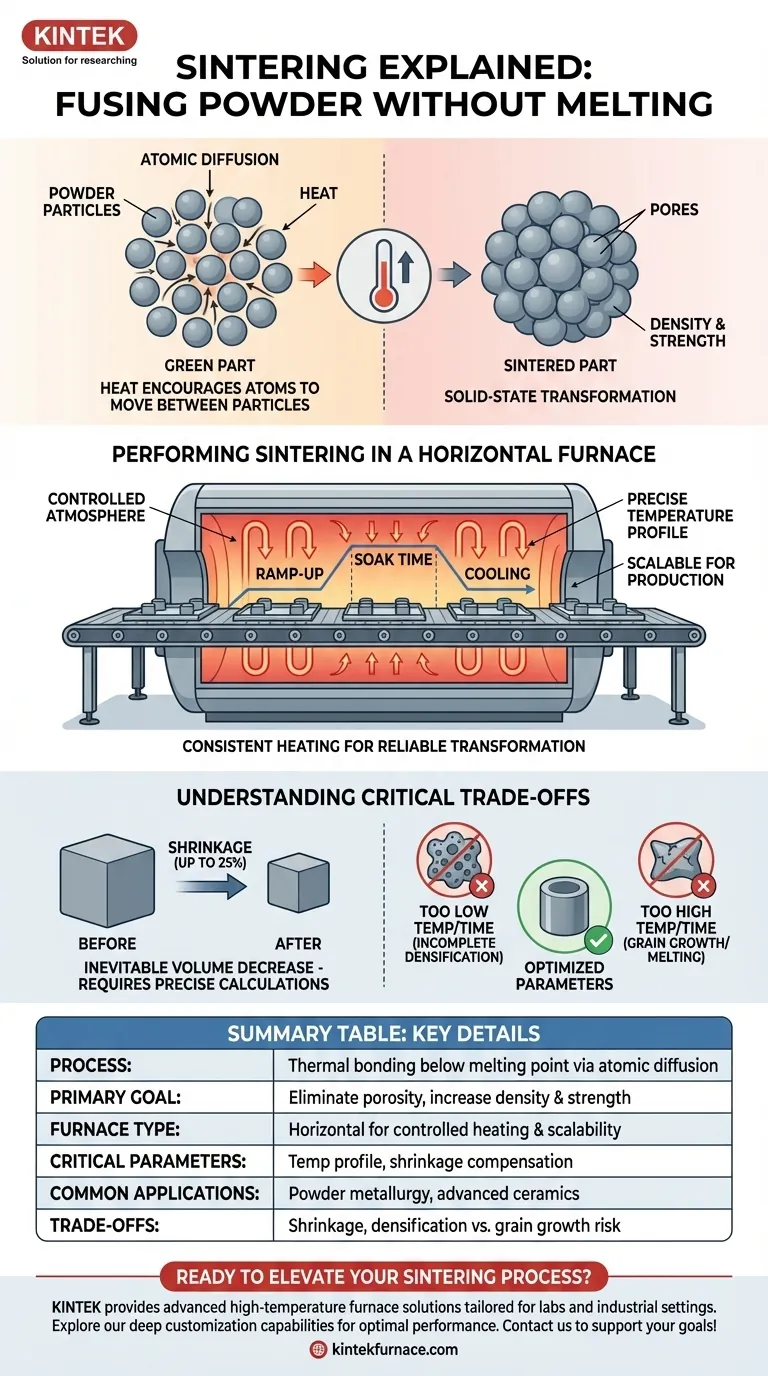
At its core, sintering is a thermal process that fuses powdered materials into a solid mass by heating them to a temperature just below their melting point. In this process, the individual particles bond together through atomic diffusion, creating a dense and strong final part without ever becoming a liquid. Horizontal furnaces are widely used for sintering because they provide the precise, controlled high-temperature environment required for this transformation to occur reliably.
The critical insight is that sintering is not about melting, but about solid-state transformation. It leverages heat to encourage atoms to move between particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic level to increase density and strength.

