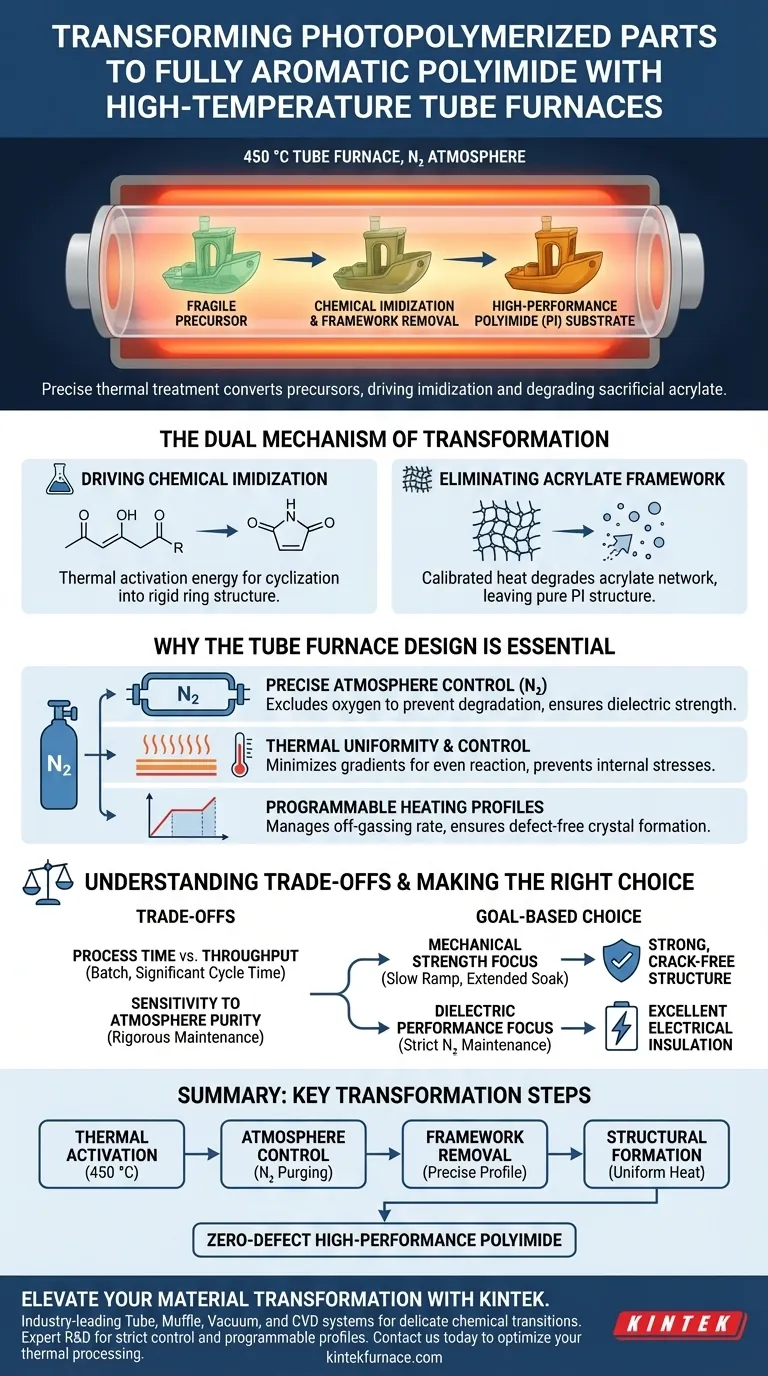
A high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel for converting photopolymerized precursors into high-performance polyimide. It creates a strictly controlled environment that heats parts up to 450 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. This specific thermal treatment drives the chemical imidization reaction while simultaneously degrading and removing the sacrificial acrylate framework used during the initial 3D printing process.
The furnace acts as a precision synthesis tool, not just a heater. By isolating the material in an inert atmosphere and applying exact thermal profiles, it transforms a fragile printed part into a fully aromatic polyimide substrate known for superior thermal stability and dielectric strength.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Driving Chemical Imidization
The primary function of the furnace is to supply the thermal activation energy required for imidization.
This is a chemical phase change where the precursor material cyclizes into a rigid ring structure. The tube furnace ensures this reaction reaches completion, converting the material into a fully aromatic polyimide (PI).
