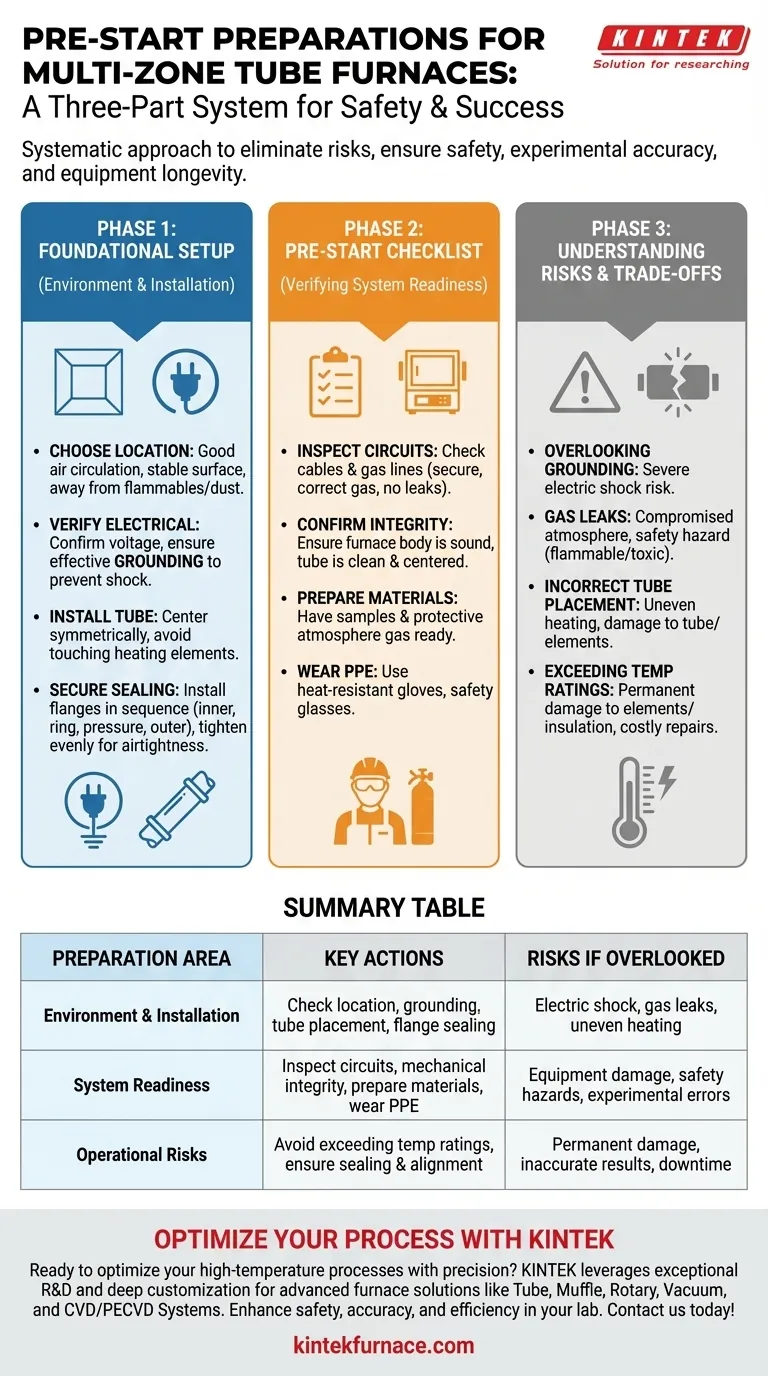
Before starting a multi-zone tube furnace, you must conduct a three-part preparation focusing on the operational environment, the physical equipment, and the specific experimental materials. This involves checking that electrical and gas circuits are functional, ensuring the furnace tube is correctly installed and sealed, and preparing your samples and any necessary protective atmosphere. A systematic approach is crucial for safety, experimental accuracy, and equipment longevity.
The core purpose of pre-start preparations is to systematically eliminate risks. By verifying the environment, the equipment, and the experimental setup, you ensure the safety of personnel, the integrity of your results, and the long-term reliability of the furnace itself.
