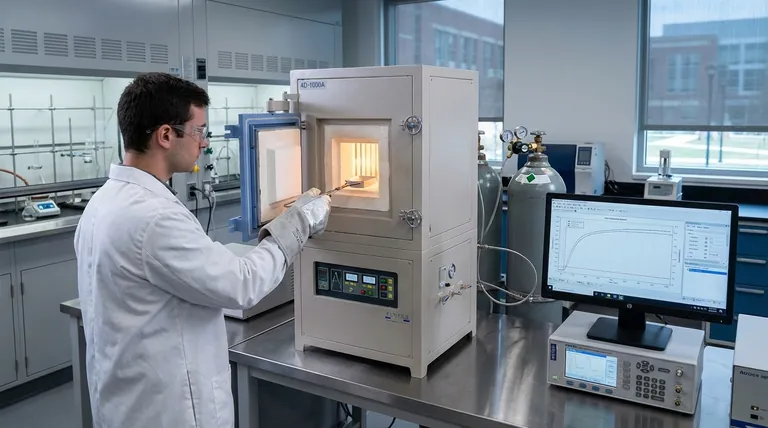
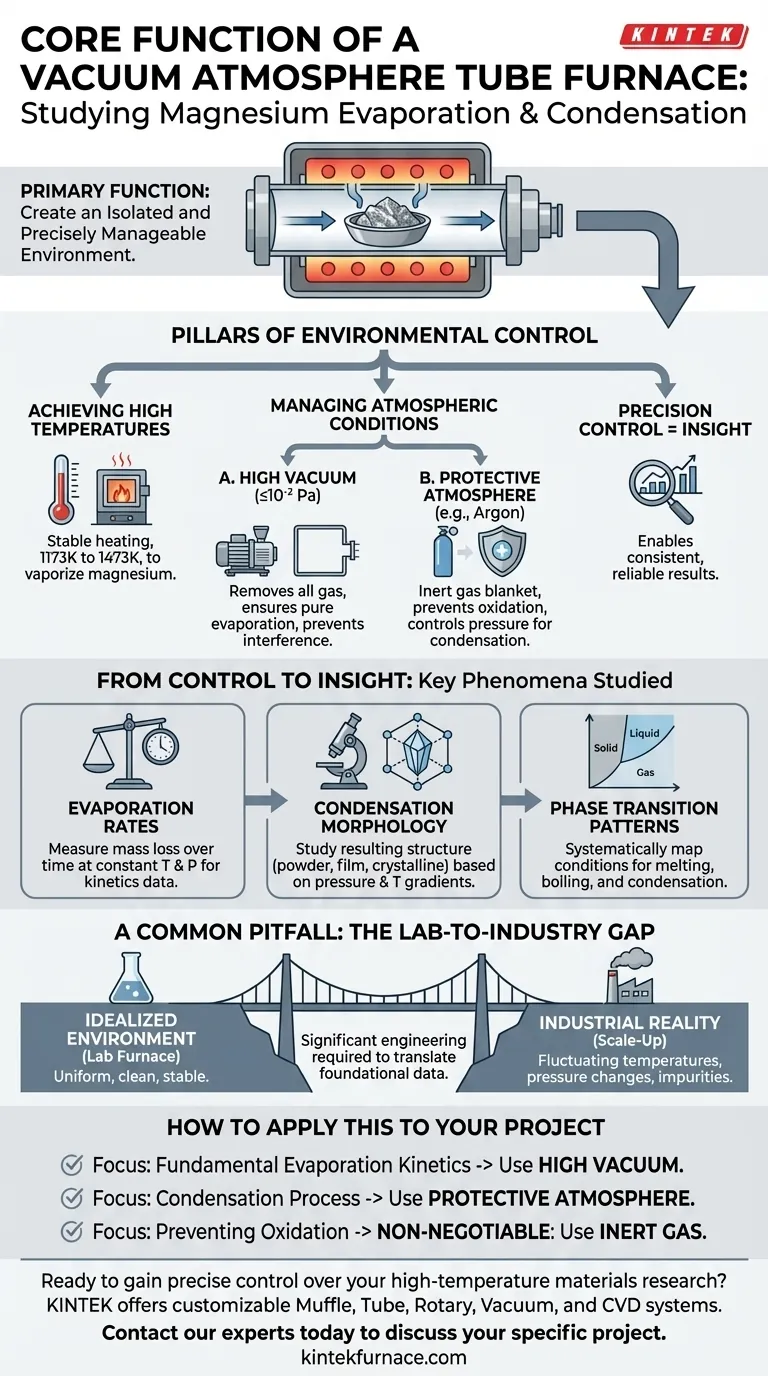
At its core, a vacuum atmosphere tube furnace serves one primary function: to create an isolated and precisely manageable environment. This allows researchers to manipulate the key variables of temperature, pressure, and atmospheric composition to systematically study how metallic magnesium evaporates into a gas and subsequently condenses back into a solid.
