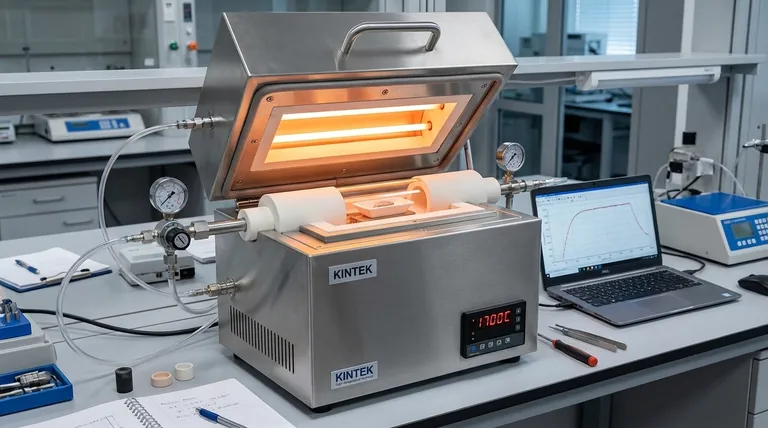
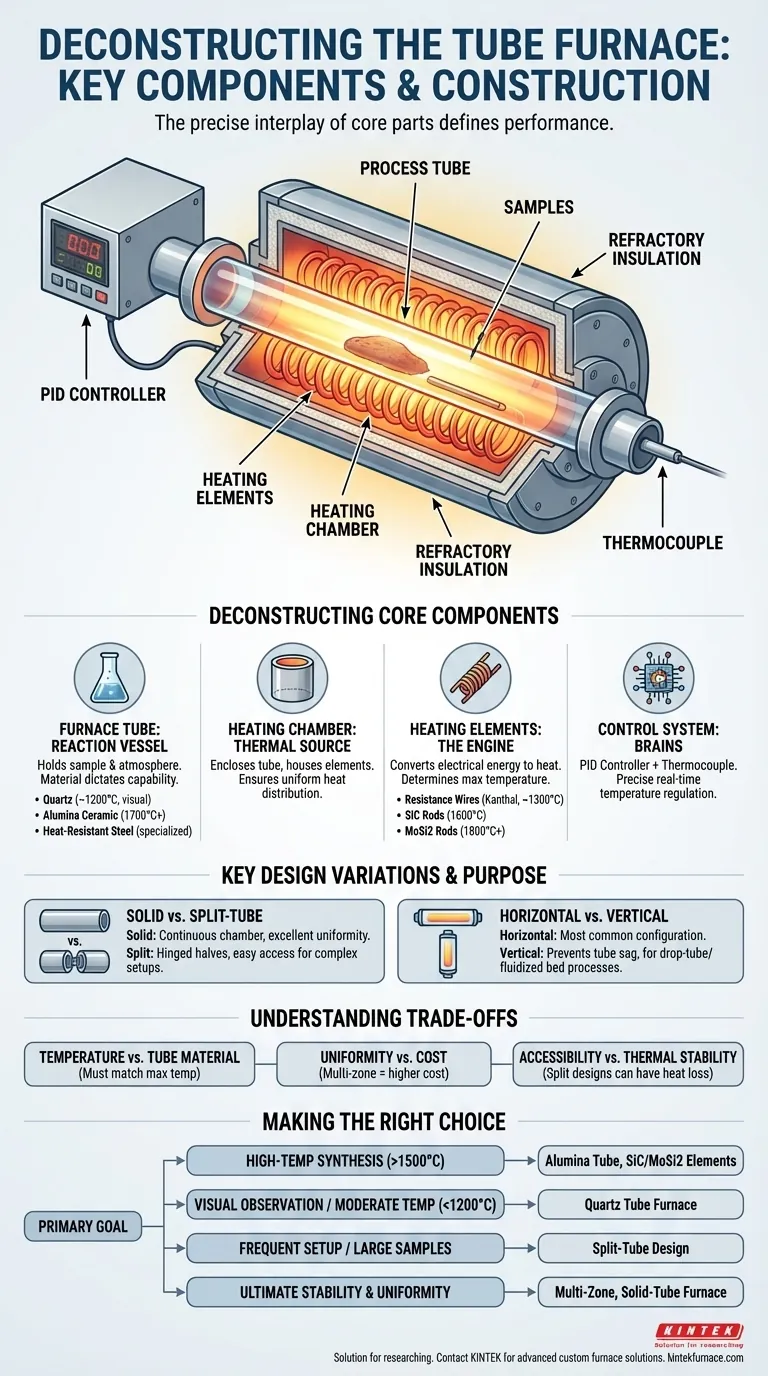
At the heart of any tube furnace is the heating chamber assembly, which consists of a process tube and the surrounding heating elements encased in refractory insulation. The process tube, made from materials like quartz or alumina, holds the sample, while heating elements, such as resistance wires or ceramic rods, are embedded in a cylindrical chamber wall around the tube to generate and transfer thermal energy.
