In short, a standard tube furnace can typically reach temperatures between 1200°C and 1800°C. The specific maximum temperature is not a universal feature but is determined by the furnace's model and, most importantly, the material used for its heating elements. These are generally available in distinct tiers, such as 1200°C, 1600°C, and 1800°C, to match different process requirements.
Selecting a tube furnace involves more than looking at the maximum temperature. The critical task is to match the furnace's entire operating system—its heating elements, temperature controls, and atmosphere management—to the precise demands of your scientific or industrial process.

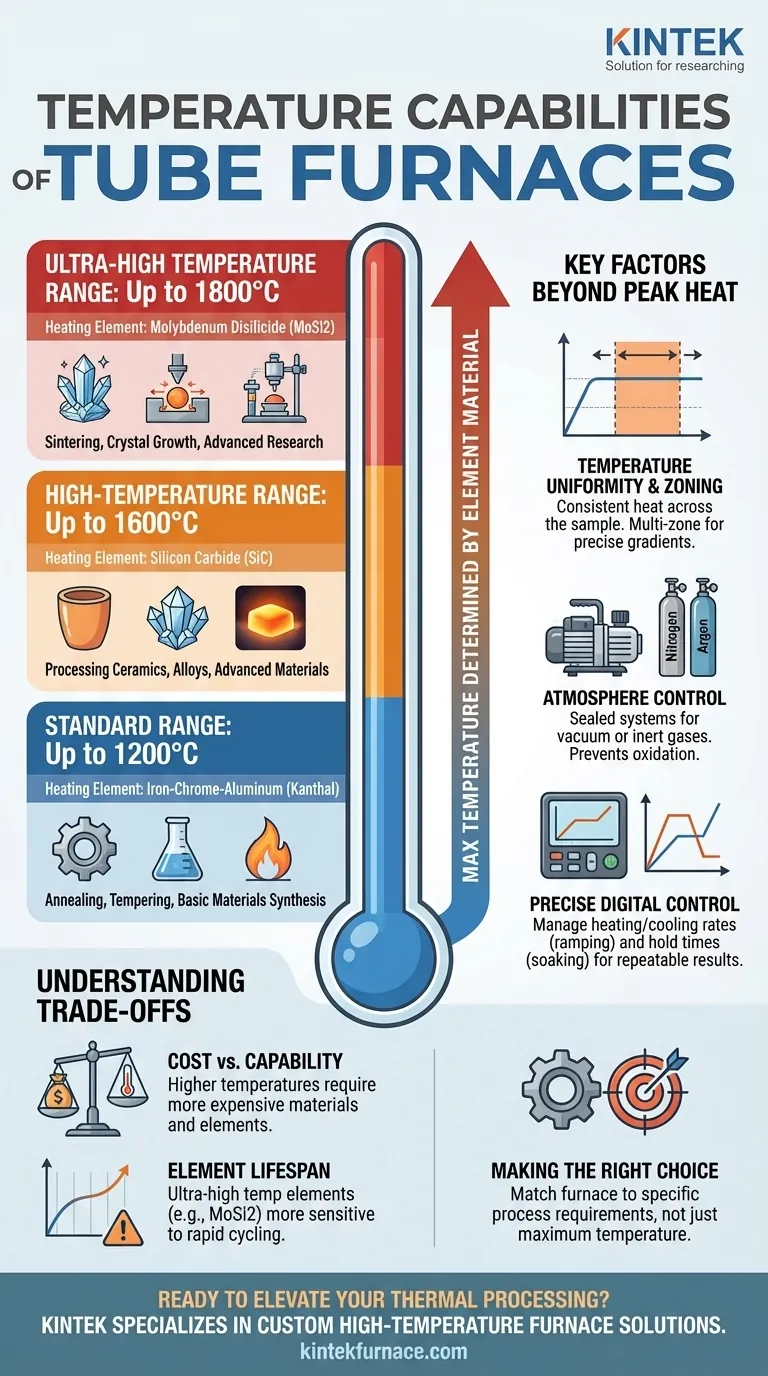
Understanding the Temperature Tiers
The maximum operating temperature of a tube furnace is directly linked to the type of heating element it employs. Different materials are required to reliably and efficiently produce heat at progressively higher temperatures.
