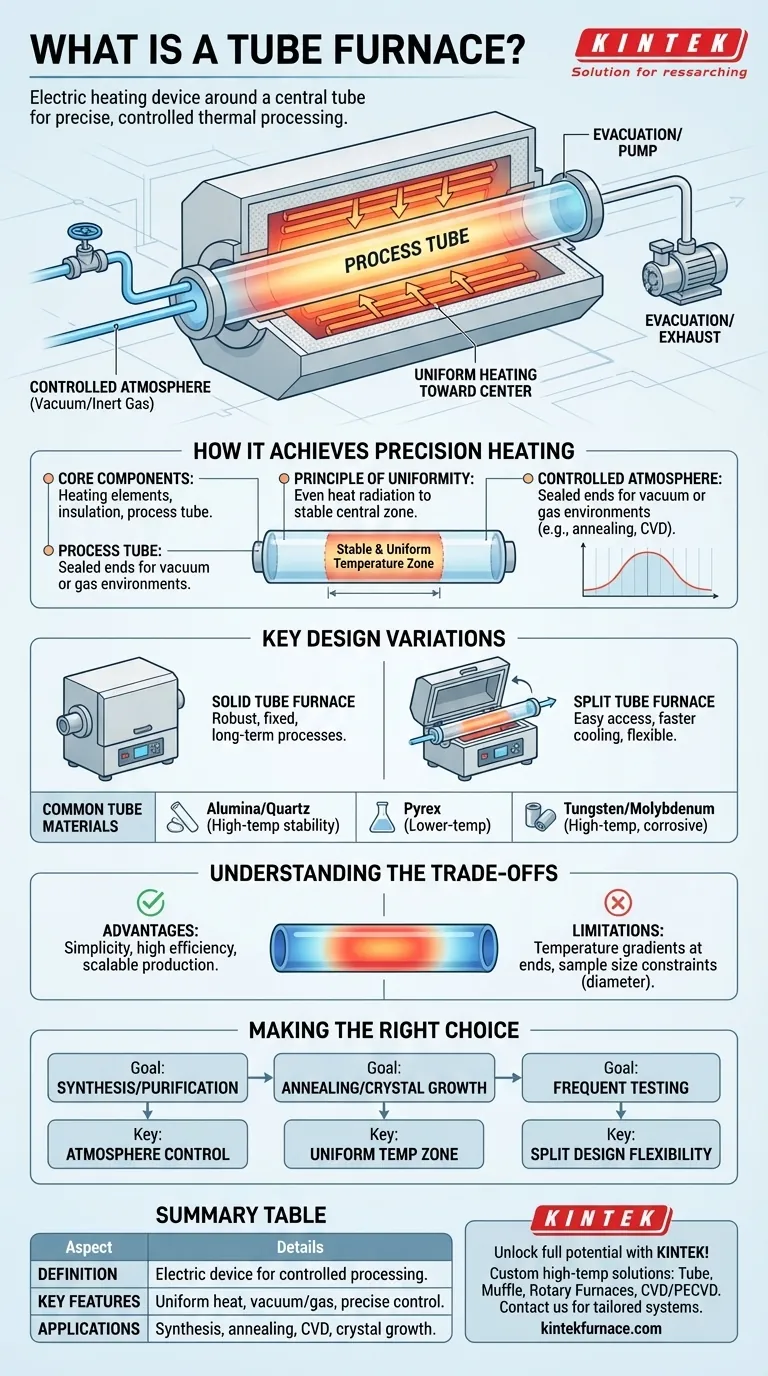
At its core, a tube furnace is an electric heating device designed around a central, cylindrical tube. This tube, containing the material to be processed, is surrounded by heating elements that provide rapid, stable, and uniform heat in a highly controlled environment.
The true value of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a precisely controlled and isolated atmosphere. This makes it an indispensable tool for processing sensitive materials that require specific vacuum or gas environments.
