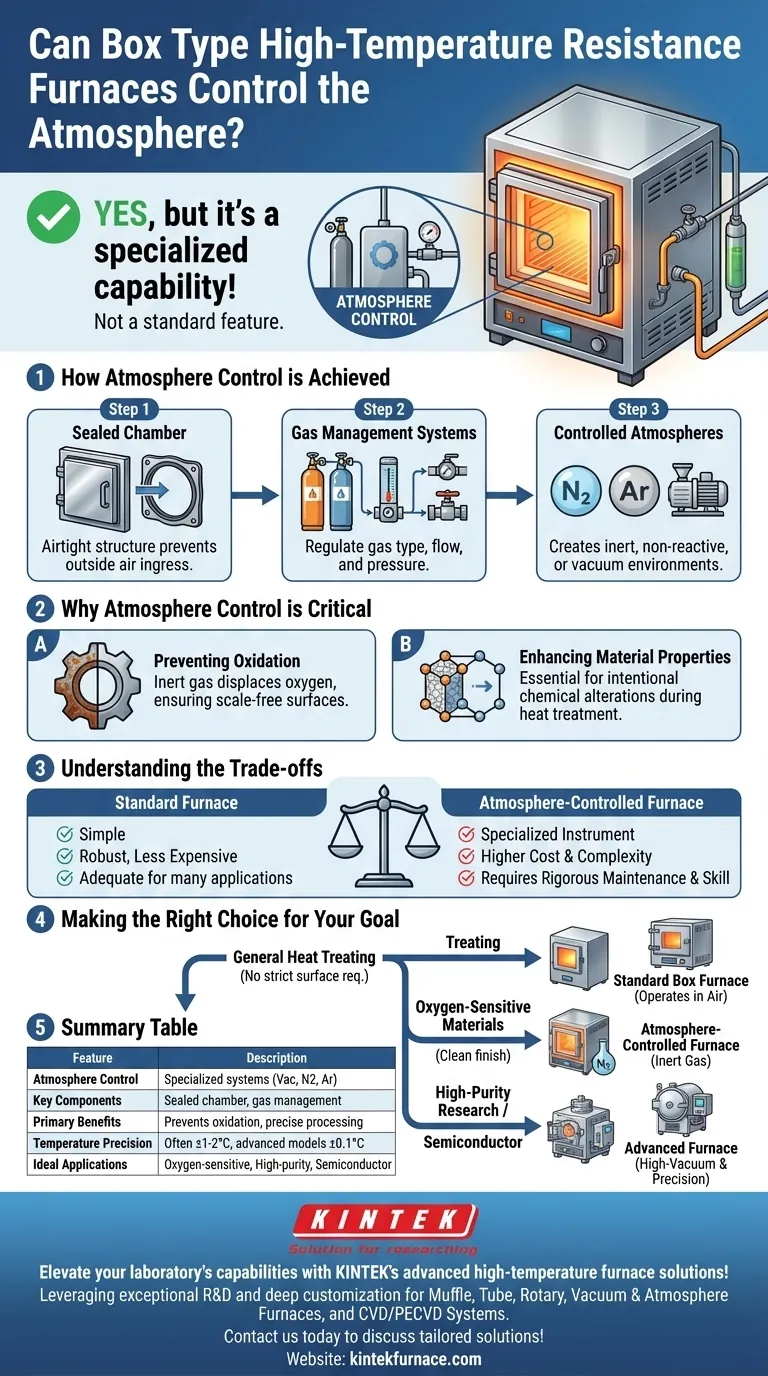
Yes, but it is a specialized capability, not a standard feature. While a basic box-type resistance furnace operates in ambient air, many models are specifically designed or can be equipped with systems for precise atmosphere control. These advanced furnaces use sealed chambers and gas management hardware to create environments like a vacuum or introduce protective gases, which is critical for high-temperature processes where material oxidation or contamination is a concern.
The ability to control the atmosphere in a box furnace transforms it from a simple heating device into a precise metallurgical tool. This capability hinges on a sealed furnace design and a dedicated gas control system, which are essential for preventing oxidation and enabling advanced material processing.
