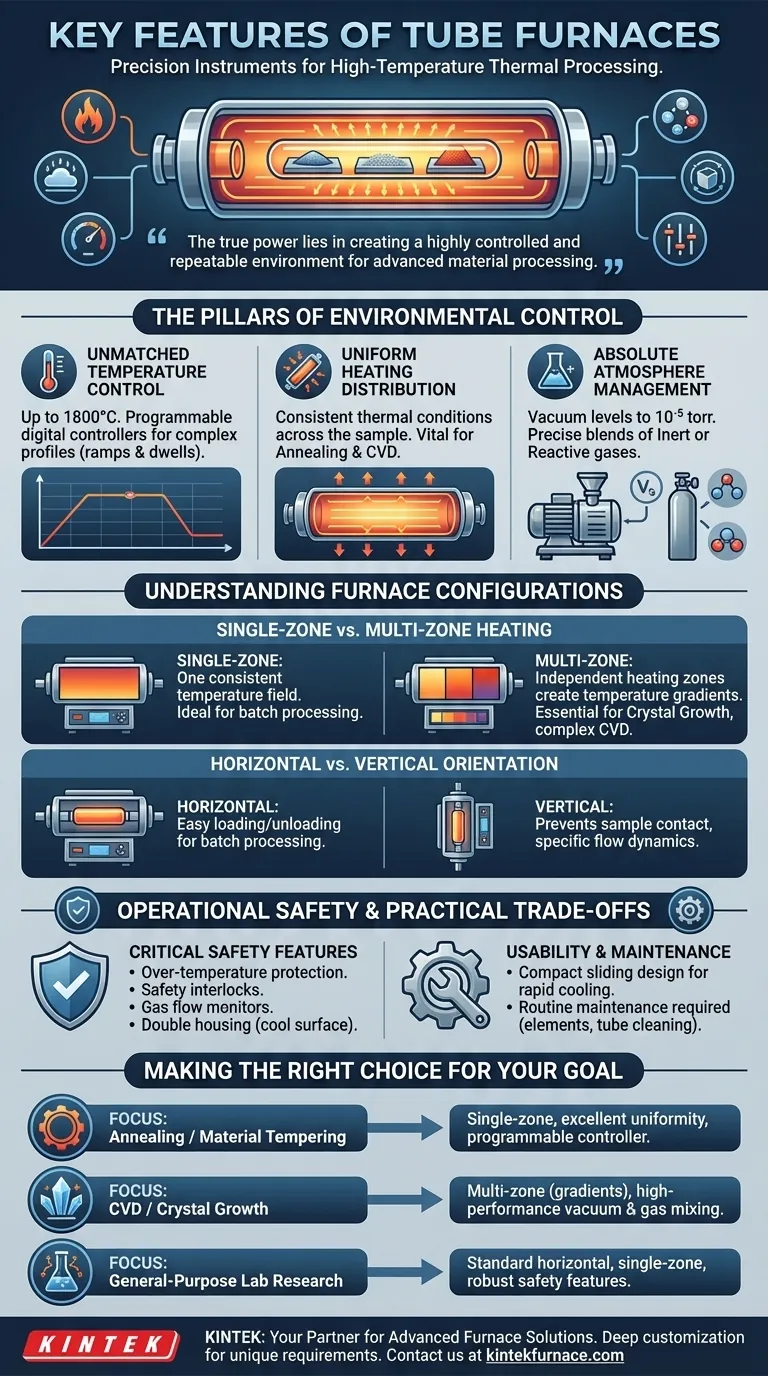
At their core, tube furnaces are precision instruments designed for high-temperature thermal processing. Their key features include the ability to reach temperatures up to 1800°C, precise single or multi-zone temperature control, and the capability to maintain a tightly controlled atmosphere, from a high-level vacuum to specific inert or reactive gases.
While their high-temperature capabilities are impressive, the true power of a tube furnace lies in its ability to create a highly controlled and repeatable environment. This precision over temperature, atmosphere, and uniformity is what enables advanced material processing and research.