The Fundamental Principle: Bonding Without Melting
Sintering is a cornerstone of modern materials science, particularly in the fields of powder metallurgy and advanced ceramics. Understanding its core mechanism is key to controlling the properties of the final product.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
When a compacted powder (often called a "green" part) is heated, the atoms in the material gain energy. This energy allows them to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This movement of atoms fills the voids, or pores, between the particles, causing them to fuse together and form strong metallurgical or ceramic bonds.
The Goal: Densification and Strength
The primary objective of sintering is to eliminate the porosity present in the initial powder compact. As the pores shrink and disappear, the material becomes denser, which dramatically increases its mechanical strength, hardness, and other critical properties. This is how materials like zirconia crowns for dental use or tungsten carbide cutting tools are fabricated from powders.
Performing Sintering in a Horizontal Furnace
A horizontal furnace is an effective and common tool for executing the sintering process due to its design, which allows for consistent heating and ease of operation.
Providing a Controlled Thermal Environment
The furnace's main job is to execute a precise temperature profile. This isn't simply about heating the part; it involves a controlled ramp-up rate, a specific "soak" time at the peak sintering temperature, and a controlled cooling rate. Each stage is critical for achieving the desired final microstructure and preventing thermal shock.
The Sintering Cycle in Practice
A typical sintering cycle begins with loading the green parts into the furnace's heated zone. The temperature is then gradually increased to the target, which can be extremely high (e.g., for zirconia). The parts are held at this temperature for a predetermined duration to allow atomic diffusion to complete. Finally, they are cooled down slowly to ensure structural integrity.
Why a Horizontal Configuration?
Horizontal furnaces are favored for their practicality. Their design simplifies the loading and unloading of parts, whether for single-item batch processing or for continuous processing where parts move through the furnace on a conveyor. This makes them highly scalable for industrial production.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process requires careful control. Misunderstanding its inherent trade-offs is a common source of failure.
The Inevitability of Shrinkage
As the voids between powder particles are eliminated, the overall volume of the part must decrease. This shrinkage is a natural and significant consequence of sintering. For materials like zirconia, shrinkage can be as high as 20-25%. This must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial design of the green part to achieve the correct final dimensions.
Temperature and Time are Paramount
The success of sintering hinges on the relationship between temperature and time.
- Too low a temperature or too short a time will result in incomplete densification, leaving a weak and porous part.
- Too high a temperature or too long a time can cause undesirable grain growth, which can make the material brittle, or even partial melting, which ruins the part's shape and properties.
Sintering vs. Other Heat Treatments
While horizontal furnaces are also used for processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering, those treatments modify the crystal structure of an existing solid metal. Sintering is fundamentally different: it creates the solid part itself from a collection of discrete particles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, align your process parameters with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: You must optimize the peak temperature and hold time to be as high and long as possible without causing adverse grain growth.
- If your primary focus is controlling final dimensions: Your most critical task is to accurately model and compensate for your specific material's shrinkage rate during the initial design phase.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and scalability: A horizontal furnace is an excellent choice for consistent, repeatable batch or continuous production.
Mastering the principles of sintering transforms a simple powder into a high-performance engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal bonding of powdered materials below melting point via atomic diffusion |
| Primary Goal | Eliminate porosity to increase density, strength, and hardness |
| Furnace Type | Horizontal furnaces for controlled heating, ease of loading/unloading, and scalability |
| Critical Parameters | Temperature profile (ramp-up, soak time, cooling rate) and material-specific shrinkage |
| Common Applications | Powder metallurgy, advanced ceramics (e.g., dental crowns, cutting tools) |
| Trade-offs | Shrinkage (up to 25%), risk of incomplete densification or grain growth if parameters are off |
Ready to elevate your sintering process with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories and industrial settings. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Whether you're aiming for maximum density, dimensional control, or scalable efficiency, our expertise ensures optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your sintering goals and deliver durable, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















