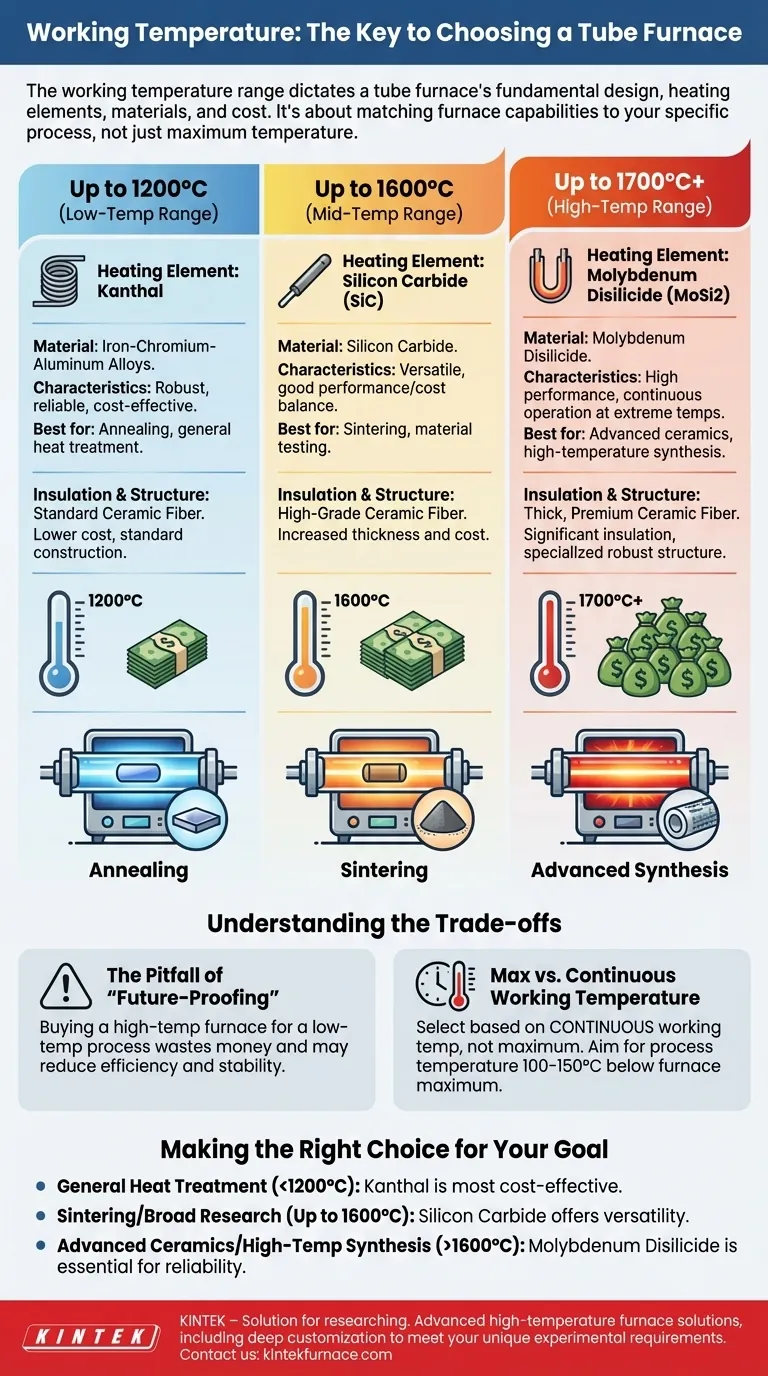
The working temperature range is the single most critical factor in choosing a tube furnace because it dictates the instrument's fundamental design, the materials used for its heating elements, and its overall cost. Selecting a furnace is not about finding the highest possible temperature, but about matching the furnace’s capabilities to the specific thermal process you need to perform.
Choosing a tube furnace requires you to look beyond the maximum temperature rating. The core task is to align your specific application's required continuous working temperature with the correct class of heating element and furnace construction to ensure accuracy, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.

