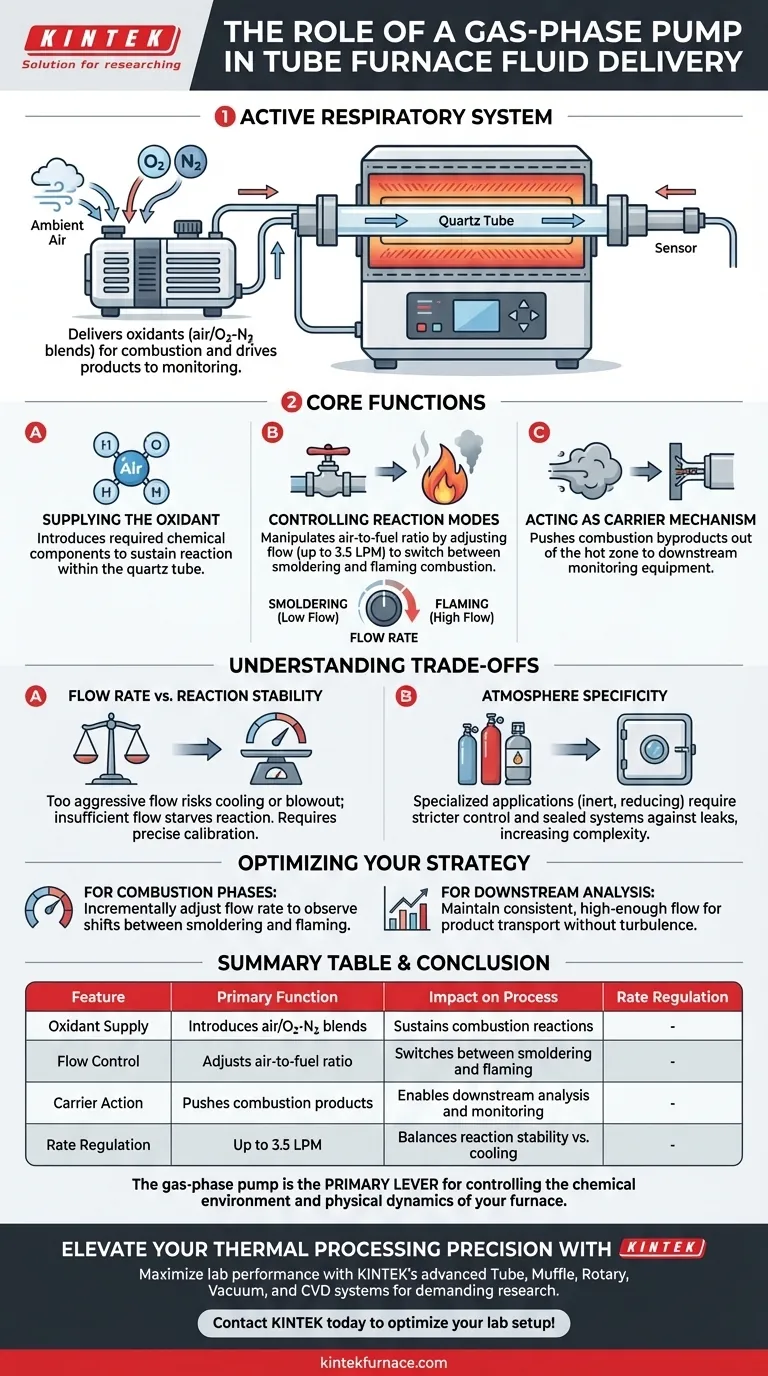
The gas-phase pump functions as the active respiratory system of a tube furnace's fluid delivery setup. Its primary role is to deliver specific gas mixtures—such as ambient air or nitrogen-oxygen blends—into the quartz tube to supply the necessary oxidants for combustion. Beyond simple delivery, it acts as the critical driver for transporting combustion products out of the furnace to downstream monitoring equipment.
By precisely adjusting flow rates, the gas-phase pump allows operators to manipulate the air-to-fuel ratio. This capability turns the pump into a dynamic control switch, enabling the transition between smoldering and flaming combustion modes.

Core Functions in the Fluid Delivery System
Supplying the Oxidant
The pump is responsible for introducing the chemical components required for reaction.
In combustion applications, it drives ambient air or specific gas blends into the heating zone. This provides the oxygen required to sustain the reaction within the quartz tube.
Controlling Reaction Modes
The pump determines the nature of the combustion through flow rate manipulation.
By adjusting the flow—typically up to 3.5 Liters Per Minute (LPM)—operators can alter the air-to-fuel ratio. High flow rates can induce flaming combustion, while restricted flow can maintain a smoldering state.
Acting as a Carrier Mechanism
Combustion products must be analyzed to understand the reaction.
The pump serves as a carrier gas source, physically pushing these byproducts out of the hot zone. This ensures that downstream sampling and monitoring equipment receive a continuous, representative stream of the exhaust gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flow Rate vs. Reaction Stability
Adjusting the flow rate is necessary to change combustion modes, but it requires precise calibration.
If the flow rate is too aggressive, you risk cooling the reaction zone or blowing out a delicate flame. Conversely, insufficient flow may starve the reaction of necessary oxidants, preventing the transition from smoldering to flaming.
Atmosphere Specificity
While standard pumps handle ambient air well, specialized applications require stricter control.
Using the pump to introduce specific inert, reducing, or oxidizing gases creates a tailored reaction atmosphere. However, this increases system complexity, as maintaining the purity of these specific gas environments requires ensuring the pump system is sealed against ambient leaks.
Optimizing Your Fluid Delivery Strategy
To ensure your tube furnace operates efficiently, tailor your pump usage to your specific experimental needs.
- If your primary focus is studying combustion phases: Utilize the pump's flow rate controls to incrementally adjust the air-to-fuel ratio, observing the shift between smoldering and flaming.
- If your primary focus is downstream analysis: Maintain a consistent flow rate that is high enough to transport products quickly to the sensors, but stable enough to prevent turbulence in the reaction zone.
The gas-phase pump is not merely a fan; it is the primary lever for controlling the chemical environment and physical dynamics of your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Primary Function | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidant Supply | Introduces air/O2-N2 blends | Sustains combustion reactions |
| Flow Control | Adjusts air-to-fuel ratio | Switches between smoldering and flaming |
| Carrier Action | Pushes combustion products | Enables downstream analysis and monitoring |
| Rate Regulation | Up to 3.5 LPM | Balances reaction stability vs. cooling |
Elevate Your Thermal Processing Precision
Maximize the performance of your lab with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding research environments. Whether you need to master combustion control or require a fully customized high-temp furnace for unique fluid delivery needs, our team is ready to help.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your lab setup!
Visual Guide
References
- Casey Coffland, Elliott T. Gall. An open-source linear actuated-quartz tube furnace with programmable ceramic heater movement for laboratory-scale studies of combustion and emission. DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.5687995
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in biomass carbon skeletons? Master Structural Integrity.
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace during molybdenum carbide synthesis? Master Catalyst Carbonization
- How does the environmental control of a high-temperature tube furnace affect the calcination of alpha-MoO3 powder?
- How is a tube high-temperature furnace utilized in the preparation of NiSA-O/Mo2C catalysts? Expert Synthesis Guide
- What factors should be considered when selecting between a tube furnace and a box furnace? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processing
- What is the function of a vertical alumina tube reactor in black liquor char gasification? Precision Kinetic Analysis
- What core task does a tubular vacuum sintering furnace perform? Optimizing Confined Carbon Chain Synthesis
- How is a laboratory tube furnace utilized in the thermal shock reduction process to produce RGO?



