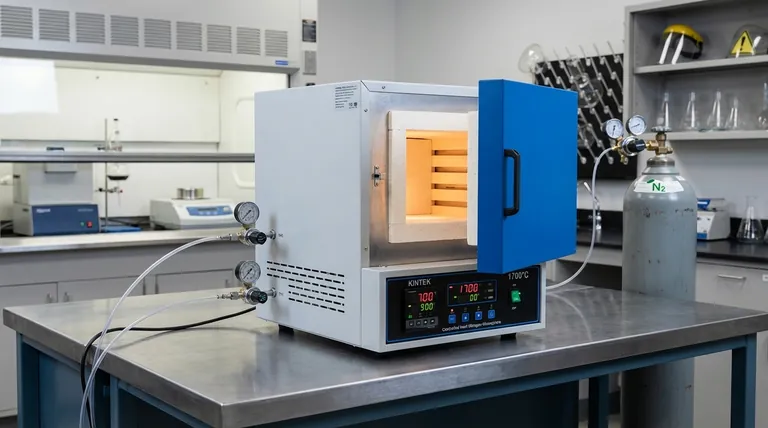

How Atmosphere Control is Achieved
The functionality of an atmosphere-controlled furnace goes far beyond just heating. It relies on an integrated system designed to precisely manage the internal environment of the furnace chamber.
The Sealed Furnace Chamber
The foundation of any atmosphere control is an airtight structure. Unlike standard furnaces that are open to the air, these models feature robust seals on doors and any other openings.
This sealed design is the first and most critical step, as it prevents outside air (primarily oxygen and moisture) from entering and contaminating the process.
Gas Management Systems
These furnaces are equipped with dedicated hardware to introduce and regulate specific gases. This typically includes high-precision gas flow meters and pressure regulating devices.
These components allow an operator to accurately control the type of gas, its flow rate, and its pressure, ensuring a stable and uniform atmosphere is maintained throughout the heat treatment cycle.
Common Controlled Atmospheres
The most common controlled atmospheres are inert or non-reactive. This is achieved by first purging the chamber of air and then filling it with a protective gas like nitrogen (N2) or argon (Ar).
Some advanced systems can also create a vacuum, removing nearly all atmospheric gases to provide an exceptionally pure environment for highly sensitive materials.
Why Atmosphere Control is Critical
Controlling the furnace environment is not just an optional enhancement; for many modern applications, it is an absolute necessity to achieve the desired material properties and quality.
Preventing Oxidation
The primary reason for using a controlled atmosphere is to prevent oxidation. At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen, forming a layer of scale or oxide on the surface.
An inert gas atmosphere displaces the oxygen, protecting the workpiece and ensuring a clean, scale-free surface finish. This is vital for parts that require tight dimensional tolerances or a pristine appearance.
Enhancing Material Properties
Beyond preventing unwanted reactions, a controlled atmosphere is essential for processes that are designed to intentionally alter a material's chemistry.
This capability is fundamental for specific chemical reactions required during certain heat treatments, ensuring the final product meets its specified metallurgical characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While atmosphere control offers significant advantages, it's important to recognize the associated complexities and costs. This is not a standard feature, and the decision to use it should be deliberate.
Standard vs. Specialized Furnaces
A standard box furnace that operates in air is a simpler, more robust, and significantly less expensive piece of equipment. It is perfectly adequate for many applications where surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed later.
An atmosphere-controlled furnace is a specialized instrument. The addition of seals, gas plumbing, sensors, and control systems increases the initial cost and the operational complexity.
Maintenance and Operational Skill
The systems required for atmosphere control demand more rigorous maintenance. Seals can degrade over time and require replacement, and gas flow sensors may need periodic calibration to remain accurate.
Operating such a furnace also requires a higher level of technical skill to manage gas purges, flow rates, and pressures correctly to ensure a successful and safe process.
Precision as a Package Deal
Furnaces equipped for atmosphere control are typically designed for high-precision work. They almost always include a high-precision temperature control system.
Temperature accuracy of ±1-2°C is common, with some advanced models achieving ±0.1°C. This pairing of features is necessary because the processes demanding atmosphere control usually also demand extremely stable and uniform temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of furnace depends entirely on your material, your process, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating without strict surface requirements: A standard box furnace operating in air is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials or achieving a clean, scale-free finish: An atmosphere-controlled furnace using inert gas is essential to protect your workpiece.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material research or semiconductor annealing: You will need an advanced furnace with both high-vacuum capability and ultra-precise temperature and atmosphere regulation.
By aligning the furnace's capabilities with your specific process requirements, you ensure both the quality of your results and the efficiency of your operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Specialized systems for vacuum or gas environments like nitrogen or argon |
| Key Components | Sealed chamber, gas flow meters, pressure regulators |
| Primary Benefits | Prevents oxidation, enables precise metallurgical processes |
| Temperature Precision | Often ±1-2°C, with advanced models achieving ±0.1°C |
| Ideal Applications | Processing oxygen-sensitive materials, high-purity research, semiconductor annealing |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether you require atmosphere control for oxidation prevention or ultra-precise temperature regulation. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















