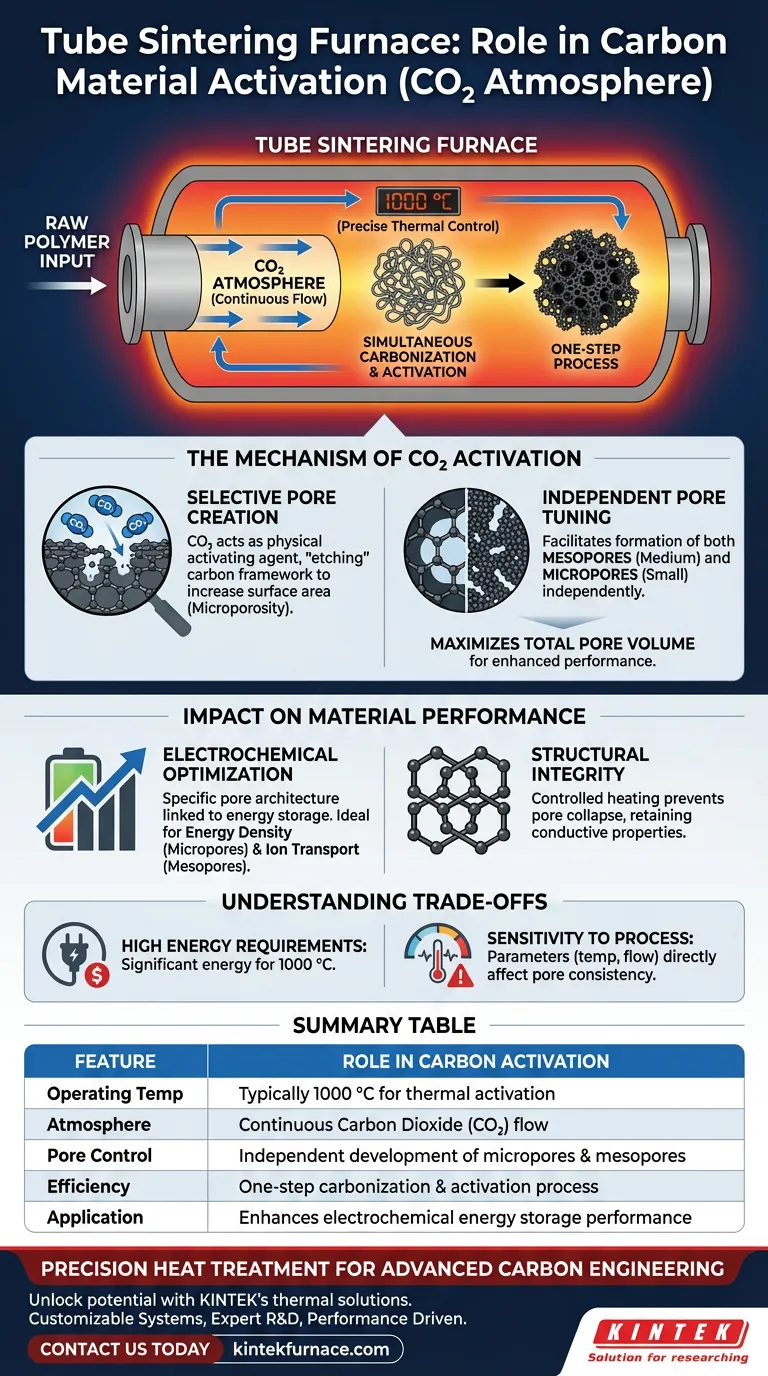
A tube sintering furnace functions as a precise, high-temperature reactor that facilitates the simultaneous carbonization and activation of organic polymers. By maintaining a stable environment at approximately 1000 °C under a continuous flow of carbon dioxide (CO2), the furnace drives the chemical transformation of raw polymers into highly porous carbon materials suitable for advanced applications.
The core value of this process lies in its ability to engineer specific pore structures. The CO2 atmosphere allows for the independent development of micropores and mesopores, maximizing total pore volume to significantly enhance electrochemical energy storage performance.
Creating the Optimal Reaction Environment
Precise Thermal Control
The tube sintering furnace provides the strictly controlled thermal environment required for activation, typically holding a temperature of around 1000 °C.
This high heat is necessary to initiate the reaction between the carbon precursor and the CO2 atmosphere.
