In principle, a horizontal tube furnace can melt a wide range of materials, including various metals like gold and copper, alloys such as steel, and non-metals like glass and certain ceramics. However, the true melting capability is not defined by the furnace's heating elements, but by the maximum temperature and chemical inertness of the process tube that contains the material.
The critical question is not simply what a tube furnace can melt, but what your specific process tube can safely handle. A material's melting point and chemical reactivity must be compatible with the tube—typically made of quartz or alumina—to achieve a successful melt without causing contamination or equipment failure.

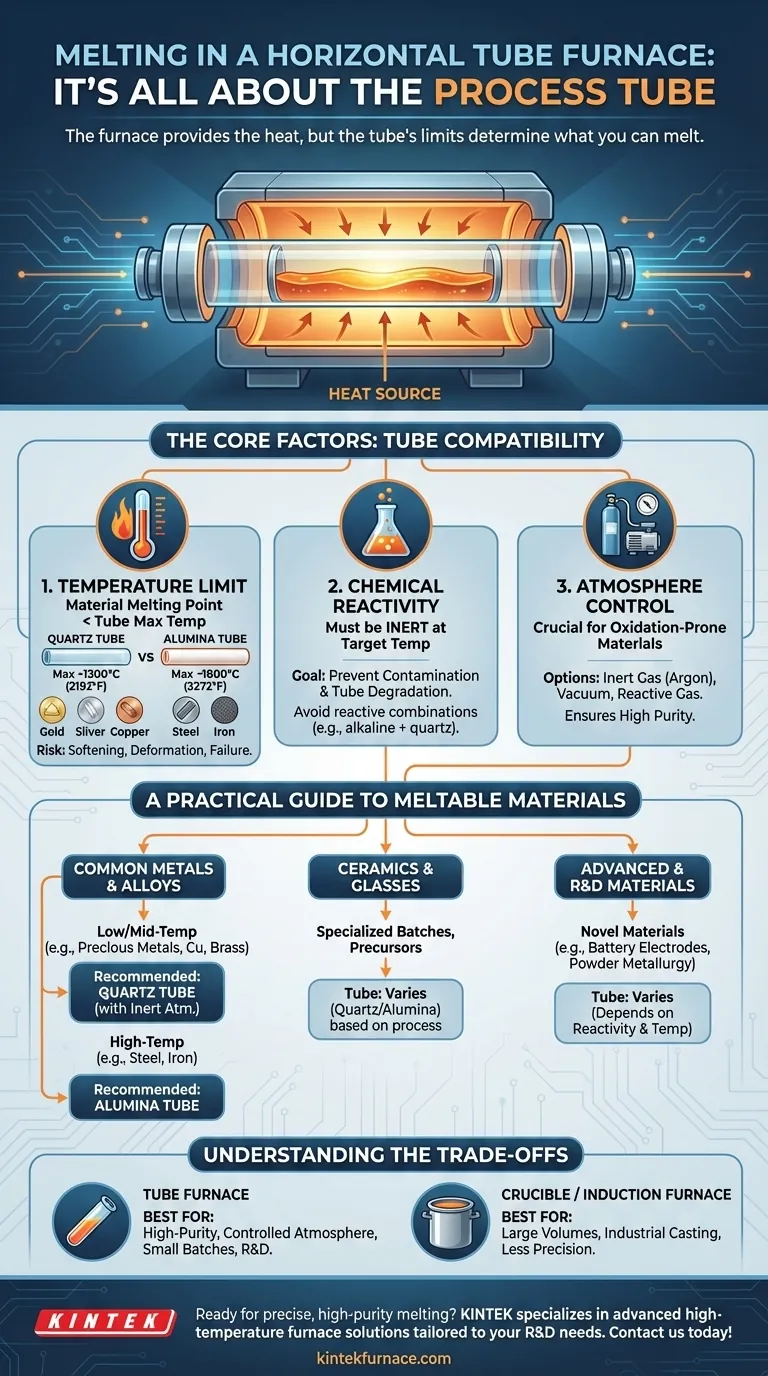
The Core Factors: It's All About the Tube
A horizontal tube furnace is a system, and its weakest link defines its limits. The process tube is the component in direct contact with the extreme heat and the material itself, making its properties the primary consideration.
