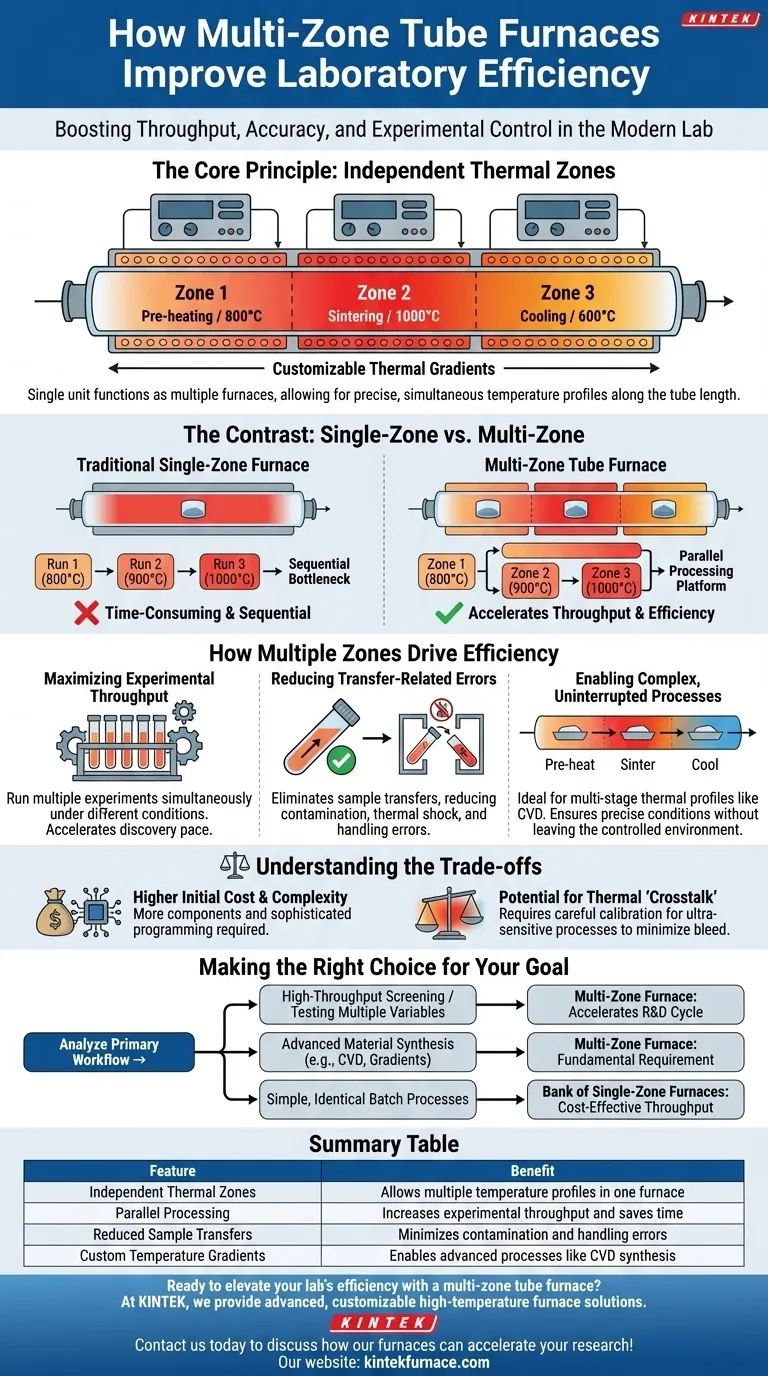
In the modern laboratory, efficiency is measured by both speed and accuracy. A multi-zone tube furnace directly improves both by allowing you to run multiple, distinct thermal processes simultaneously within a single tube. This eliminates the need to run experiments sequentially or transfer samples between different furnaces, dramatically increasing experimental throughput while reducing the risk of contamination and handling errors.
The core limitation of a traditional furnace is that it creates a process bottleneck—only one temperature profile can run at a time. A multi-zone furnace breaks this bottleneck by transforming a single piece of equipment into a parallel processing platform, enhancing both the quantity and quality of your work.
