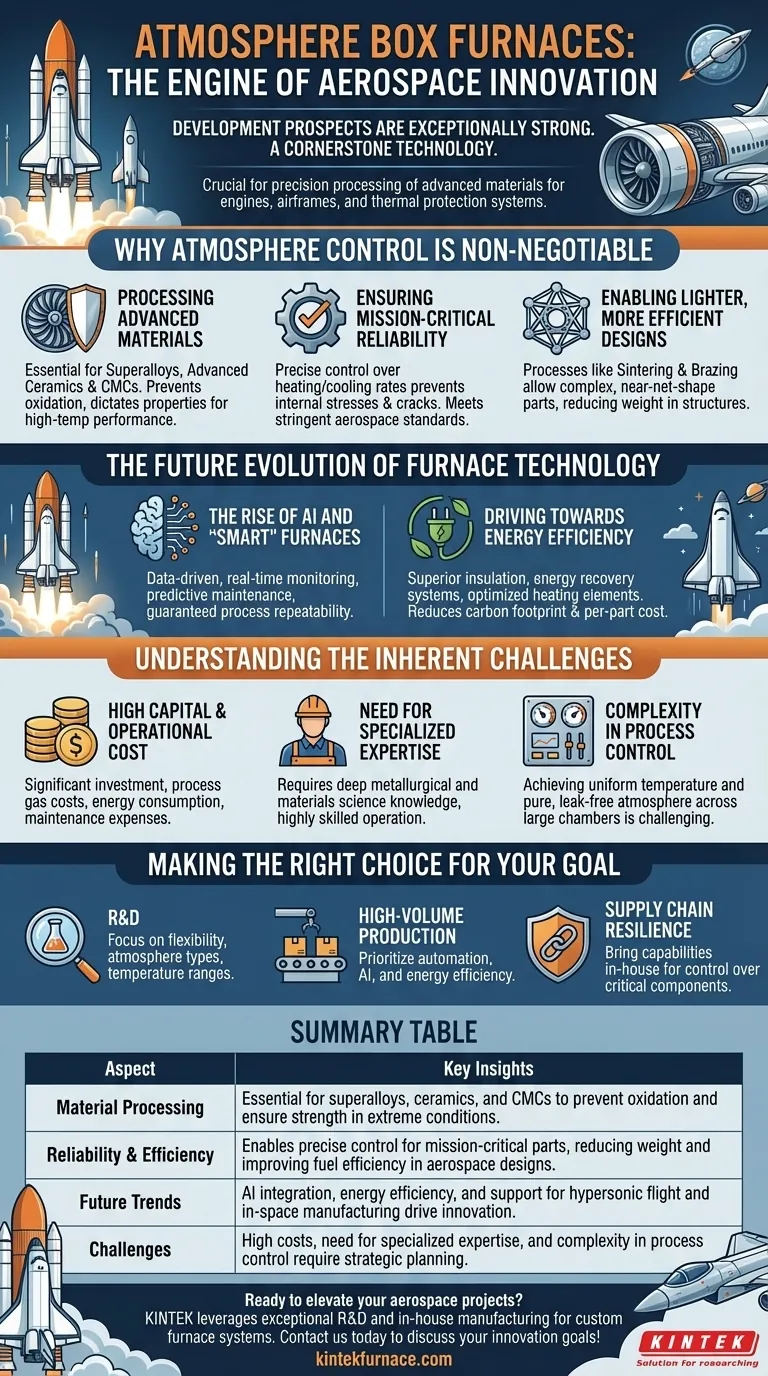
To be direct, the development prospects are exceptionally strong. Atmosphere box furnaces are no longer just a piece of manufacturing equipment; they are a cornerstone technology for the aerospace industry. Their ability to precisely process the advanced materials needed for engines, airframes, and thermal protection systems makes them indispensable for current and future aerospace innovation.
The core issue in modern aerospace is the relentless demand for materials that are lighter, stronger, and more heat-resistant. Atmosphere box furnaces are the critical tool that enables engineers to create these materials, moving from theoretical properties to reliable, mission-critical components.

Why Atmosphere Control is Non-Negotiable in Aerospace
The extreme operating conditions of aircraft and spacecraft dictate the materials used to build them. Atmosphere box furnaces provide the controlled environment necessary to forge these materials with the required properties, a task impossible in a standard furnace.