Material Melting Point vs. Tube Temperature Limit
The melting point of your material must be comfortably below the maximum continuous operating temperature of the process tube.
Using a tube too close to its thermal limit risks softening, deformation, or catastrophic failure. Common tube materials have distinct temperature ceilings:
- Fused Quartz Tubes: Generally used for processes up to 1100-1200°C (2012-2192°F). They offer excellent thermal shock resistance but are not suitable for very high-temperature metals.
- Alumina (Corundum) Tubes: These high-purity ceramic tubes can withstand much higher temperatures, often up to 1700-1800°C (3092-3272°F), making them necessary for melting higher-temperature metals and certain ceramics.
Chemical Reactivity and Contamination
At high temperatures, materials become much more chemically reactive. A molten sample can attack and degrade the process tube, ruining both the experiment and the equipment.
You must ensure the tube material is chemically inert to your sample at the target temperature. For example, highly alkaline materials can etch a quartz tube, so an alumina tube might be a better choice. The goal is to prevent the tube from contaminating your melt and to keep the melt from destroying the tube.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
One of the greatest strengths of a tube furnace is its ability to control the atmosphere around the sample. The sealed tube can be purged and filled with an inert gas (like argon), a reactive gas, or evacuated to create a vacuum.
This is critical for melting materials that readily oxidize in air, such as copper, aluminum, or titanium alloys. This atmospheric control ensures high purity in the final melted material, a feature not easily achieved in open-air crucible furnaces.
A Practical Guide to Meltable Materials
With the tube's limitations in mind, we can categorize the materials that are commonly melted in horizontal tube furnaces.
Common Metals and Alloys
Low to mid-temperature metals are excellent candidates.
- Precious Metals: Gold (1064°C) and silver (962°C) are easily melted in quartz tubes.
- Copper and Brass: With melting points around 1084°C and ~930°C respectively, these are also well-suited for quartz tube systems, especially when an inert atmosphere is needed to prevent oxidation.
- Steel and Iron: Melting steel (around 1450°C) requires a high-temperature alumina tube and careful atmosphere control.
Ceramics and Glasses
Tube furnaces are not typically used for bulk glass production but are ideal for synthesizing or melting small, specialized batches of glass and ceramic precursors. The precise temperature ramps and controlled atmosphere are perfect for developing materials with specific properties.
Advanced and Research Materials
This is where tube furnaces truly excel. They are staples in R&D for processing novel materials in small quantities. Examples include:
- Battery electrode materials
- Silicon-based anode materials
- Specialty powder metallurgy components
Understanding the Trade-offs
A tube furnace is a specialized tool. It is not always the right choice, especially when compared to industrial-scale melting equipment.
The Limitation: Batch Size and Geometry
The most obvious limitation is volume. You can only melt a quantity of material that fits within the diameter of the process tube, which is typically quite small. This makes tube furnaces impractical for applications requiring large volumes of molten material, such as casting.
Why Not Use a Crucible Furnace?
Crucible furnaces hold the material in an open or loosely covered pot (the crucible) and are designed for melting larger batches of material. They are the workhorses for foundries and jewelry making but offer far less precision and atmospheric control than a tube furnace.
What About an Induction Furnace?
Induction furnaces are extremely fast and efficient for melting conductive metals. They use electromagnetic induction to heat the material directly, without heating the chamber walls. While incredibly powerful for industrial metal melting, they lack the fine atmospheric control and temperature uniformity for delicate research applications where a tube furnace shines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on your specific material and objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melting of small samples in a controlled atmosphere: A horizontal tube furnace is the ideal tool, provided you match the process tube to your material's properties.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of metal for casting: A crucible or induction furnace is a more practical and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel materials: The precise temperature and atmosphere control of a tube furnace makes it an indispensable instrument.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between your material, the process tube, and the atmosphere is the key to successful melting.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Typical Melting Points | Recommended Tube Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precious Metals | Gold, Silver | ~960-1064°C | Quartz |
| Copper Alloys | Copper, Brass | ~930-1084°C | Quartz |
| Steel and Iron | Steel | ~1450°C | Alumina |
| Ceramics/Glasses | Glass precursors | Varies | Alumina or Quartz |
| Advanced Materials | Battery electrodes | Varies | Depends on reactivity |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity melting for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can design furnaces that precisely meet your experimental requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your melting processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















