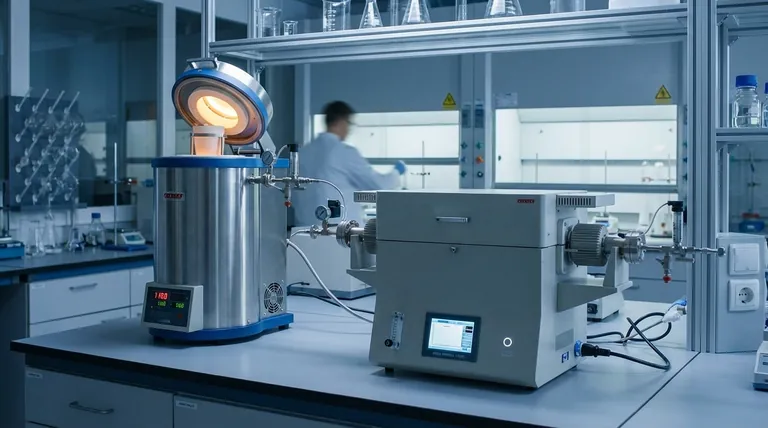
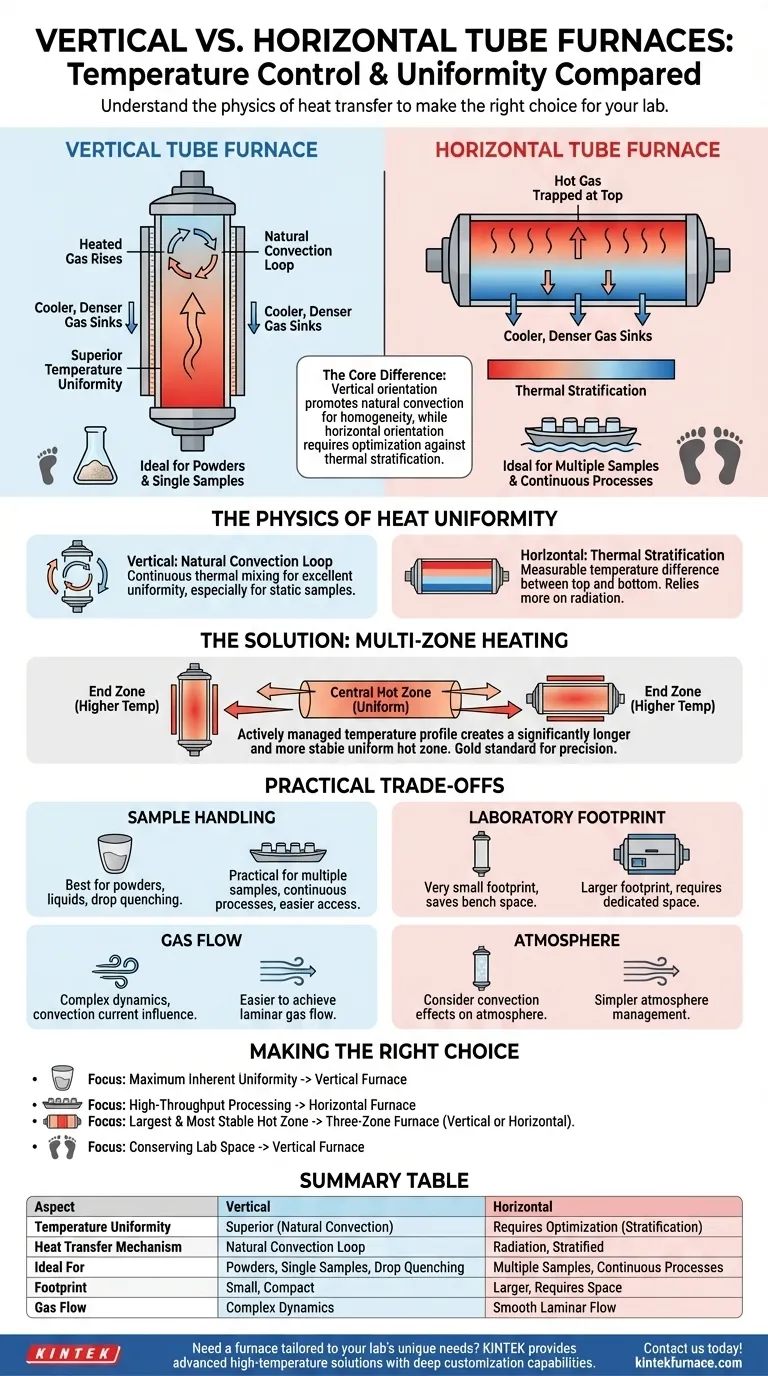
At its core, a vertical tube furnace generally provides superior temperature uniformity due to natural convection, while a horizontal tube furnace can achieve high uniformity but often requires more careful optimization to overcome thermal stratification. The vertical orientation allows heated gas to circulate naturally, creating a more homogenous thermal environment along the sample's length.
