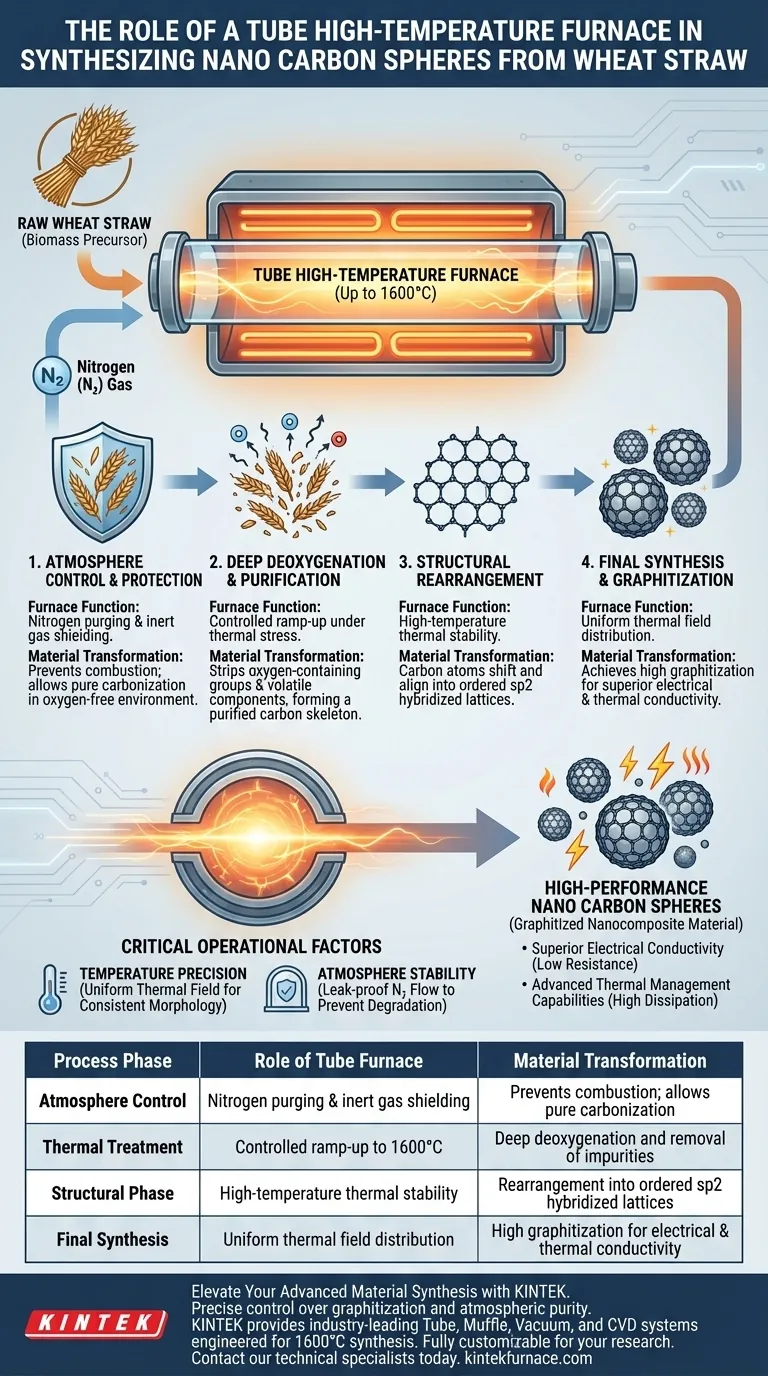
The tube high-temperature furnace acts as the definitive reaction vessel for transforming raw wheat straw into high-performance nano carbon materials. It provides a strictly controlled, nitrogen-protected environment capable of reaching extreme temperatures up to 1600°C, which forces the biomass precursor to undergo the deep chemical and structural changes necessary for synthesis.
Core Takeaway The furnace does not simply burn the material; it drives a precise atomic reorganization known as graphitization. By maintaining a 1600°C oxygen-free environment, the furnace converts disordered biomass into a highly ordered sp2 hybridized carbon lattice, which is the prerequisite for achieving superior electrical conductivity and thermal management capabilities.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Establishing the Protective Atmosphere
The first critical function of the furnace is atmosphere control. Before heating begins, the tube allows for the introduction of inert gases, specifically nitrogen.
