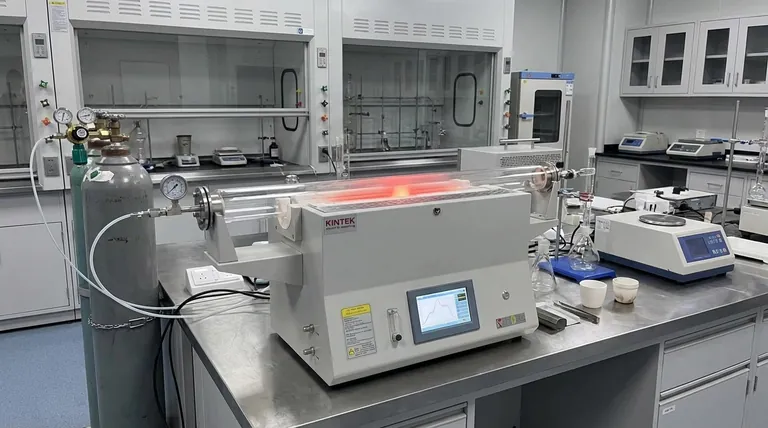
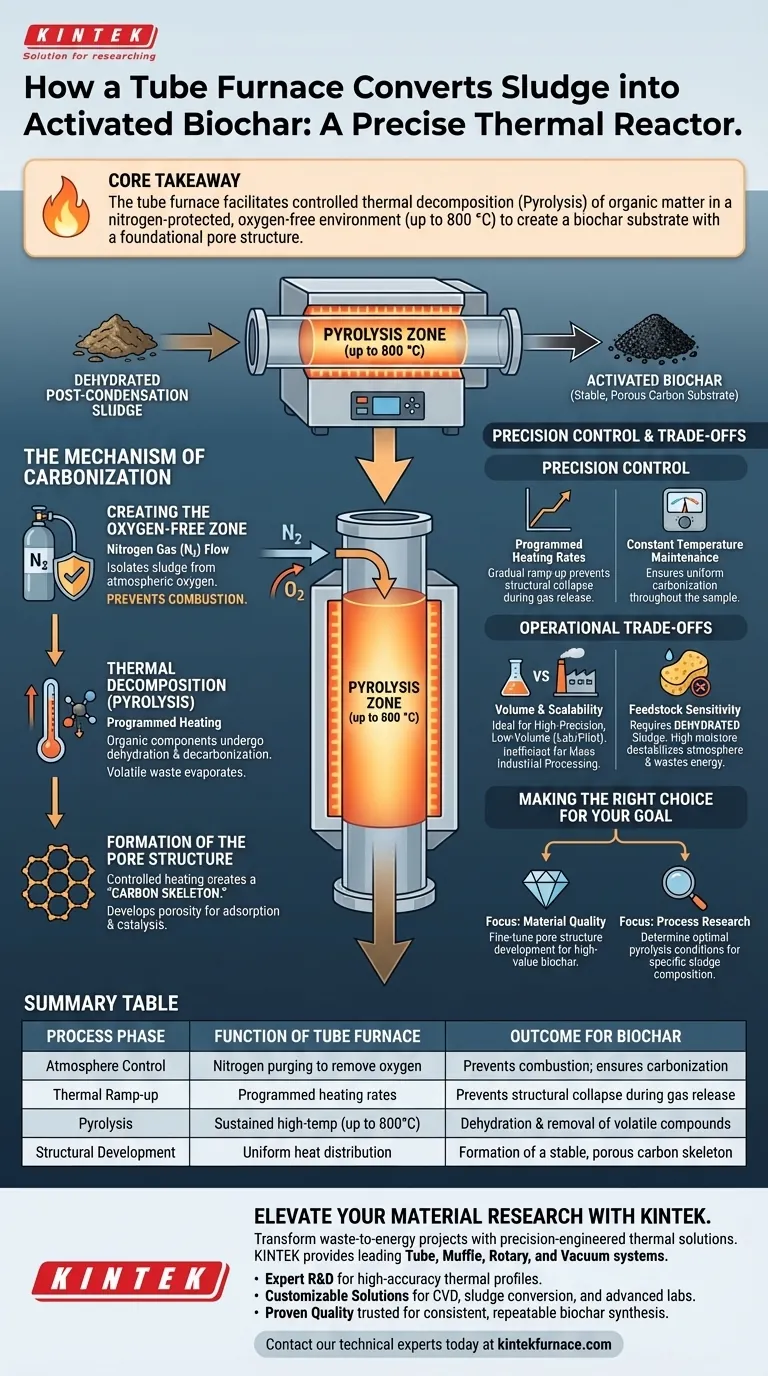
The tube furnace serves as the precise thermal reactor required to convert dehydrated post-condensation sludge into activated biochar. It provides a sealed, high-temperature environment where organic matter is chemically decomposed rather than burned, a process known as pyrolysis. By maintaining an inert atmosphere and strictly regulating heat, the furnace transforms volatile waste into a stable, porous carbon substrate.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace enables the carbonization of sludge by maintaining a nitrogen-protected, oxygen-free atmosphere at temperatures up to 800 °C. Its primary function is to facilitate the controlled thermal decomposition of organic matter, resulting in a biochar substrate with a foundational pore structure suitable for further activation.