Foundational Setup: The Environment and Installation
Proper preparation begins long before you power on the furnace for a specific run. The initial installation and surrounding environment are the foundation for safe and effective operation.
Choosing the Right Location
The furnace should be placed in a controlled environment. This means a location with good air circulation, free from physical vibrations, and clear of any flammable gases, explosive materials, or high levels of dust.
Verifying the Electrical Connection
Before first use, confirm the power supply voltage matches the furnace's requirements. Critically, you must ensure the equipment is connected to an effective electrical ground to prevent the risk of severe electric shock.
Correct Furnace Tube Installation
The furnace tube must be installed with precision. It should be positioned symmetrically, passing through the center of the furnace chamber without making direct contact with the heating elements. An incorrectly placed tube can lead to uneven heating or damage.
Securing the Sealing Flanges
Properly sealing the tube is vital, especially when using a controlled atmosphere. The flanges must be installed in the correct sequence—inner sleeve, sealing ring, pressure ring, and outer sleeve. Tighten the screws evenly to prevent skewing and ensure an airtight seal.
The Pre-Start Checklist: Verifying System Readiness
Immediately before each experimental run, perform these checks to confirm the system is ready for operation.
Inspecting Power and Gas Circuits
Visually inspect all electrical cables and connections for damage. If using a protective atmosphere, check that the gas supply lines are securely connected, the correct gas is being used, and there are no audible or detectable leaks.
Confirming Mechanical Integrity
Ensure the furnace body is in good working condition with no visible damage. Check that the furnace tube is clean, free of cracks, and still positioned correctly in the center of the chamber.
Preparing Experimental Materials
Have all necessary materials ready before you begin. This includes the samples to be processed and a confirmed supply of the protective atmosphere or process gas required for your experiment.
Wearing Protective Equipment
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, especially when handling hot components or working near the furnace opening.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inherent Risks
Overlooking any preparation step introduces a specific risk. Understanding these trade-offs is key to developing a robust safety and operational culture.
The Risk of Overlooking Grounding
Failing to ensure proper grounding is a critical safety failure. It creates a significant risk of electric shock for any operator who comes into contact with the furnace's chassis in the event of an electrical fault.
The Hazard of Gas Leaks
An incomplete or rushed flange seal can lead to gas leaks. This can ruin an experiment by compromising the controlled atmosphere, or it can create a serious safety hazard if the gas is flammable or toxic.
The Impact of Incorrect Tube Placement
If the tube touches the heating elements, it can cause localized overheating, potentially damaging both the tube and the elements. Asymmetrical placement will also result in an inaccurate temperature profile across your sample.
The Consequence of Exceeding Temperature Ratings
Never program the furnace to operate above its maximum rated temperature. Doing so can cause permanent damage to the heating elements and refractory insulation, leading to costly repairs and equipment downtime.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
A disciplined pre-start procedure is not about bureaucracy; it's about control. Use this workflow to align your preparations with your primary objective for each run.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize the electrical grounding check, confirm the environment is free of flammables, and always monitor for gas leaks.
- If your primary focus is experimental accuracy: Double-check the furnace tube's symmetrical placement and ensure the flanges are perfectly sealed to maintain atmospheric integrity.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Never exceed the furnace's rated temperature, ensure the tube never touches the heating elements, and conduct regular maintenance inspections.
By treating these preparatory steps as an essential part of the process, you ensure every experiment is conducted safely, accurately, and efficiently.

Summary Table:
| Preparation Area | Key Actions | Risks if Overlooked |
|---|---|---|
| Environment & Installation | Check location, electrical grounding, tube placement, flange sealing | Electric shock, gas leaks, uneven heating |
| System Readiness | Inspect power/gas circuits, mechanical integrity, prepare materials, wear PPE | Equipment damage, safety hazards, experimental errors |
| Operational Risks | Avoid exceeding temperature ratings, ensure proper sealing and alignment | Permanent damage, inaccurate results, downtime |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing safety, accuracy, and efficiency in your lab. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients



















