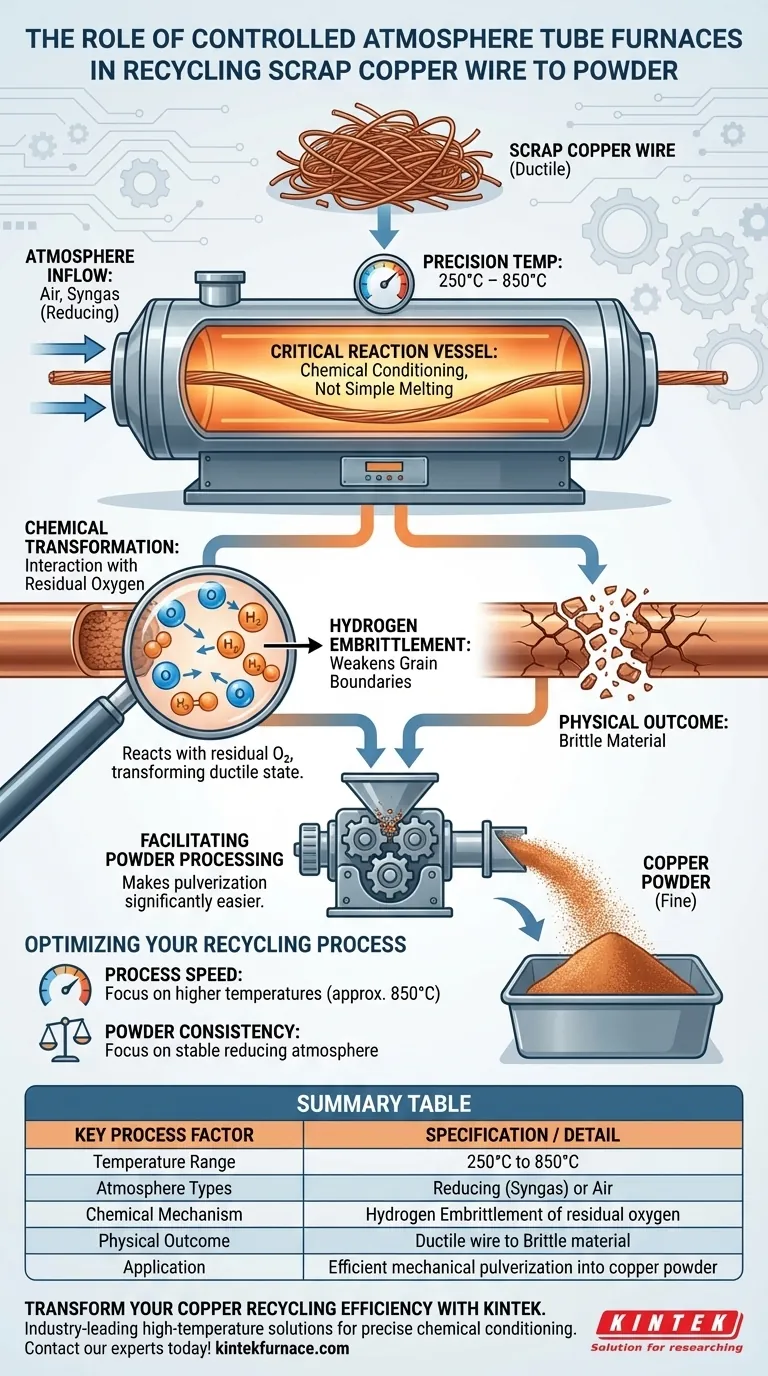
Controlled atmosphere tube furnaces function as the critical reaction vessels in the recycling of scrap copper wire, specifically for the purpose of powder production. By maintaining precise temperatures between 250°C and 850°C, these furnaces create the necessary environment to alter the mechanical properties of the wire through chemical conditioning rather than simple melting.