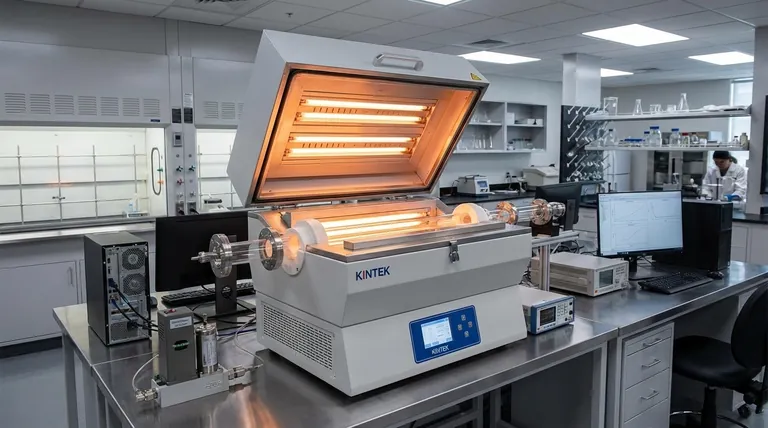

The Core Principle: Independent Thermal Zones
A multi-zone tube furnace may look like a single unit, but it functions as several furnaces in one. This design is the foundation of its efficiency gains.
What Defines a "Zone"?
Each "zone" is a section of the tube furnace with its own independent heating elements and temperature controller. A three-zone furnace, for example, has three distinct sections that can be set to three different temperatures.
These zones are arranged sequentially along the length of the process tube, allowing for a highly controlled and customizable thermal environment.
Creating Custom Temperature Profiles
The independence of each zone allows you to create a specific temperature gradient along the tube. You could have one zone for pre-heating, a central zone for sintering at a high temperature, and a third for controlled cooling.
This capability is essential for advanced processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where precise temperature gradients are required for material synthesis.
The Contrast with Single-Zone Furnaces
A single-zone furnace operates like a one-lane road; only one process can run at a time. If you need to sinter samples at 800°C, 900°C, and 1000°C, you must run three separate cycles.
A three-zone furnace turns this into a multi-lane highway. You can place each sample in a different zone and process all three simultaneously, completing the work in a fraction of the time.
How Multiple Zones Drive Efficiency
The benefits of parallel processing extend beyond just saving time. They fundamentally change the laboratory workflow for the better.
Maximizing Experimental Throughput
The most obvious benefit is the ability to run multiple experiments in parallel. This is a crucial advantage in research and development settings where iterating on different parameters is key.
Instead of waiting for one thermal cycle to finish before starting the next, your team can process multiple samples under different conditions at once, accelerating the pace of discovery.
Reducing Transfer-Related Errors
Moving a hot sample from one furnace to another introduces significant risk. This includes potential contamination from exposure to the atmosphere, thermal shock that can crack the sample, and simple human error in handling.
By keeping the entire process within a single, sealed tube, a multi-zone furnace eliminates these transfer steps, improving the reliability and repeatability of your results.
Enabling Complex, Uninterrupted Processes
Certain advanced material synthesis techniques require a sample to move through different temperature stages in a continuous, uninterrupted process.
A multi-zone furnace is ideal for this. You can establish a stable, multi-stage thermal profile and then slowly push the sample through each zone, ensuring it experiences the precise conditions required at each step without ever leaving the controlled environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a multi-zone furnace is not universally superior. Its value is tied directly to your specific application.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Multi-zone furnaces are more expensive than their single-zone counterparts due to the additional heating elements, controllers, and power electronics. They also require more sophisticated programming to manage the different zones effectively.
Potential for Thermal "Crosstalk"
Although the zones are controlled independently, some thermal energy will inevitably bleed from a hotter zone to an adjacent cooler one. High-quality furnaces are designed to minimize this "crosstalk," but it is a physical reality that requires careful calibration for ultra-sensitive processes.
When a Single-Zone Furnace is a Better Fit
If your lab exclusively performs identical batch processes at a single temperature, a multi-zone furnace may be an unnecessary expense. In this scenario, investing in multiple, less-expensive single-zone furnaces could provide a better return on investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a multi-zone furnace is the correct investment, analyze your primary laboratory workflow.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening or testing multiple variables: A multi-zone furnace is a direct path to accelerating your research and development cycle.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis requiring temperature gradients (e.g., CVD): A multi-zone furnace is not just efficient; it is often a fundamental requirement for the process.
- If your primary focus is running simple, identical batch processes: A bank of single-zone furnaces may provide the throughput you need in a more cost-effective manner.
Ultimately, choosing a multi-zone furnace is an investment in parallel processing capability and enhanced experimental control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Independent Thermal Zones | Allows multiple temperature profiles in one furnace |
| Parallel Processing | Increases experimental throughput and saves time |
| Reduced Sample Transfers | Minimizes contamination and handling errors |
| Custom Temperature Gradients | Enables advanced processes like CVD synthesis |
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency with a multi-zone tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can accelerate your research and deliver reliable, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering



















