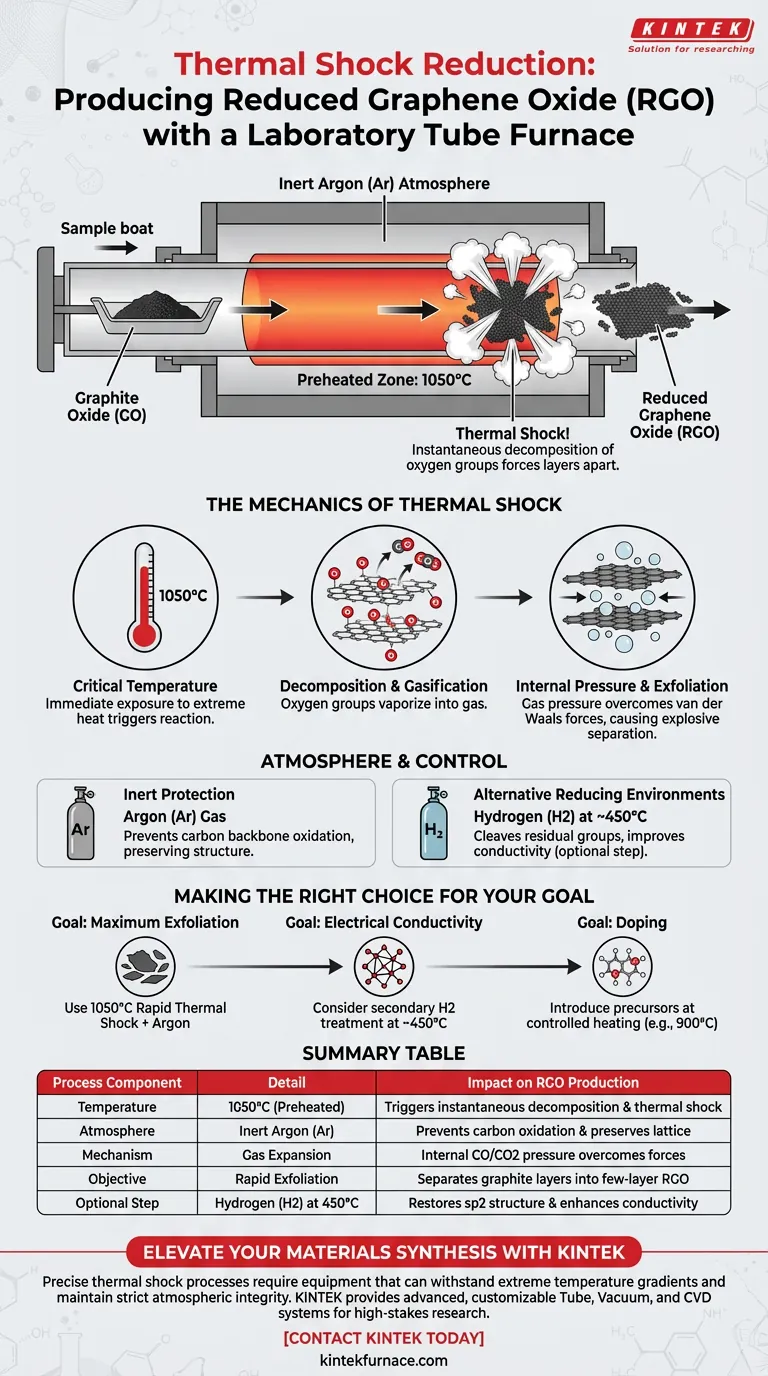
The laboratory tube furnace acts as a high-precision thermal reactor for rapid exfoliation. It facilitates the production of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) by maintaining a preheated zone, typically at 1050°C, under an inert argon atmosphere. When graphite oxide is introduced into this environment, the sudden temperature spike triggers the instantaneous decomposition of internal oxygen groups, forcing the material layers apart.
Core Takeaway The effectiveness of the tube furnace lies in its ability to convert chemical potential into mechanical force via "thermal shock." The extreme heat causes oxygen-containing groups to instantly vaporize into gas, generating high internal pressure that mechanically separates graphite layers into few-layer reduced graphene oxide.

The Mechanics of Thermal Shock
The Critical Role of Temperature
To achieve genuine thermal shock, the furnace must be preheated to extreme temperatures, often cited as 1050°C in standard protocols. This is not a gradual heating process; the material must experience the temperature differential immediately upon entry. This rapid shift is what differentiates thermal shock from standard annealing or sintering.