One-Step Process Efficiency
Unlike multi-stage methods that separate carbonization (heating in inert gas) and activation (chemical treatment), this setup enables a one-step process.
The furnace converts organic polymers directly into activated carbon, streamlining production without sacrificing material quality.
Atmosphere Management
The tube design allows for the consistent introduction and flow of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) throughout the heating chamber.
This ensures that the activating agent is evenly distributed, preventing localized inconsistencies in the material's final structure.
The Mechanism of CO2 Activation
Selective Pore Creation
In this specific atmosphere, CO2 acts as a physical activating agent that "etches" the carbon framework.
This interaction is responsible for converting the dense polymer derived carbon into a material with a highly developed pore structure.
Independent Pore Tuning
A critical advantage of using a tube sintering furnace with CO2 is the ability to independently develop different pore sizes.
The process facilitates the formation of both mesopores (medium pores) and micropores (small pores) within the same structure.
Enhancing Surface Area
By systematically removing carbon atoms via the CO2 reaction, the furnace dramatically increases the material's total pore volume.
This specifically enhances microporosity, which is the primary driver for surface area in high-performance carbon materials.
Impact on Material Performance
Electrochemical Optimization
The specific pore architecture created in the furnace is directly linked to energy storage capabilities.
By optimizing the ratio of micropores to mesopores, the material becomes highly effective for electrochemical energy storage.
Structural Integrity
While the furnace promotes porosity, the controlled heating rate ensures the carbon skeleton remains robust.
This balance prevents the collapse of the pore structure, ensuring the material retains its conductive properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High Energy Requirements
Operating a sintering furnace at 1000 °C requires significant energy input, which can impact the overall cost-efficiency of the production process.
Sensitivity to Process Parameters
The "independent development" of pores is highly sensitive to the stability of the temperature and gas flow.
Fluctuations in the furnace environment can lead to inconsistent pore size distributions, negatively affecting the material's electrochemical performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When utilizing a tube sintering furnace for CO2 activation, align your process parameters with your specific end-use requirements:
- If your primary focus is Energy Density: Prioritize the specific enhancement of microporosity to maximize surface area for charge storage.
- If your primary focus is Ion Transport: Ensure the process allows for sufficient mesopore development to facilitate the movement of ions to the active sites.
The tube sintering furnace is not merely a heating element; it is a precision tool for tailoring the micro-architecture of carbon to meet the rigorous demands of modern energy storage.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Carbon Activation |
|---|---|
| Operating Temp | Typically 1000 °C for thermal activation |
| Atmosphere | Continuous Carbon Dioxide (CO2) flow |
| Pore Control | Independent development of micropores and mesopores |
| Efficiency | One-step carbonization and activation process |
| Application | Enhances electrochemical energy storage performance |
Precision Heat Treatment for Advanced Carbon Engineering
Unlock the full potential of your carbon materials with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Whether you are developing high-surface-area electrodes or specialized adsorbents, our expert-designed systems provide the thermal stability and atmosphere control essential for precise pore engineering.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Customizable Systems: We offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your unique R&D and manufacturing requirements.
- Expert R&D: Backed by deep expertise in high-temperature lab furnaces.
- Performance Driven: Ensure repeatable results in CO2 activation and sintering.
Ready to elevate your material performance? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Belén Lobato, Ana Arenillas. Designing and Optimizing Electrode Materials for Energy Harvesting in CAPMIX Cells. DOI: 10.3390/nano14242031
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are a tube furnace and nitrogen flow required? Master Carbon Microsphere Activation with Precision
- Why is a high-precision dual-zone furnace required for 1T-TaS2 crystals? Achieve Perfect CVT Phase Integrity
- What are the key benefits of using split tube furnaces? Unlock Superior Access and Control for Your Lab
- What is the significance of using perforated tapered silicone stoppers to seal quartz tube reactors? Achieve Precision.
- What core functions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide? Master TiN-Carbon Composite Pyrolysis
- Why is a high-performance tube furnace required for chemical activation? Achieve Precision Pore Control at 700°C
- What is the key component of a tube furnace and how is it constructed? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- How does an atmosphere tube furnace support energy conservation and environmental protection? Boost Efficiency and Cut Emissions



















