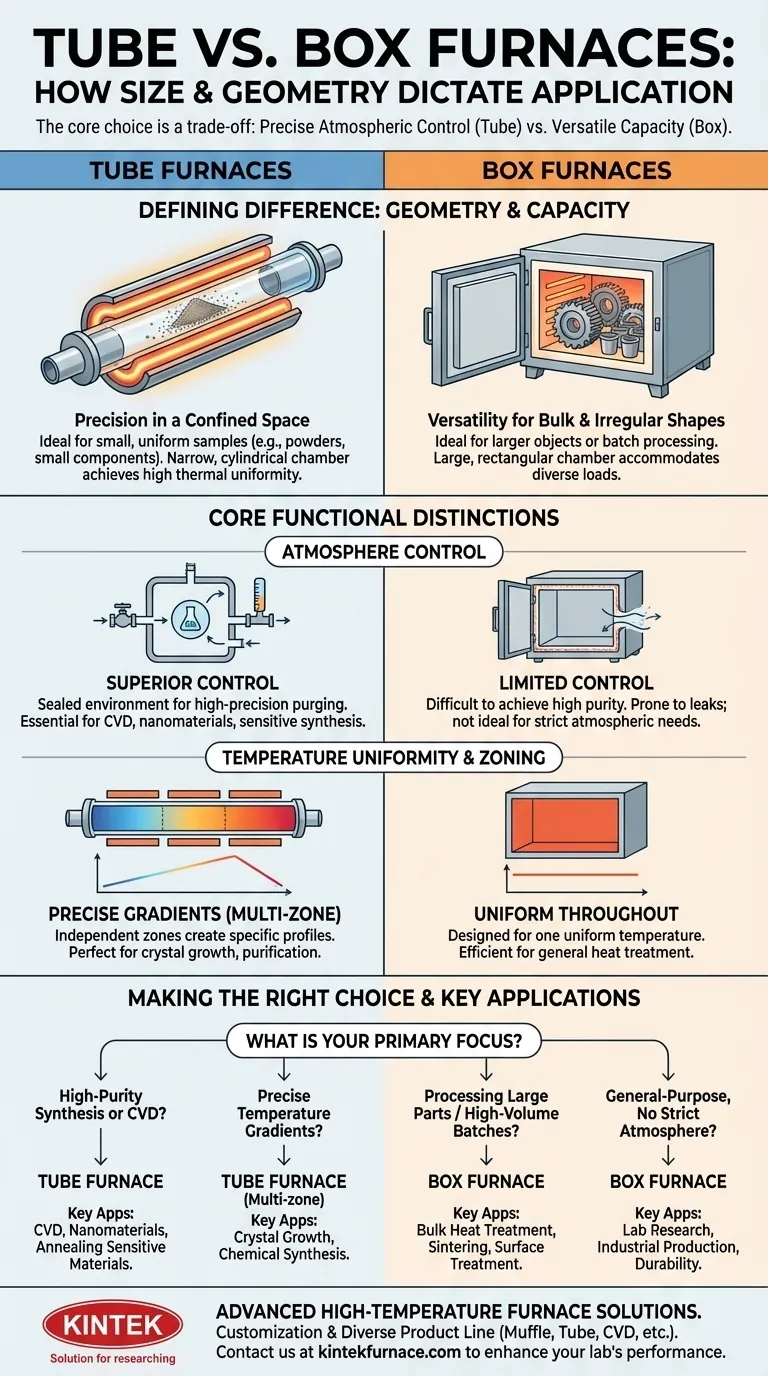
In principle, the size of a furnace directly dictates the applications it can handle. Tube furnaces, with their narrow, cylindrical chambers, are designed for processing small, uniform samples like powders or small components. In contrast, box furnaces possess large, rectangular chambers built to accommodate bigger, irregularly shaped objects or batches of multiple items simultaneously.
The decision between a tube and box furnace extends beyond simple sample size. The core choice is a trade-off between the precise atmospheric control and thermal gradients of a tube furnace and the versatile capacity and bulk processing capabilities of a box furnace.

