than your typical operating point. This initial extra cost is often recovered in reduced maintenance and replacement parts.
Size vs. Operational Cost
A larger furnace tube increases throughput but also comes with higher initial and operational costs. It requires more power to heat and more process gas to purge. Carefully evaluate your sample size and batch requirements to avoid paying for oversized capacity you will never use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace by defining your primary application first, then matching the specifications to that need.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or annealing: A standard furnace with a quartz tube, a 1200°C maximum temperature, and a basic vacuum system is the most cost-effective and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature ceramic processing or sintering: Invest in a furnace rated for at least 1700°C with MoSi2 elements and a high-purity alumina tube.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials synthesis requiring high purity: Prioritize the vacuum system; a turbomolecular pump is essential, even if your temperature requirements are modest.
By aligning these technical specifications with your core scientific or production goals, you invest in a tool that delivers reliable results and true long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Price | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | High | Higher temps require advanced elements (e.g., MoSi2, tungsten) and materials, increasing cost significantly. |
| Tube Material and Size | Medium to High | Quartz is cost-effective for <1200°C; alumina for higher temps or reactive materials. Larger tubes add expense. |
| Vacuum System Performance | High | Low vacuum (roughing pumps) is cheaper; high vacuum (turbo pumps) adds thousands for purity needs. |
| Control Precision and Safety | Medium | Advanced PID controllers, uniform heating zones, and safety features raise costs but ensure reliability. |
Ready to optimize your lab with a custom vacuum tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research efficiency and deliver reliable, long-term value!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