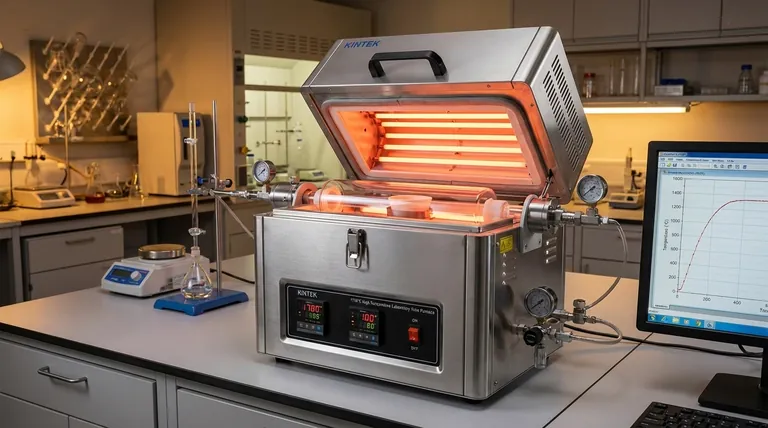

How a Tube Furnace Achieves Precision Heating
A tube furnace operates on a straightforward principle: transferring heat from an external source to a sample within an isolated chamber. This simplicity is the key to its reliability and precision.
The Core Components
The system consists of three main parts: the external heating elements, the insulation chamber, and the central process tube. The heating elements generate thermal energy, which is directed inward by the surrounding insulation.
The Principle of Uniformity
The cylindrical design ensures that heat radiates evenly toward the center of the tube. While the ends of the tube are naturally cooler, this creates a highly stable and uniform temperature zone in the middle, which is ideal for consistent material processing.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
The enclosed nature of the tube is its most significant feature. By sealing the ends, operators can evacuate the air to create a vacuum or introduce specific gases. This allows for processes like annealing in an inert atmosphere or chemical vapor deposition that would be impossible in open air.
Key Design Variations and Their Purpose
Not all tube furnaces are the same. Their construction and materials are tailored to specific applications, and understanding these differences is key to selecting the right tool.
Solid vs. Split Tube Furnaces
A solid tube furnace is built with a single, continuous insulation chamber. This design is robust and excellent for fixed, long-term processes.
A split tube furnace features a chamber made of two semi-cylindrical halves that can be opened. This allows for much easier placement and removal of the process tube and sample, and can also enable faster cooling.
Common Tube Materials
The process tube itself must withstand high temperatures and be compatible with the materials being processed.
- Alumina and Fused Quartz are common, general-purpose materials known for their high-temperature stability.
- Pyrex is used for lower-temperature applications.
- Tungsten or Molybdenum are reserved for high-temperature processes involving corrosive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces have inherent characteristics that present both advantages and limitations. An objective assessment is necessary for any serious application.
The Advantage: Simplicity and Efficiency
The design is mature, simple, and relatively inexpensive. Operation is straightforward, and the high thermal efficiency keeps power consumption lower than many alternative heating methods. Multiple units can also be combined for scaled-up, continuous production.
The Limitation: Inherent Temperature Gradients
The laws of physics dictate that the ends of the tube will always be cooler than the center. While this creates a predictable, uniform hot zone, it also means the usable processing area is smaller than the full length of the tube.
The Constraint: Sample Size and Shape
By definition, a tube furnace limits your sample to what can fit inside the tube's diameter. It is not suitable for processing large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects that require uniform heating across their entire surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct tube furnace configuration depends entirely on the goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or purification: The ability to control the atmosphere with a vacuum or specific gases is your most critical feature.
- If your primary focus is thermal annealing or crystal growth: The stable and highly uniform temperature zone in the center of the furnace is paramount.
- If your primary focus is frequent testing or rapid sample changes: A split tube design offers the operational flexibility and faster turnaround you need.
Ultimately, choosing the right tube furnace is about matching its specific design strengths to the precise environmental and thermal demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Electric heating device with a cylindrical tube for controlled thermal processing. |
| Key Features | Uniform heating, controlled atmosphere (vacuum/gas), precise temperature control. |
| Design Variations | Solid (robust for long-term use), Split (easy access and faster cooling). |
| Common Applications | Material synthesis, thermal annealing, crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition. |
| Pros | High thermal efficiency, simple operation, scalable for continuous production. |
| Cons | Temperature gradients at ends, limited by tube diameter for sample size. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















