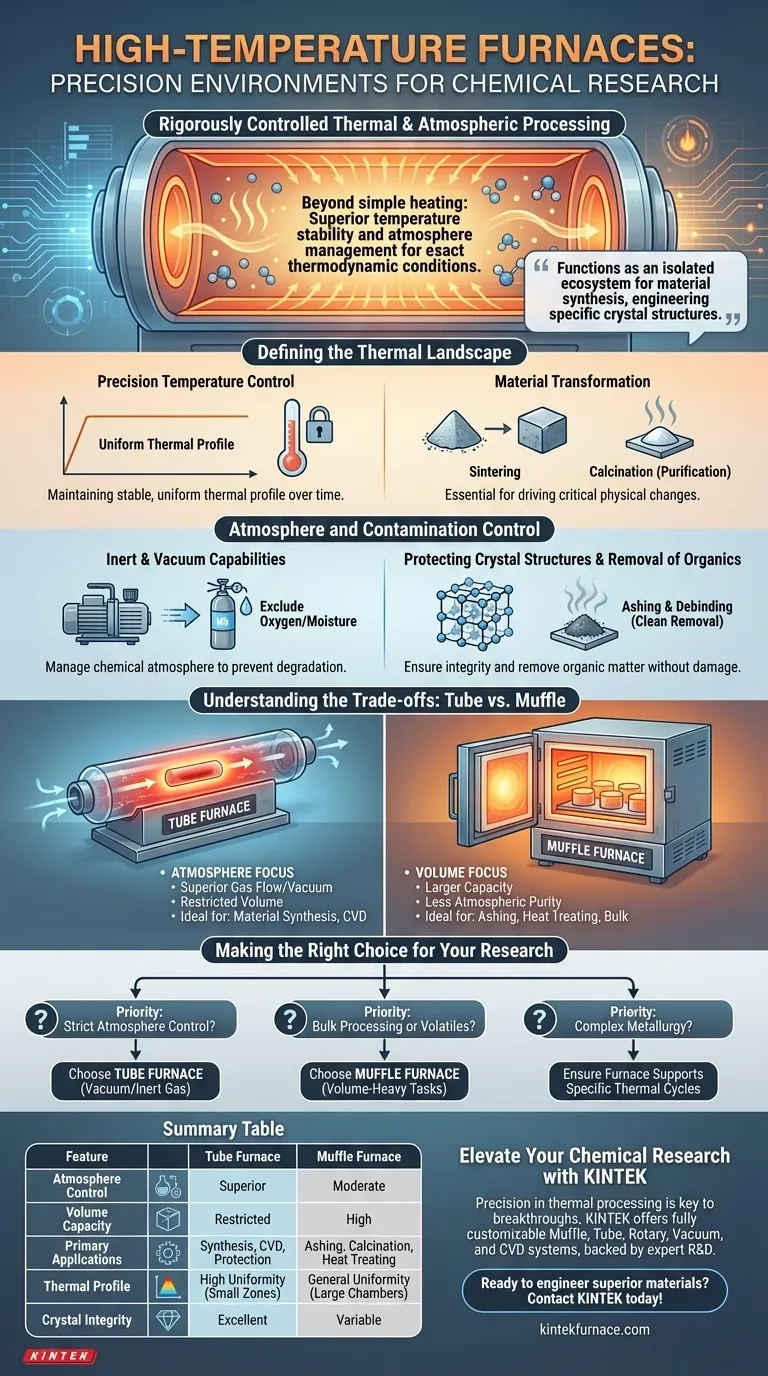
High-temperature tube and muffle furnaces provide a rigorously controlled thermal and atmospheric environment designed for precision chemical processing. These environments go beyond simple heating; they offer superior temperature stability and atmosphere management capabilities—such as vacuum sealing or inert gas protection—to ensure reactions occur under exact thermodynamic conditions.
These furnaces function as isolated ecosystems for material synthesis. By strictly controlling both heat and the surrounding atmosphere, they enable researchers to engineer materials with specific crystal structures and predictable physicochemical properties, free from external contamination.