How Temperature Governs Furnace Design
The required operating temperature directly determines the materials and engineering of the furnace's most critical components. This relationship is not linear; as temperature requirements increase, the complexity and cost of the furnace grow exponentially.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The heart of any furnace is its heating element, which converts electrical energy into heat. Different materials perform optimally within specific temperature bands.
-
Up to 1200°C (Kanthal): For lower-temperature applications like annealing and general heat treatment, furnaces typically use elements made from iron-chromium-aluminum alloys, commonly known as Kanthal. These are robust, reliable, and highly cost-effective.
-
Up to 1600°C (Silicon Carbide): For mid-to-high range processes like sintering and many material science tests, silicon carbide (SiC) elements are the standard. They offer excellent performance and a good balance between temperature capability and cost.
-
Up to 1700°C+ (Molybdenum Disilicide): For the most demanding applications, such as developing advanced ceramics or high-stakes research, furnaces require molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements. These can sustain extremely high temperatures for continuous operation but come at a significant premium.
Insulation and Structural Integrity
Higher operating temperatures demand more sophisticated thermal insulation. A 1700°C furnace requires thicker, higher-grade ceramic fiber insulation than a 1200°C model to maintain temperature stability, ensure energy efficiency, and keep the outer casing safe to touch.
This increased insulation and the need for more robust structural components to handle thermal stress are major drivers of furnace size, weight, and cost.
The Direct Impact on Price
The choice of heating elements and the required level of insulation create distinct price tiers. A furnace rated for 1700°C can be several times more expensive than one rated for 1200°C, even if their tube dimensions are identical.
Matching Temperature Range to Your Application
Your specific process dictates the temperature you need. Understanding this connection prevents you from over-investing in unnecessary capability or, worse, choosing a furnace that cannot perform your task.
Annealing and Standard Heat Treatment
These processes typically occur at lower temperatures, well within the capabilities of furnaces equipped with Kanthal elements. This makes them the most economical choice for these common applications.
Sintering and Material Testing
Sintering powders into a solid mass or conducting many standard material tests requires higher temperatures. A furnace with SiC elements provides the versatility needed for this broad category of laboratory work.
Advanced Synthesis and High-Performance Ceramics
Research and production involving specialized materials often push the boundaries of thermal processing. These applications mandate the use of a furnace with MoSi2 elements to reliably achieve and maintain the necessary temperatures above 1600°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right furnace involves being aware of common pitfalls and understanding the difference between specifications and real-world performance.
The Pitfall of "Future-Proofing"
Buying a 1700°C furnace for a process that only requires 1100°C is often a mistake. High-temperature furnaces can be less efficient and may have poorer temperature stability when operated at the low end of their range. You pay a premium for a capability you don't use.
Maximum vs. Continuous Working Temperature
Always select a furnace based on its continuous working temperature, not its absolute maximum rating. A furnace's maximum temperature is often a peak it can only sustain for short periods. For reliable, repeatable results, your process temperature should be at least 100-150°C below the furnace's stated maximum.
Uniformity and Zone Control
Achieving a uniform temperature across the entire sample is critical for consistent results. As operating temperatures increase, so do thermal gradients. For high-precision work, consider a multi-zone furnace, which uses multiple independent heating zones and controllers to ensure a highly uniform hot zone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on the sustained temperature your process demands.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or annealing (below 1200°C): A furnace with Kanthal heating elements offers the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is sintering common materials or broad research (up to 1600°C): A furnace with silicon carbide (SiC) elements provides a versatile balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or high-temperature synthesis (above 1600°C): You must invest in a furnace with molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements for reliable, continuous operation.
By aligning your required working temperature with the furnace's core material technology, you ensure both technical success and fiscal responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Recommended Heating Element | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Kanthal | Annealing, general heat treatment | Cost-effective, reliable |
| Up to 1600°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Sintering, material testing | Versatile, balanced performance |
| Above 1600°C | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Advanced ceramics, high-temperature synthesis | High performance, premium cost |
Ready to optimize your lab with the perfect tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes with reliable, cost-effective equipment tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