The Defining Difference: Geometry and Capacity
The fundamental distinction between these two furnace types is their internal geometry, which directly influences their ideal use cases.
Tube Furnaces: Precision in a Confined Space
A tube furnace's heating chamber is a long, narrow tube. This design is exceptionally well-suited for materials that can be contained within it, such as small particle ores, glass powder, and ceramic powders.
The constrained volume and shape are perfect for achieving high thermal uniformity along the sample's length. Models are available in horizontal, vertical, and combination configurations to suit different material handling needs.
Box Furnaces: Versatility for Bulk and Irregular Shapes
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, offers a spacious, open chamber. This makes it the default choice for heat-treating larger components or running many smaller samples at once in a batch process.
Applications like the surface treatment of large stainless steel parts or sintering multiple components are impractical in a tube furnace but are easily handled by a box furnace.
Beyond Size: Core Functional Distinctions
While capacity is the most obvious difference, the deeper functional distinctions are what truly guide the selection process for a specific scientific or industrial task.
Atmosphere Control: The Tube Furnace Advantage
This is the most critical functional difference. The small, sealed environment of a tube furnace allows for superior atmosphere control. Gases can be purged and introduced with high precision.
This capability is essential for sensitive processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), the synthesis of nanomaterials, and semiconductor fabrication, which demand a strictly controlled, pure, or inert environment.
Temperature Uniformity and Zoning
Tube furnaces often feature multiple heating zones that can be independently controlled. This allows an operator to create a precise temperature gradient across the sample's length.
This feature is invaluable for specialized applications like crystal growth and certain types of chemical synthesis and purification where a specific thermal profile is required. Box furnaces, by contrast, are designed to create one uniform temperature throughout their larger chamber.
Material Processing and Applications
Tube furnaces excel at processes requiring environmental precision, including calcination, pyrolysis, and annealing of sensitive materials.
Box furnaces are workhorses built for durability and a wide range of applications, from small labs to industrial production. Their robust insulation systems allow for faster thermal cycling, making them efficient for repeated production tasks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace means acknowledging the inherent limitations of each design.
The Constraint of Sample Size
The primary limitation of a tube furnace is its diameter. It simply cannot accommodate large or awkwardly shaped objects, which immediately disqualifies it for many industrial heat-treatment applications.
The Challenge of Atmosphere in Box Furnaces
While it's possible to introduce gas into a box furnace, achieving the high-purity, perfectly sealed atmosphere of a tube furnace is difficult and inefficient. The large volume and door seals make them prone to leaks and contamination.
Furnace Tube Material
For a tube furnace, the process itself dictates the tube material. Stainless steel is used for general-purpose work, while high-performance alloys like Inconel are required for high-temperature, corrosive environments. Quartz or ceramic tubes are necessary for ultra-high temperatures and when chemical inertness is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, focus on the primary requirement of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis or CVD: Choose a tube furnace for its unmatched atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is processing large parts or high-volume batches: Choose a box furnace for its capacity and versatility.
- If your primary focus is creating precise temperature gradients: Choose a multi-zone tube furnace for its independent heating controls.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment without strict atmospheric needs: A box furnace offers greater flexibility for a wider range of sample sizes and shapes.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace requires matching the unique geometric and atmospheric capabilities of the equipment to the specific demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Geometry | Narrow, cylindrical | Large, rectangular |
| Ideal Sample Types | Small, uniform (e.g., powders) | Large, irregular, or batch items |
| Atmosphere Control | High precision, sealed environment | Limited, prone to leaks |
| Temperature Uniformity | Multi-zone gradients possible | Uniform throughout chamber |
| Key Applications | CVD, nanomaterials, synthesis | Bulk heat treatment, sintering |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you require precise atmospheric control for sensitive processes or versatile capacity for bulk processing, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your laboratory's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