The Mechanism of Carbonization
The conversion of sludge into biochar is not simple incineration; it is a complex thermochemical transformation. The tube furnace provides the specific conditions necessary to drive this change.
Creating the Oxygen-Free Zone
The most critical role of the tube furnace is to isolate the sludge from atmospheric oxygen.
By continuously flowing nitrogen gas through the tube, the furnace creates a protective, inert environment.
Without this exclusion of oxygen, the high processing temperatures would cause the sludge to combust into ash rather than carbonizing into biochar.
Thermal Decomposition (Pyrolysis)
Once the inert atmosphere is established, the furnace applies programmed heating to drive pyrolysis.
As the temperature rises—often reaching 800 °C—the organic components within the dehydrated sludge undergo dehydration and decarbonization.
This heat forces volatile compounds to evaporate, leaving behind the rigid carbon material.
Formation of the Pore Structure
The result of this controlled heating is the creation of a "carbon skeleton."
The tube furnace facilitates the development of an initial pore structure within the residual material.
This porosity is the defining characteristic of biochar, serving as the physical foundation that makes the material effective for adsorption or catalytic applications.
The Importance of Precision Control
Processing sludge requires exact parameters to ensure the resulting biochar has consistent properties. The tube furnace offers superior control compared to open-fire or less regulated heating methods.
Programmed Heating Rates
The furnace allows for specific ramp-up rates, controlling how quickly the sludge is brought to the target temperature.
This gradual increase is vital for preventing structural collapse of the material during rapid gas release.
Constant Temperature Maintenance
Once the target temperature is reached, the furnace maintains strict thermal stability.
Holding the material at a constant temperature ensures that carbonization is uniform throughout the entire sample.
This consistency allows for the thorough transformation of waste sludge into a high-quality biochar substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While tube furnaces provide exceptional control for biochar production, there are operational limitations to consider.
Volume and Scalability
Tube furnaces are primarily designed for high-precision, lower-volume processing.
They are ideal for laboratory research or pilot-scale testing but may be inefficient for mass industrial processing of large tonnage sludge.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The efficiency of the tube furnace relies heavily on the state of the input material.
As implied by the requirement for "dehydrated" sludge, the furnace is not designed to handle high-moisture raw sludge efficiently; excess water requires significant energy to vaporize and can destabilize the internal atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tube furnace in biochar conversion, align its capabilities with your specific project requirements.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Utilize the furnace's programmable heating rates to fine-tune the pore structure development, ensuring high-value biochar.
- If your primary focus is process research: Leverage the precise temperature and atmosphere controls to determine the exact optimal pyrolysis conditions for your specific sludge composition.
The tube furnace is the essential tool for turning variable organic waste into a consistent, structurally sound carbon material through precise environmental control.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Tube Furnace | Outcome for Biochar |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Nitrogen purging to remove oxygen | Prevents combustion; ensures carbonization over incineration |
| Thermal Ramp-up | Programmed heating rates | Prevents structural collapse during gas release |
| Pyrolysis | Sustained high-temp (up to 800°C) | Dehydration and removal of volatile organic compounds |
| Structural Development | Uniform heat distribution | Formation of a stable, porous carbon skeleton |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Transform your waste-to-energy projects with precision-engineered thermal solutions. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of pyrolysis and carbonization research.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our furnaces are built for high-accuracy thermal profiles and inert atmosphere stability.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored systems for CVD, sludge conversion, and advanced lab high-temp needs.
- Proven Quality: Trusted by researchers to deliver consistent, repeatable results in biochar synthesis.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace for your unique laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Barbara Pieczykolan. Investigation of Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Synthetic Dyes on Biochar Derived from Post-Coagulation Sludge. DOI: 10.3390/ijms26167912
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature tube furnace? Driving Topotactic Reduction of Nickelate Films
- How does the heating method of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace differ from ordinary tube furnaces? Discover Key Differences for Better Lab Efficiency
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in N-CP synthesis? Mastering Precision Carbonization
- How does the melt-diffusion process for Te1S7 use tube furnaces? Achieve High-Precision Molecular Confinement
- Why is a silicate glass fixed-bed reactor used instead of stainless steel? Ensure Pure Methanol Decomposition Data
- What types of reactions can tube furnaces be used for besides synthesis and purification? Explore Versatile Thermal Processing Applications
- What is the function of the high-purity quartz tube in CVT for ZrTe5? Ensure High Purity and Vacuum Integrity
- What is an atmosphere tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing



