Decomposition and Gasification
At these high temperatures, the oxygen-containing functional groups interlaced between the graphite oxide layers become unstable. They rapidly decompose into gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Internal Pressure and Exfoliation
The generation of these gases occurs within the confined spaces between graphite layers. This creates significant internal expansion pressure. This pressure overcomes the van der Waals forces holding the layers together, causing them to exfoliate explosively and form reduced graphene oxide.
Atmosphere and Chemical Control
Inert Protection
The process typically utilizes an argon protective atmosphere. This is essential to prevent the carbon backbone of the graphene from burning away (oxidizing) at such high temperatures. The inert gas ensures that the decomposition is limited to the oxygen functional groups, preserving the graphitic structure.
Alternative Reducing Environments
While thermal shock is the primary mechanism, the tube furnace allows for chemical flexibility. As noted in supplementary industrial contexts, introducing hydrogen (H2) at lower temperatures (e.g., 450°C) can help cleave specific residual groups like carboxyls. This assists in restoring the sp2 carbon structure and improving electrical conductivity, though it operates on a different principle than pure thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Structural Integrity vs. Exfoliation
While the 1050°C thermal shock is excellent for exfoliation and producing high surface area material, it is a violent process. The rapid gasification can leave behind structural defects or vacancies in the carbon lattice, which may impact maximum theoretical conductivity compared to slower, chemical reduction methods.
Equipment Limitations
Unlike a high-pressure closed vessel which operates at lower temperatures (e.g., 90°C) to facilitate uniform chemical reactions, the tube furnace relies on an open flow system. This creates a dynamic environment that is excellent for gas removal but requires precise control over flow rates to maintain a stable thermal field.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific configuration of your tube furnace—temperature, ramp rate, and atmosphere—should be dictated by the specific properties you need in your final RGO.
- If your primary focus is maximum exfoliation: Utilize the rapid thermal shock method at 1050°C under Argon to maximize gas expansion and layer separation.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Consider a secondary treatment or a lower temperature process (approx. 450°C) with a Hydrogen reducing atmosphere to repair the sp2 structure.
- If your primary focus is doping: Use the furnace to introduce precursors (like nitrogen or phosphorus sources) at controlled heating rates (e.g., 900°C) rather than pure thermal shock.
Successful RGO production relies not just on high heat, but on the precise synchronization of temperature shock and atmospheric control.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Detail | Impact on RGO Production |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1050°C (Preheated) | Triggers instantaneous decomposition and thermal shock |
| Atmosphere | Inert Argon (Ar) | Prevents carbon oxidation and preserves lattice structure |
| Mechanism | Gas Expansion | Internal CO/CO2 pressure overcomes van der Waals forces |
| Objective | Rapid Exfoliation | Separates graphite layers into few-layer graphene flakes |
| Optional Step | Hydrogen (H2) at 450°C | Restores sp2 structure and enhances electrical conductivity |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal shock processes require equipment that can withstand extreme temperature gradients while maintaining strict atmospheric integrity. KINTEK provides advanced, customizable Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed specifically for high-stakes laboratory research and R&D manufacturing.
Whether you are perfecting RGO exfoliation or developing next-generation nanomaterials, our expert-engineered furnaces offer the stability and control you need to achieve repeatable results. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique heating requirements and discover how our high-temperature solutions can accelerate your breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Osman Eksik. Large-scale Production of Few-Layer Reduced Graphene Oxide by the Rapid Thermal Reduction of Graphene Oxide and Its Structural Characterization. DOI: 10.18596/jotcsa.1327988
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a Tube Furnace? Master Precision Heating for Sensitive Materials
- What types of atmospheres can be controlled in a drop tube furnace? Master Precise Gas Control for Superior Materials
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube sintering furnace for selenization? Optimize PC-CNT Porosity
- What is a laboratory tube furnace and how is it designed? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab
- How does a dual-temperature zone tube furnace control crystal quality? Master PVT for Organic Single Crystals
- What is the function of a dual-temperature zone tube furnace in CVD? Enhance MoS2/GaN Synthesis Precision
- Why is a high-precision gas flow control system required for vermiculite heat treatment? Ensure Perfect Atmosphere
- Why is it necessary to use a tube furnace for air oxidation of the 3D copper framework? Master Lithiophilic Interfaces



