This creates a protective shield around the wheat straw. Without this oxygen-free environment, the high temperatures would cause the biomass to combust into ash rather than carbonizing into functional nanospheres.
Deep Deoxygenation
Once the atmosphere is secured, the furnace ramps up to extreme temperatures. Under this thermal stress, the wheat straw undergoes deep deoxygenation.
This process systematically strips away oxygen-containing functional groups and other volatile components. The result is a purified carbon skeleton, free of the impurities that typically hinder material performance.
Structural Rearrangement
As the temperature approaches 1600°C, the material undergoes a physical transformation alongside the chemical one. The carbon atoms begin to shift and align.
This creates a "structural rearrangement" where the atoms organize into a thermodynamically stable configuration. This is the transition from amorphous, chaotic carbon to an ordered structure.
Impact on Material Properties
Forming the sp2 Hybridized Lattice
The ultimate goal of using such high temperatures is to achieve an sp2 hybridized carbon lattice. This specific atomic arrangement creates the fundamental "honeycomb" structure associated with graphite and graphene.
The tube furnace's ability to hold stable high heat is the only way to force this hybridization in biomass precursors.
Ensuring High Graphitization
The degree of order in the carbon structure is referred to as "graphitization." A high degree of graphitization is directly linked to the material's final utility.
The highly graphitized microstructure produced in the furnace ensures the resulting nanocomposite films have low electrical resistance. It also maximizes their ability to dissipate heat, making them suitable for advanced thermal management applications.
Critical Operational Factors
The Importance of Temperature Precision
While the primary goal is reaching 1600°C, the precision of the heating rate is equally important. The furnace must provide a uniform thermal field to ensure every nano carbon sphere forms identically.
Inconsistent heating can lead to variations in the carbon lattice, resulting in "hot spots" or areas of low conductivity in the final material.
Risks of Atmosphere Instability
The integrity of the tube environment is non-negotiable. Even a microscopic leak of oxygen at these temperatures will degrade the carbon lattice immediately.
The furnace must maintain positive pressure or a constant flow of nitrogen to ensure the reducing atmosphere remains uniform throughout the entire synthesis cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your nano carbon spheres, align your furnace parameters with your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is maximum electrical conductivity: Prioritize reaching and holding the upper temperature limit (1600°C) to maximize the sp2 lattice formation and graphitization level.
- If your primary focus is consistent particle morphology: Focus on the precision of the heating rate and the uniformity of the thermal field to ensure the structural rearrangement happens evenly across the sample.
Success in this synthesis relies not just on heat, but on the absolute control of the atomic environment.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Role of Tube Furnace | Material Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Nitrogen purging & inert gas shielding | Prevents combustion; allows pure carbonization |
| Thermal Treatment | Controlled ramp-up to 1600°C | Deep deoxygenation and removal of impurities |
| Structural Phase | High-temperature thermal stability | Rearrangement into ordered sp2 hybridized lattices |
| Final Synthesis | Uniform thermal field distribution | High graphitization for electrical & thermal conductivity |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise control over graphitization and atmospheric purity is the difference between biomass ash and high-performance nano carbon. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems engineered to deliver the uniform thermal fields and leak-proof environments required for 1600°C synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or industrial needs. Contact our technical specialists today to discover how KINTEK’s high-temperature solutions can optimize your material properties and research outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Junchao Ren, Qingfa Zhang. All‐Biomass Nanocomposite Films via Facile and Sustainable Design Procedure for Thermal Management and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202510372
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the conversion of sludge into biochar? Master Precise Thermal Pyrolysis
- Why is a vacuum-sealed quartz tube necessary for 4.5 inch InP crystals? Ensure Stability and Purity
- What is the role of a gas-phase pump in a tube furnace? Master Fluid Delivery & Combustion Control
- What role do controlled atmosphere tube furnaces play in recycling scrap copper wire? Precision Powder Production
- What are the primary applications of lab tubular furnaces in material science and engineering? Precision Heat for Advanced Materials
- How does a two-stage heating process in a laboratory tube furnace contribute to the structural formation of SiCN(Ni)/BN?
- What is the role of a tube furnace system in the growth of bilayer MoS2? Master CVD Synthesis with Precision Control
- What is the critical role of a tube furnace in the preparation of beta-PbO powder? Optimize Lead-Acid Battery Recycling



