The primary function of these furnaces is to induce hydrogen embrittlement through a reducing atmosphere. This process chemically interacts with residual oxygen in the copper, transforming the wire from a ductile state into a brittle material that can be easily crushed into powder.

The Mechanism of Atmosphere Control
Creating the Reaction Environment
The furnace acts as a sealed chamber that introduces specific gases, such as air or syngas. This controlled environment is essential because standard ambient air would not allow for the specific chemical reactions required to alter the copper's internal structure.
Precision Temperature Management
The process relies on a broad but specific thermal window ranging from 250°C to 850°C. Maintaining stability within this range ensures the annealing treatment is effective without destroying the material or wasting energy.
Chemical Transformation of the Copper
Interacting with Residual Oxygen
The key to this recycling process is the reaction between the environmental gases introduced into the tube and the residual oxygen naturally present within the scrap copper wire. The furnace facilitates this gas-solid interaction.
Inducing Hydrogen Embrittlement
When a reducing atmosphere is used, the furnace promotes hydrogen embrittlement. This specific reaction weakens the grain boundaries of the metal.
Facilitating Powder Processing
By embrittling the copper, the furnace effectively prepares the material for the next stage of recycling. The wire loses its natural ductility, making it significantly easier to pulverize into fine copper powder during subsequent mechanical processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Sensitivity
While effective, this method requires rigorous control over gas ratios and temperature gradients. Inaccurate settings can fail to induce the necessary brittleness, resulting in wire that is still too tough to process into powder efficiently.
Atmosphere Selection
Choosing between different atmospheres (like air vs. syngas) dictates the type of chemical reaction. Using the wrong atmosphere for the specific type of scrap input may result in incomplete annealing or oxidation rather than the desired embrittlement.
Optimizing Your Recycling Process
To ensure you are getting the most out of your controlled atmosphere tube furnace, consider the desired outcome of your copper powder.
- If your primary focus is process speed: Prioritize higher temperatures within the 850°C range to accelerate the reaction rates between the gas and residual oxygen.
- If your primary focus is powder consistency: Focus on the stability of the reducing atmosphere to ensure uniform hydrogen embrittlement across the entire batch of wire.
Success in this application relies on viewing the furnace not just as a heater, but as a precise chemical reactor.
Summary Table:
| Key Process Factor | Specification / Detail |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 250°C to 850°C |
| Atmosphere Types | Reducing (Syngas) or Air |
| Chemical Mechanism | Hydrogen Embrittlement of residual oxygen |
| Physical Outcome | Transformation from ductile wire to brittle material |
| Application | Efficient mechanical pulverization into copper powder |
Transform Your Copper Recycling Efficiency with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your powder production from scrap materials? KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions tailored for precise chemical conditioning. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific metallurgical needs.
Whether you need superior atmosphere stability for hydrogen embrittlement or rapid thermal cycling, our lab and industrial furnaces ensure maximum consistency and material performance.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your unique application!
Visual Guide
References
- Falah Mustafa Al-Saraireh. The Effect of Annealing Conditions on Copper's Brittleness and Powder Production Efficiency. DOI: 10.21062/mft.2025.035
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of autoclaves and tube reactors in hydrometallurgical leaching? Unlock Refractory Ore Potential
- What is the core function of a vacuum atmosphere tube furnace when studying the evaporation and condensation behavior of metallic magnesium?
- Why are certain high-performance ceramics sintered in a vacuum tube furnace? Achieve Full Density and Purity
- What are the advantages of corundum tube furnaces? Unlock High-Temp, Corrosion-Resistant Processing
- Why is it necessary to perform annealing in a tube furnace with a nitrogen atmosphere for VO2@AlF3 core-shell powder?
- What industrial and research applications are tube furnaces used for? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Solutions
- How do temperature control and uniformity differ between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces? Optimize Your Lab's Heat Processing
- What is the function of vacuum-sealed tubes and controlled heating? Master Ruthenium Precursor Embedding



