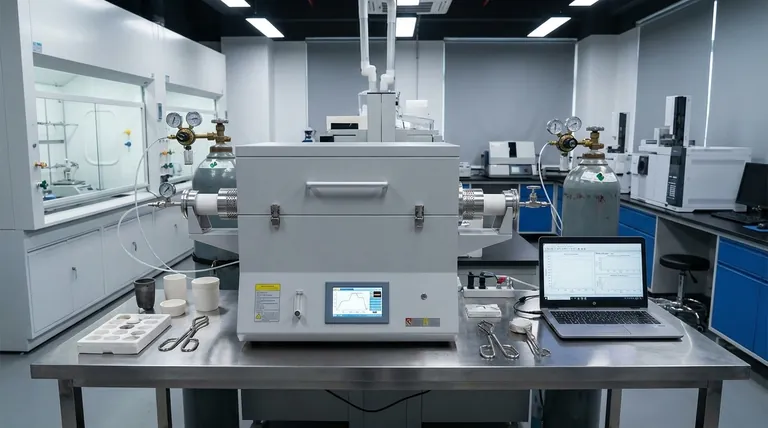

The Pillars of Environmental Control
The primary function of a tube furnace is to provide a stable, controlled environment. This is achieved through three key areas of functionality.
Unmatched Temperature Control
Tube furnaces offer exceptional control over temperature. This is not just about reaching high heat, but about maintaining it with precision.
Programmable digital controllers allow for high accuracy and the ability to execute complex temperature profiles, such as ramps and dwells, which are critical for many processes.
Uniform Heating Distribution
A key design goal is uniform heating, which ensures the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
This consistency is vital for processes like annealing, where uniform material properties are the desired outcome, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where temperature variance can ruin a synthesis.
Absolute Atmosphere Management
The sealed tube design allows for complete control over the internal atmosphere.
Using specialized end caps and vacuum flanges, these furnaces can achieve vacuum levels as low as 10⁻⁵ torr, which is necessary for removing contaminants or preventing oxidation.
They can also be integrated with gas mixing systems to introduce precise blends of inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or reactive gases, enabling specific chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Understanding the Furnace Configurations
Tube furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their physical configuration is directly tied to their intended application and how samples are handled.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Heating
A single-zone furnace is the most common type, designed to create one consistent temperature field across its length. This is ideal for most batch processing tasks.
A multi-zone furnace has several independently controlled heating zones. This allows for the creation of a specific temperature gradient along the tube, which is essential for specialized applications like certain types of crystal growth or complex CVD processes.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientation
Horizontal furnaces are the standard configuration, offering easy loading and unloading of samples for batch processing.
Vertical furnaces orient the tube upright. This design can be beneficial for preventing sample contact with the tube walls, minimizing contamination, or for processes involving specific material flow dynamics.
Durable and Lab-Friendly Construction
Most modern tube furnaces are built with a durable stainless steel housing. Many are designed with a compact, bench-top footprint, making them accessible for installation in almost any laboratory setting.
Operational Safety and Practical Trade-offs
High-temperature equipment demands a focus on safety and an understanding of its operational realities.
The Critical Role of Safety Features
To protect both the operator and the experiment, tube furnaces are equipped with multiple safety systems.
These include over-temperature protection to prevent thermal runaway, safety interlocks that shut off power if the furnace is opened, and gas flow monitors.
Many designs also feature a double housing that keeps the external surface temperature low (around 30°C) even when the interior is at 800°C or higher.
Usability and Maintenance
Features like a compact sliding design allow for rapid cooling and easier sample loading, improving workflow efficiency.
However, a tube furnace requires routine maintenance. This includes periodically inspecting heating elements, cleaning the furnace tube, checking insulation integrity, and calibrating temperature sensors to ensure continued accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal set of features depends entirely on your specific application.
- If your primary focus is annealing or material tempering: Prioritize a single-zone furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and a highly accurate programmable controller.
- If your primary focus is CVD or crystal growth: A multi-zone furnace for creating temperature gradients, combined with high-performance vacuum and gas mixing systems, is essential.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab research: A standard horizontal, single-zone furnace with robust safety features and a versatile controller offers the most flexibility.
By understanding how each feature serves a specific purpose, you can confidently select a tube furnace that perfectly aligns with your research or production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Up to 1800°C with programmable digital controllers | Enables complex thermal profiles for precise material processing |
| Uniform Heating | Consistent thermal distribution across the sample | Ensures reliable results in annealing and CVD processes |
| Atmosphere Management | Vacuum to 10⁻⁵ torr and gas mixing for inert/reactive environments | Supports specific chemical reactions and prevents contamination |
| Configurations | Single-zone, multi-zone, horizontal, vertical orientations | Adapts to various applications like crystal growth or batch processing |
| Safety Features | Over-temperature protection, interlocks, double housing | Protects operators and experiments, maintaining low external temperatures |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a tailored tube furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether for annealing, CVD, or general research. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















