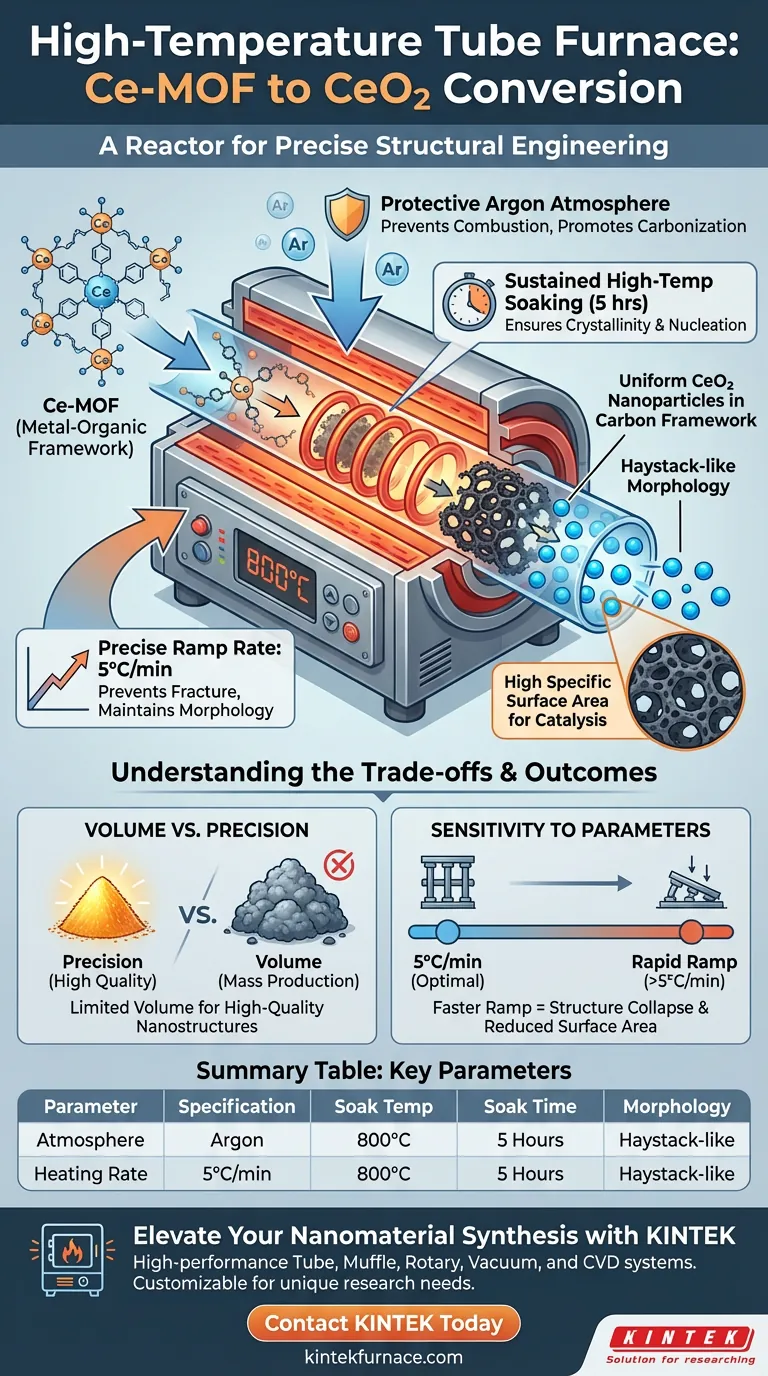
The primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in this context is to orchestrate the controlled decomposition and carbonization of Ce-MOF into CeO2. By heating the material to 800°C under a protective argon atmosphere, the furnace facilitates the removal of organic components while simultaneously inducing the in-situ conversion of cerium sources into uniformly dispersed nanoparticles.
The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a reactor for precise structural engineering. It ensures the simultaneous evolution of cerium nanoparticles and a carbon framework, resulting in a high-surface-area "haystack-like" morphology that would be impossible to achieve with uncontrolled heating.

The Mechanics of the Conversion Process
Precise Thermal Decomposition
The conversion of Ce-MOF is a delicate process requiring a specific heating profile. The furnace does not simply blast the material with heat; it applies a steady ramp rate of 5°C/min.