Eliminating the Acrylate Framework
During the photopolymerization (3D printing) phase, an acrylate framework is often used to shape the part.
The high-temperature environment of the furnace, specifically reaching 450 °C, is calibrated to completely degrade this acrylate network. This leaves behind only the pure polyimide structure, ensuring the final part possesses the intended mechanical properties without impurities from the printing process.
Why the Tube Furnace Design is Essential
Precise Atmosphere Control
Achieving a fully aromatic polyimide requires the total exclusion of oxygen to prevent material degradation.
The tube furnace allows for a sealed, controlled nitrogen atmosphere. This inert environment protects the chemical integrity of the polyimide as it forms, ensuring the final product maintains high dielectric strength and thermal resistance.
Thermal Uniformity and Profile Control
Chemical synthesis in solid states requires more than just high heat; it requires even heat.
Tube furnaces are designed to minimize temperature gradients along the length of the chamber. This uniformity ensures that the entire part reacts at the same rate, preventing internal stresses or incomplete imidization that could occur with uneven heating.
Programmable Heating Profiles
The transformation process is rarely a simple ramp to maximum temperature.
Advanced controllers allow for complex profiles, including specific ramp rates and soak times. This precise modulation is necessary to manage the rate of acrylate off-gassing and to ensure the crystal structure of the polyimide forms correctly without defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Time and Throughput
While effective, tube furnaces are typically batch-processing tools with limited cavity space.
The requirement for controlled heating, soaking at 450 °C, and gradual cooling means the cycle time is significant. This ensures quality but limits the volume of parts that can be processed compared to continuous conveyor systems.
Sensitivity to Atmosphere Purity
The quality of the final polyimide is directly tied to the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
If the nitrogen flow is inconsistent or the seals are compromised, oxidation can occur immediately at these temperatures. This requires rigorous maintenance of gas lines and seals, as even minor leaks can result in brittle or contaminated parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your polyimide parts, align your furnace operation with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Prioritize a slow ramp rate and extended soak time to allow the acrylate framework to escape gently without creating micro-cracks in the polyimide structure.
- If your primary focus is dielectric performance: Ensure your nitrogen atmosphere is strictly maintained to prevent even trace oxidation, which can compromise the material's electrical insulation properties.
The tube furnace is the bridge between a printed shape and a functional engineering material; its value lies in its ability to execute this chemical transition with absolute precision.
Summary Table:
| Transformation Phase | Furnace Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Activation | Heats up to 450 °C | Drives chemical imidization and ring cyclization |
| Atmosphere Control | Nitrogen purging | Prevents oxidation and ensures dielectric strength |
| Framework Removal | Precise thermal profile | Completely degrades sacrificial acrylate networks |
| Structural Formation | Uniform heat distribution | Eliminates internal stress and prevents micro-cracking |
Elevate Your Material Transformation with KINTEK
Transitioning from a 3D-printed shape to a high-performance engineering material requires absolute thermal precision. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically designed to handle delicate chemical transitions like polyimide synthesis.
Our expert-backed R&D ensures our furnaces deliver the strict atmosphere control and programmable heating profiles necessary for zero-defect results. Whether you need a standard laboratory setup or a fully customized high-temperature solution, KINTEK is your partner in advanced manufacturing.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to consult with our engineering team.
Visual Guide
References
- Heather D. Wotton, Christopher B. Williams. Enabling Additively Manufactured Electronics Through Laser Induced Graphene and Copper Deposition on Fully‐Aromatic Polyimides. DOI: 10.1002/admt.202401801
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the specialized functions of a high-temperature tube furnace in the final sintering of proton ceramics?
- How does annealing in a tube vacuum furnace optimize WS2 thin films? Master Structural Integrity & Efficiency
- What are the benefits of using a high vacuum tube furnace for Ti-Si-C-Mo coatings? Maximize Coating Performance
- What design features contribute to the durability and safety of modern lab tube furnaces? Ensuring Long-Term Reliability and Operator Protection
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for PCN exfoliation? Unlock Superior 2D Nanosheet Catalysis
- What is the necessity of a precision tube resistance furnace in molten salt electrolysis research? Ensure Unrivaled Precision & Reproducibility!
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace ensure environmental stability for SOEC? Precision Heat & Atmosphere Control
- Why is a laboratory tube furnace considered essential for fabricating carbonized lignin nanofiber electrodes?



