Defining the Thermal Landscape
Precision Temperature Control
The defining feature of these furnaces is superior temperature control precision. This is not merely about reaching high temperatures; it is about maintaining a stable, uniform thermal profile over time.
Thermodynamic Reliability
Chemical research often requires specific thermodynamic conditions to drive reactions correctly. Whether for solid-phase material synthesis or catalyst activation, the environment ensures the energy input is consistent, allowing for reproducible results.
Material Transformation
This precise thermal environment drives critical physical changes. It is essential for processes like sintering ceramic powders to form solid objects or calcination, where volatile components are driven off to leave a purified base material.
Atmosphere and Contamination Control
Inert and Vacuum Capabilities
A major advantage of these furnaces is the ability to manage the chemical atmosphere. Through vacuum or inert gas protection, researchers can exclude oxygen or moisture that would otherwise degrade the sample or cause unwanted side reactions.
Protecting Crystal Structures
By controlling the gas environment, you ensure the integrity of the final material. This protection is vital for obtaining specific crystal structures that define the material's physicochemical properties.
Removal of Organics
The environment is also engineered for purification. Processes like ashing and debinding rely on this controlled heat to cleanly remove organic matter or binders from metal injection molding processes without damaging the inorganic substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Volume vs. Atmosphere Control
While both furnace types provide heat, they prioritize different environmental factors. Muffle furnaces typically offer larger internal volumes, making them ideal for bulk processes like heat treating metals or annealing.
Atmosphere Limitations
However, standard muffle furnaces are often less efficient at maintaining strict atmospheric purity compared to tube furnaces.
The Tube Furnace Advantage
Tube furnaces generally provide a more restricted volume but offer superior control over gas flow and vacuum conditions. If your research demands a constantly flowing inert gas over the sample, the tube geometry is usually the superior choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To select the correct processing environment, you must prioritize your experimental variables.
- If your primary focus is strict atmosphere control (e.g., preventing oxidation): Prioritize a tube furnace environment that supports vacuum or inert gas flow to protect crystal lattice formation.
- If your primary focus is bulk processing or removing volatiles: Utilize a muffle furnace environment, which is optimized for volume-heavy tasks like ashing, calcination, or general heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is complex metallurgy: Ensure the furnace supports the specific thermal ramp-up and cool-down cycles required for sintering or tempering.
Ultimately, the correct furnace environment transforms a volatile chemical reaction into a controlled, repeatable scientific process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace Environment | Muffle Furnace Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Superior (Vacuum, Inert Gas Flow) | Moderate (Limited Gas Control) |
| Volume Capacity | Restricted (Smaller Samples) | High (Bulk Processing) |
| Primary Applications | Material Synthesis, CVD, Protection | Ashing, Calcination, Heat Treating |
| Thermal Profile | High Uniformity in Small Zones | General Uniformity in Large Chambers |
| Crystal Integrity | Excellent Protection | Variable |
Elevate Your Chemical Research with KINTEK
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between a failed experiment and a breakthrough. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs, ensuring perfect thermodynamic conditions and atmosphere management for your material synthesis.
Ready to engineer superior materials? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yongxia Wang, Jinli Qiao. Atomically Dispersed Fe Anchored on Nitrogen‐Doped Graphene as Advanced Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Electrode in Rechargeable Zn–Air Battery. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202500731
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a benchtop tube furnace ensure the quality of silicon nitride green bodies? Master Debinding Precision
- What role do tubular furnaces play in heat treatment processes? Precision Control for Material Properties
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- What materials can be melted in horizontal tube furnaces? Unlock precise high-temperature melting for metals, ceramics, and more
- What are some examples of research applications for lab tubular furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Experiments
- How does the melt-diffusion process for Te1S7 use tube furnaces? Achieve High-Precision Molecular Confinement
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Heat and Atmosphere Control
- What are the typical applications for tube furnaces? Master Precise Thermal Processing



