The effectiveness of a tube furnace is not defined by a single component, but by the precise interplay between the furnace tube material, the heating element type, and the overall furnace configuration. Understanding how these parts work together is the key to matching the equipment to your specific experimental or production goal.

Deconstructing the Core Components
A tube furnace functions as a system. While the furnace tube is the central component where the process occurs, it relies entirely on the heating chamber and control system to function.
The Furnace Tube: The Reaction Vessel
This is the core component that contains your sample and atmosphere. The material it's made from is a critical decision that dictates the furnace's capabilities.
Common materials include quartz glass, which is excellent for temperatures up to ~1200°C and allows for visual observation of the sample.
For higher temperatures, alumina ceramic tubes are required, capable of operating reliably at 1700°C or more. For specialized applications, metallic tubes like heat-resistant steel are also used.
The Heating Chamber: The Source of Thermal Energy
The heating chamber is a cylindrical cavity that encloses the furnace tube. It is constructed from high-temperature ceramic or other refractory materials.
Its primary purpose is to house the heating elements and ensure that heat is distributed as uniformly as possible around the process tube.
The Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
Arranged within or around the heating chamber wall, these elements convert electrical energy into heat. The type of element determines the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Resistance wires (e.g., Kanthal) are common for temperatures up to ~1300°C. For higher heat, Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) rods are used, capable of reaching 1600°C and over 1800°C, respectively.
The Control System: The Brains of the Operation
Modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller to precisely regulate temperature. A thermocouple placed near the heating elements provides real-time feedback, allowing the system to make constant adjustments and maintain a stable setpoint.
Key Design Variations and Their Purpose
Not all tube furnaces are built the same. The physical construction is adapted for different laboratory and industrial needs.
Solid vs. Split-Tube Furnaces
A solid tube furnace features a single, continuous cylindrical heating chamber. This design offers excellent temperature uniformity and stability.
A split-tube furnace is built in two semi-cylindrical halves joined by hinges. This allows the chamber to be opened, providing easy access to the process tube for placing complex setups or large samples without dismantling the entire apparatus.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientation
The orientation dictates how the sample is processed. Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration.
Vertical furnaces are used to prevent high-temperature sag in long furnace tubes, for drop-tube experiments, or in processes like fluidized bed combustion where gravity is part of the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a tube furnace involves balancing competing factors. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for successful operation.
Temperature vs. Tube Material
The most significant trade-off is the relationship between temperature and the process tube. You cannot use a quartz tube at the maximum temperature of a MoSi2 furnace; the tube would melt. You must always ensure your tube's maximum service temperature is higher than your desired operating temperature.
Uniformity vs. Cost
Achieving a highly uniform heated zone across a long section of the tube is a complex engineering challenge. Furnaces with multiple heating zones, each with its own controller and thermocouple, provide superior uniformity but come at a significantly higher cost.
Accessibility vs. Thermal Stability
A split-tube furnace offers superior access but introduces a seam in the insulation and heating chamber. This can create a point of heat loss and potentially a less uniform temperature profile compared to a comparable solid-tube design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is essential for achieving your goals. Base your decision on the primary demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (>1500°C): You need an alumina tube paired with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements.
- If your primary focus is visual observation or moderate temperatures (<1200°C): A furnace designed for a quartz tube is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is frequent setup changes or processing large samples: A split-tube design offers the critical accessibility you need to work efficiently.
- If your primary focus is ultimate temperature stability and uniformity: A multi-zone, solid-tube furnace provides the highest level of thermal control.
Understanding these core components and their interplay empowers you to select or operate a tube furnace with precision and confidence.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Tube | Holds sample and atmosphere | Quartz, Alumina, Steel |
| Heating Elements | Generate thermal energy | Kanthal, SiC, MoSi2 |
| Control System | Regulates temperature | PID Controller, Thermocouple |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with precision and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