Understanding magnesium's behavior requires isolating it from unwanted reactions and external influences. The furnace's value lies not just in heating the metal, but in its ability to dictate the exact conditions—either a high vacuum or a protective inert gas—that govern the rate of evaporation and the physical structure of the resulting material.

The Pillars of Environmental Control
To accurately study the behavior of any material at high temperatures, you must first have absolute control over its surroundings. The furnace provides a platform to manage the three most critical factors influencing magnesium's phase transitions.
Achieving High Temperatures
Metallic magnesium requires significant thermal energy to transition into a vapor phase.
A tube furnace provides precise, stable heating, capable of reaching and maintaining temperatures in the 1173K to 1473K range necessary for this process.
Managing Atmospheric Conditions
The atmosphere inside the furnace is just as critical as the temperature. Uncontrolled gases, especially oxygen, would react with the hot magnesium, corrupting the experiment.
The furnace offers two distinct operational modes to prevent this.
The Role of High Vacuum
By pumping the air out to a high vacuum (up to 10⁻² Pa), the furnace removes virtually all other gas molecules.
This creates a near-perfectly clean environment, ensuring that the observed evaporation is purely a function of temperature and magnesium's intrinsic properties, free from chemical reactions or atmospheric interference.
The Use of a Protective Atmosphere
Alternatively, the furnace can be filled with a non-reactive, or inert, gas like argon at a specific flow rate.
This protective "blanket" of argon prevents oxidation while allowing researchers to study how different pressure levels influence the rates of evaporation and condensation.
From Control to Insight
The ability to precisely control the environment directly enables the study of key physical phenomena. Without this control, the results would be inconsistent and unreliable.
Determining Evaporation Rates
By holding temperature and pressure constant, researchers can accurately measure how quickly the magnesium mass is lost to evaporation, providing fundamental data for industrial and scientific models.
Analyzing Condensation Morphology
The pressure and temperature gradients within the furnace directly impact how the magnesium vapor condenses back into a solid.
Controlling these factors allows for the systematic study of the resulting physical structure—whether it forms a fine powder, a dense film, or crystalline structures.
Mapping Phase Transition Patterns
Ultimately, this tool allows for the fundamental study of magnesium's phase transitions. By systematically changing one variable at a time, researchers can map out the precise conditions under which it melts, boils, and condenses.
A Common Pitfall: The Lab-to-Industry Gap
While the tube furnace is an exceptional tool for research, it's essential to recognize its primary limitation.
An Idealized Environment
The furnace creates a highly uniform, clean, and stable environment that rarely exists in large-scale industrial applications like metal refining or physical vapor deposition (PVD).
The Challenge of Scale-Up
The data and principles derived from these experiments are foundational. However, translating these findings to an industrial process requires significant engineering to account for less stable temperatures, pressure fluctuations, and the presence of impurities.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your specific research question will determine how you should configure the furnace's capabilities.
- If your primary focus is on fundamental evaporation kinetics: You will leverage the high vacuum capability to isolate the process from all other atmospheric variables.
- If your primary focus is developing a condensation process: You will use the protective argon atmosphere to control pressure, which directly influences the morphology of the condensed material.
- If your primary focus is on preventing material oxidation: The use of an inert argon atmosphere is non-negotiable to create a shield against reactive gases.
Ultimately, the vacuum atmosphere tube furnace empowers you to deconstruct a complex physical process into a set of simple, controllable variables.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose in Mg Evaporation/Condensation Study |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Heating | Provides stable temperatures (1173K-1473K) needed to vaporize magnesium. |
| Vacuum Environment (≤10⁻² Pa) | Creates a clean, reaction-free space to study fundamental evaporation kinetics. |
| Protective Inert Gas (e.g., Argon) | Prevents oxidation and allows control over condensation pressure & morphology. |
| Environmental Isolation | Enables systematic study by isolating variables (T, P) for reliable, reproducible data. |
Ready to gain precise control over your high-temperature materials research?
Our vacuum atmosphere tube furnaces are engineered to provide the exact environmental control you need to study complex processes like metallic magnesium evaporation and condensation. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique research requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can tailor a furnace solution for your specific project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios



