This gradual increase allows for the orderly breakdown of organic ligands. It prevents rapid off-gassing that could fracture the material structure before the desired morphology is set.
Protective Atmosphere Control
A critical advantage of the tube furnace is its ability to maintain a specific atmosphere. The process requires a protective argon environment throughout the heating cycle.
This inert gas prevents the complete combustion of the organic components. Instead of burning away entirely, the organics are carbonized, forming a structural matrix around the metal centers.
Sustained High-Temperature Soaking
Once the furnace reaches 800°C, it maintains this temperature for a duration of 5 hours. This "soak time" is essential for the crystallinity of the final product.
It provides the necessary activation energy for the cerium species to nucleate and grow into stable nanoparticles.
Material Outcomes and Structure
Creation of the "Haystack" Morphology
The specific combination of temperature, ramp rate, and atmosphere engineered by the furnace results in a unique architecture. The material forms a haystack-like structure.
This structure is highly desirable because it retains a very high specific surface area, which is often the key performance metric for catalytic applications.
Uniform Particle Dispersion
The furnace facilitates in-situ conversion. Because the precursor (Ce-MOF) contains metal centers explicitly spaced by organic linkers, the thermal treatment preserves this spacing.
The result is cerium oxide nanoparticles that are uniformly dispersed within the derived carbon framework, preventing agglomeration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Volume vs. Precision
While the tube furnace excels at creating high-quality nanostructures, it is generally limited in sample volume. It is designed for precision over mass production.
Attempting to overload the tube can disrupt the gas flow dynamics, leading to uneven carbonization or oxidation in parts of the sample.
Sensitivity to Parameters
The resulting "haystack" structure is highly sensitive to the programmed parameters. The tube furnace relies on the accuracy of the ramp rate and soak time.
Accelerating the ramp rate beyond 5°C/min to save time will likely collapse the porous structure, significantly reducing the specific surface area and altering the material's properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your CeO2 conversion, focus on these operational variables:
- If your primary focus is high surface area: Strictly adhere to the 5°C/min ramp rate, as rapid heating will collapse the delicate haystack structure.
- If your primary focus is phase purity: Ensure the argon flow is continuous and leak-free for the full 5-hour duration to prevent unwanted oxidation of the carbon framework.
By strictly controlling the thermal profile and atmosphere within the tube furnace, you transform a simple heating step into a precise method for nano-engineering.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose in Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Protective Argon Gas | Prevents combustion; promotes carbonization |
| Heating Rate | 5°C/min (Gradual) | Prevents structural fracturing; maintains morphology |
| Soak Temp | 800°C | Provides activation energy for nanoparticle nucleation |
| Soak Time | 5 Hours | Ensures crystallinity and uniform dispersion |
| Morphology | Haystack-like | Maximizes specific surface area for catalysis |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise structural engineering like the Ce-MOF to CeO2 conversion requires more than just heat; it requires absolute control over every thermal variable. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding lab applications.
Our furnaces provide the ramp-rate accuracy and atmosphere stability necessary to achieve uniform nanoparticle dispersion and high-surface-area morphologies. Whether you need a standard setup or a system customizable for your unique research needs, KINTEK delivers the reliability your research deserves.
Ready to optimize your material outcomes?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
References
- Hao Xiao, Dan Sun. MOF-Derived CeO2 Nanorod as a Separator Coating Enabling Enhanced Performance for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29081852
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the space and footprint considerations for vertical and horizontal tube furnaces? Optimize Your Lab Layout
- Why are the high-temperature carbonization and activation of sugarcane bagasse typically conducted in a tube furnace?
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- Why is the encapsulation of raw materials in a vacuum-sealed quartz tube necessary for crystal growth? Key to Purity
- How do high-temperature laboratory tube furnaces ensure environmental stability? Precision Thermal Reduction Tips
- What distinguishes a compact tube furnace from other types? Ideal for Small-Scale Lab Precision
- What are the applications of fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powdered Materials
- What role does a tube high-temperature furnace play in the synthesis of nano carbon spheres? Unlock sp2 Hybridization



