The choice between a vertical and horizontal furnace is not a matter of which is universally "better," but which orientation's inherent heat transfer physics best aligns with your specific material, process, and practical constraints.

The Physics of Heat Uniformity
To select the right furnace, you must first understand how heat behaves differently in each orientation. The physical arrangement directly impacts heat transfer efficiency and temperature stability.
Vertical Furnaces: The Advantage of Natural Convection
In a vertical furnace, the heating elements surround the process tube. As the gas or atmosphere inside the tube heats up, it naturally rises.
When this gas reaches the cooler, upper parts of the tube (or the top of the sealed chamber), it cools, becomes denser, and sinks back down the sides. This creates a continuous, natural convection loop that constantly mixes the atmosphere inside the tube, actively evening out temperature differences.
This self-regulating thermal mixing is the primary reason vertical furnaces are renowned for their excellent temperature uniformity, especially for static samples like powders or materials in a crucible.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Challenge of Stratification
A horizontal furnace also has heating elements surrounding the tube, but its orientation works against natural convection.
Hot gas still rises, but it becomes trapped at the top of the horizontal tube, while cooler, denser gas sinks to the bottom. This creates thermal stratification—a measurable temperature difference between the top and bottom of the tube.
Heat transfer in this setup relies more heavily on radiation from the furnace walls to the sample. While effective, this can lead to slight inconsistencies, requiring careful sample placement and temperature profiling to ensure all parts of the sample receive equal energy.
The Solution: Multi-Zone Heating
For applications demanding the highest level of precision, both furnace types can be configured as three-zone furnaces.
These systems have a main central heating zone and two smaller, independently controlled end zones. The end zones are set to a slightly higher temperature to compensate for the inevitable heat loss that occurs at the openings of the tube.
This actively managed temperature profile creates a significantly longer and more stable uniform hot zone, making it the gold standard for processes that are highly sensitive to thermal gradients.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Temperature uniformity is critical, but it isn't the only factor. The physical design of each furnace creates distinct advantages and disadvantages for day-to-day use.
Sample Handling and Loading
Vertical furnaces excel when working with powders, granulated materials, or liquids in crucibles, as gravity keeps everything perfectly positioned. They are also ideal for experiments involving drop quenching, where a sample is quickly dropped from the hot zone into a quenching medium below.
Horizontal furnaces are far more practical for processing multiple samples at once (e.g., in a sample boat) or for continuous processes where materials are pushed or pulled through the tube. Access is simpler and less constrained by gravity.
Laboratory Footprint
The choice often comes down to physical space. A vertical furnace has a very small footprint, making it ideal for crowded labs where benchtop space is at a premium.
A horizontal furnace, by its nature, requires a much wider area. It typically demands dedicated bench or floor space to accommodate its length and provide clearance at both ends.
Atmosphere and Gas Flow
The furnace orientation impacts how process gases flow. In a horizontal furnace, it is relatively easy to achieve a smooth, laminar gas flow over the sample.
In a vertical furnace, the gas flow must either work with or against the natural convection currents. This can create more complex flow dynamics that may need to be considered for atmosphere-sensitive processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your process requirements should dictate your furnace selection. Use these guidelines to make a decision based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum inherent uniformity for powders or single samples: A vertical furnace is the most direct path to achieving a homogenous thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing of multiple samples: A horizontal furnace offers superior ease of loading and is better suited for sample boats.
- If your primary focus is the absolute largest and most stable hot zone: A three-zone furnace, either vertical or horizontal, is the necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is conserving laboratory space: A vertical furnace provides a significant advantage with its compact, tower-style design.
By understanding how orientation dictates heat transfer, you can confidently select a furnace that is fundamentally suited to the physics of your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vertical Tube Furnace | Horizontal Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Superior due to natural convection | Requires optimization to overcome stratification |
| Heat Transfer Mechanism | Natural convection loop | Radiation, with thermal stratification |
| Ideal for | Powders, single samples, drop quenching | Multiple samples, continuous processes |
| Footprint | Small, compact | Larger, requires more space |
| Gas Flow | Complex dynamics | Smooth laminar flow |
Need a furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your experimental requirements for superior temperature control and uniformity. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and achieve optimal results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















