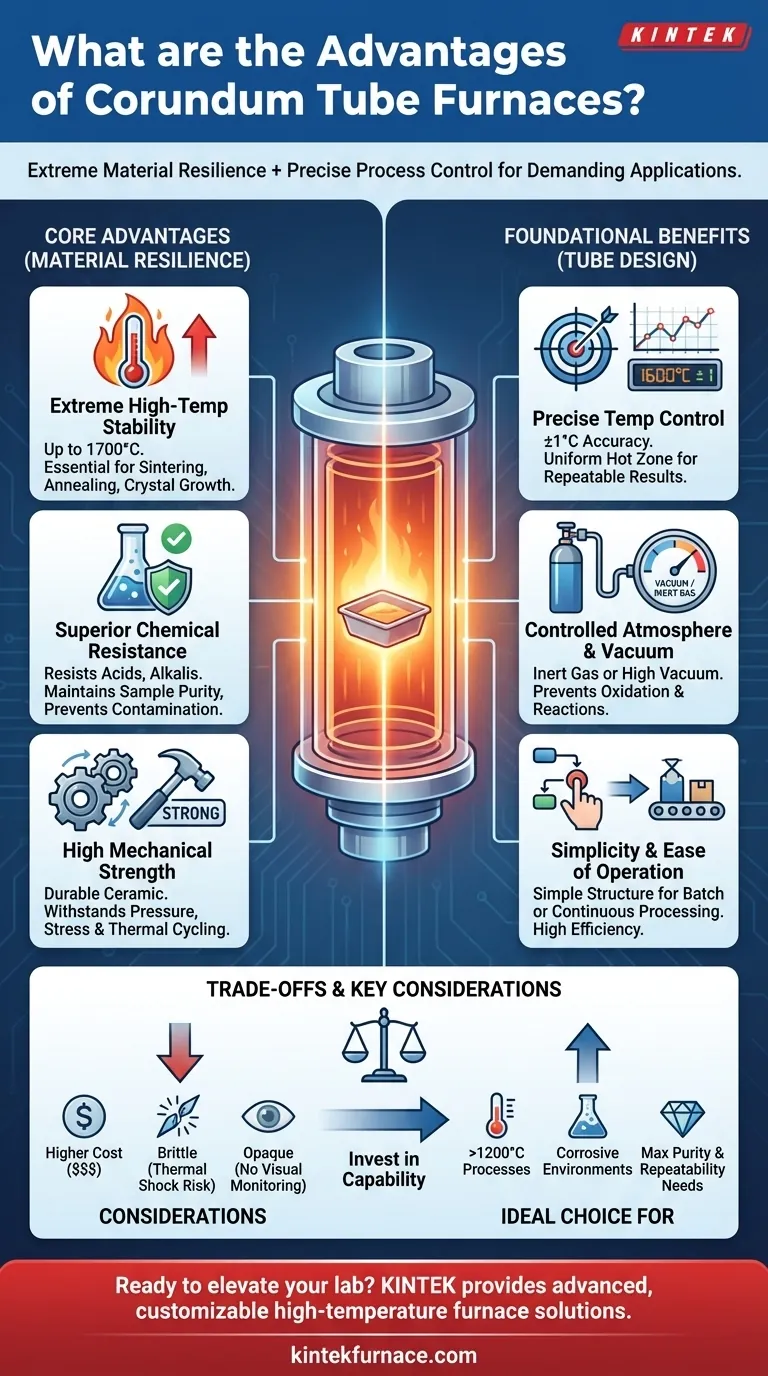
At its core, a corundum tube furnace offers a powerful combination of extreme material resilience and the inherent process control of a tube furnace design. Its primary advantages are exceptional high-temperature resistance, excellent chemical inertness, and high mechanical strength, making it the superior choice for demanding thermal processing applications.
A corundum tube is specified when process conditions—primarily temperature and chemical environment—are too harsh for standard materials like quartz. It enables high-purity, high-temperature experiments and processing that would otherwise be impossible.

The Core Advantages of the Corundum Material
The choice of corundum (high-purity alumina) as the furnace tube material is what provides the most significant advantages for extreme applications.
Extreme High-Temperature Stability
Corundum tubes can consistently operate at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C and up to 1700°C.
This makes them essential for advanced processes like high-temperature pyrolysis, sintering, annealing, and crystal growth, where lower-rated materials would fail.
Superior Chemical Resistance
The material exhibits excellent resistance to chemical corrosion from a wide range of acids, alkalis, and other harsh substances.
This inertness is critical for maintaining the purity of the sample inside the tube, as it prevents leaching and contamination that can occur with less robust materials.
High Mechanical Strength
Corundum is a hard, durable ceramic with high mechanical strength. It can withstand pressure differentials and the mechanical stress of complex experimental setups.
This durability translates to a longer service life and greater reliability, especially in environments where the tube may be subjected to thermal cycling.
Foundational Benefits of the Tube Furnace Design
A corundum tube leverages the well-established advantages inherent to all tube furnaces, creating a highly controlled processing environment.
Precise and Uniform Temperature Control
Tube furnaces are designed to create a highly uniform hot zone in the center of the tube, with cooler zones at the ends.
Modern controllers provide extremely precise temperature regulation, often within ±1°C of the setpoint, ensuring process repeatability and accuracy.
Controlled Atmosphere and Vacuum Capability
The sealed nature of the tube design is ideal for controlling the internal atmosphere. This allows for processing under inert gases (like argon or nitrogen), reactive gases, or in a high-vacuum environment.
This control is vital for preventing unwanted oxidation or reactions during sensitive material processing.
Simplicity and Ease of Operation
Tube furnaces possess a simple and mature structure, making them straightforward to operate and maintain.
Their design allows for both batch processing and continuous production, where materials are fed through the tube, increasing efficiency and throughput for certain applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, choosing a corundum tube furnace involves key considerations that may not be suitable for every application.
Higher Initial Cost
Corundum is a high-performance ceramic, and as a result, corundum tubes are significantly more expensive than their quartz counterparts. This investment must be justified by the process requirements.
Brittleness and Thermal Shock
Like most ceramics, corundum is brittle. While mechanically strong, it can crack or shatter if dropped or subjected to extreme and rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). Careful handling is required.
Opacity
Unlike a quartz tube, a corundum tube is opaque. This means you cannot visually monitor the sample during the heating process, which can be a drawback for certain types of experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct tube material is a critical decision based entirely on your specific processing goals.
- If your primary focus is processing materials above 1200°C or with corrosive chemicals: The high-temperature stability and chemical inertness of a corundum tube furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is on processes below 1100°C with non-corrosive materials: A more economical quartz tube furnace will likely provide the same level of temperature and atmosphere control for a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity and repeatability in a demanding environment: A corundum tube furnace offers the best protection against contamination and failure under extreme conditions.
Ultimately, choosing a corundum tube furnace is an investment in capability, enabling you to reliably execute the most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme High-Temperature Stability | Operates up to 1700°C | Enables advanced processes like sintering and crystal growth |
| Superior Chemical Resistance | Resists acids, alkalis, and harsh substances | Maintains sample purity and prevents contamination |
| High Mechanical Strength | Durable ceramic withstands stress and pressure | Ensures long service life and reliability |
| Precise Temperature Control | Uniform hot zone with ±1°C accuracy | Guarantees process repeatability and accuracy |
| Controlled Atmosphere Capability | Sealed design for inert or vacuum environments | Prevents oxidation and unwanted reactions |
| Ease of Operation | Simple structure for batch or continuous processing | Increases efficiency and throughput |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a high-performance corundum tube furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