Processing Advanced Materials
Many next-generation materials are highly reactive with oxygen and other elements at high temperatures. A controlled atmosphere is essential.
For superalloys, used in jet engine turbine blades and rocket engine components, an inert or vacuum atmosphere prevents oxidation, which would otherwise compromise the alloy's strength and high-temperature performance.
For advanced ceramics and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), used in thermal protection systems and engine shrouds, the furnace atmosphere dictates the final chemical composition and density during sintering, directly impacting their ability to withstand re-entry heat.
Ensuring Mission-Critical Reliability
In aerospace, component failure is not an option. The precision of the heat treatment process directly correlates to the reliability and lifespan of a part.
An atmosphere furnace allows for exact control over heating and cooling rates. This prevents internal stresses, cracks, and undesirable microstructures, ensuring every part meets stringent aerospace certification standards for strength and fatigue resistance.
Enabling Lighter, More Efficient Designs
The drive for fuel efficiency and higher payloads is a drive for lighter components.
Processes like sintering and brazing, performed in atmosphere furnaces, allow for the creation of complex, near-net-shape parts from materials like titanium and nickel alloys. This reduces the need for heavy fasteners or extensive machining, leading to significant weight savings in satellite structures and airframes.
The Future Evolution of Furnace Technology
The role of the atmosphere box furnace is expanding from a simple heating tool to an intelligent, integrated system that actively supports innovation.
The Rise of AI and "Smart" Furnaces
Future furnaces will be data-driven. AI integration will allow for real-time monitoring and adjustment of temperature and gas flow, optimizing each cycle for perfect results.
This intelligence will also enable predictive maintenance and guarantee process repeatability, which is critical for scaling up the production of new materials from the lab to the factory floor.
Driving Towards Energy Efficiency
Heat treatment is an energy-intensive process. As sustainability and operational costs become more critical, new furnace designs will focus on superior insulation, energy recovery systems, and optimized heating elements.
This not only reduces the carbon footprint but also lowers the per-part cost, making advanced materials more economically viable for a wider range of applications.
Supporting Next-Generation Aerospace Goals
The ambitions of the aerospace industry rely on materials that do not yet exist in mass production.
Atmosphere furnaces are fundamental to developing the ultra-high-temperature materials needed for hypersonic flight. They are also key enablers for future concepts like in-space manufacturing, where small, efficient furnaces could one day create parts on-demand in orbit.
Understanding the Inherent Challenges
While indispensable, this technology is not without its complexities. A clear understanding of the trade-offs is essential for strategic planning.
High Capital and Operational Cost
State-of-the-art atmosphere furnaces represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, the cost of process gases (like argon or nitrogen), high energy consumption, and regular maintenance contribute to high operational expenses.
The Need for Specialized Expertise
Developing the correct thermal "recipe" for an advanced alloy or composite requires deep metallurgical and materials science knowledge. Operating and maintaining these complex systems demands highly skilled technicians and engineers.
Complexity in Process Control
Achieving and maintaining a perfectly uniform temperature and a pure, leak-free atmosphere across a large chamber is a significant technical challenge. It requires sophisticated sensors, vacuum systems, and control logic to ensure process integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategic approach to adopting this technology should align directly with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is Research & Development: Invest in furnaces that offer maximum flexibility in atmosphere types, temperature ranges, and data logging to pioneer new materials and processes.
- If your primary focus is High-Volume Production: Prioritize automated furnaces with AI-driven process control and proven energy efficiency to maximize throughput, yield, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is Supply Chain Resilience: Consider bringing atmosphere furnace capabilities in-house to gain control over the heat treatment of your most critical components and reduce external dependencies.
Ultimately, mastering advanced thermal processing is no longer a niche capability but a strategic imperative for leading in the aerospace industry.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Material Processing | Essential for superalloys, ceramics, and CMCs to prevent oxidation and ensure strength in extreme conditions. |
| Reliability & Efficiency | Enables precise control for mission-critical parts, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency in aerospace designs. |
| Future Trends | AI integration, energy efficiency, and support for hypersonic flight and in-space manufacturing drive innovation. |
| Challenges | High costs, need for specialized expertise, and complexity in process control require strategic planning. |
Ready to elevate your aerospace projects with advanced high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with custom furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior material processing and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