Standard Range: Up to 1200°C
Furnaces in this category are the most common and are suitable for a wide array of general-purpose applications. They often use robust and cost-effective iron-chrome-aluminum (Kanthal) heating elements.
These are workhorses for processes like annealing, tempering, and basic materials synthesis where extreme heat is not required.
High-Temperature Range: Up to 1600°C
To achieve temperatures beyond 1200°C, furnaces must use more advanced elements. Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are frequently used in this range.
These furnaces serve more demanding applications, including processing certain ceramics, alloys, and advanced materials that require higher thermal energy.
Ultra-High Temperature Range: Up to 1800°C
Reaching the upper limits of tube furnace technology requires the most specialized heating elements. Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the standard for this class, capable of continuous operation at very high temperatures.
These systems are essential for advanced research, high-temperature sintering of technical ceramics, crystal growth, and specialized materials testing.
Key Factors Beyond Maximum Temperature
A furnace's utility is defined by more than just its peak heat. True process control depends on how that heat is managed and in what environment it is applied.
Temperature Uniformity and Zoning
Simply reaching 1800°C is not enough; the temperature must be consistent across the sample. The heated zone is the length within the tube where the temperature is stable and uniform.
For greater control, multi-zone furnaces use multiple, independently controlled heating elements. This allows you to create a precise temperature gradient or ensure an exceptionally uniform flat zone for sensitive processes.
Atmosphere Control
Many modern processes cannot be performed in ambient air. Atmosphere control is a critical capability that works in tandem with temperature.
This is achieved with sealed end caps and gas systems that allow you to operate under a vacuum (down to 10⁻⁵ torr) or introduce specific gases like nitrogen or argon. This prevents oxidation and enables specific chemical reactions.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern tube furnaces use programmable digital controllers. This allows you to precisely manage not just the final temperature but also the rate of heating and cooling (ramping) and the duration of the hold time (soaking). This control is vital for repeatable and successful results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace requires balancing capability with practical constraints. Higher performance invariably comes with trade-offs.
Cost vs. Temperature Capability
The primary trade-off is cost. The materials required for higher temperatures—from the MoSi2 heating elements to the advanced ceramic insulation—are significantly more expensive. A 1800°C furnace is a far greater investment than a 1200°C model.
Element Lifespan and Operating Conditions
Ultra-high temperature heating elements like MoSi2 can be more sensitive to rapid thermal cycling and certain atmospheres compared to their lower-temperature counterparts. Following the manufacturer's operating guidelines is critical to maximizing their lifespan.
Configuration: Horizontal vs. Vertical
The orientation of the tube—either horizontal or vertical—does not typically dictate the maximum temperature. Instead, it is a practical choice based on your application. Horizontal furnaces are common and easy to load, while vertical furnaces can be advantageous for processes involving falling powders, avoiding sample contact with the tube wall, or specific convection patterns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Base your decision on a clear understanding of your process requirements, not just the highest number on a specification sheet.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work, annealing, or calibration: A 1200°C furnace offers the best balance of cost, durability, and capability.
- If your primary focus is processing specific alloys, glasses, or developing new materials: A 1600°C furnace provides the versatility needed for these more demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics research, sintering, or crystal growth: An 1800°C furnace is a necessary tool for achieving the extreme conditions these processes require.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace means investing in the capability that precisely matches your goal.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Heating Element | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (Kanthal) | Annealing, tempering, basic materials synthesis |
| Up to 1600°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Processing ceramics, alloys, advanced materials |
| Up to 1800°C | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | High-temperature sintering, crystal growth, research |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our advanced furnaces can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















