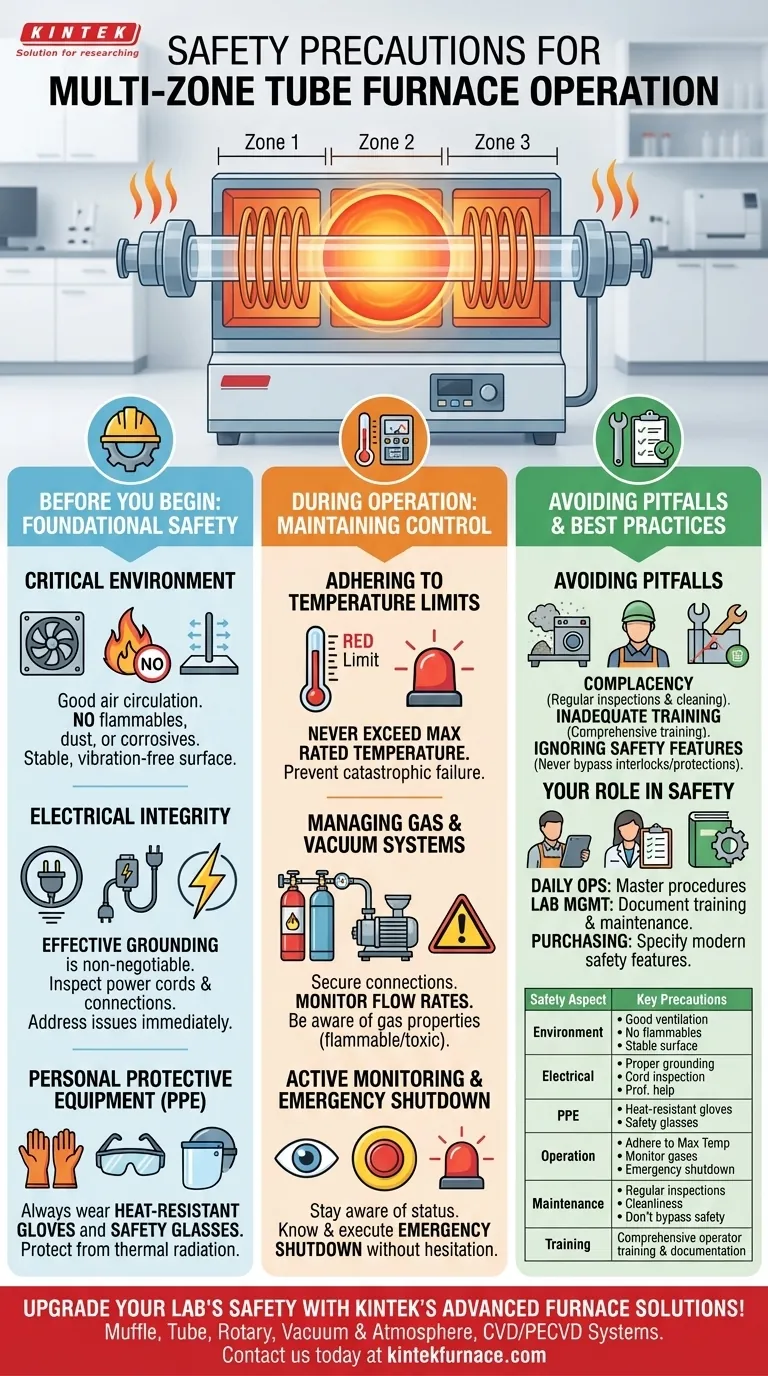
Operating a multi-zone tube furnace safely requires a systematic approach that addresses electrical, thermal, and atmospheric hazards at every stage. Key precautions include ensuring the furnace is properly grounded, maintaining a well-ventilated environment clear of flammables, always wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and strictly adhering to the manufacturer's operational limits, especially maximum temperature.
True furnace safety is not a checklist but a continuous discipline. It requires understanding that the primary risks—extreme heat, high voltage, and controlled atmospheres—must be managed proactively through proper environmental setup, diligent operational monitoring, and consistent maintenance.

Before You Begin: Foundational Safety
Proper preparation is the most critical step in mitigating furnace-related risks. Before powering on the equipment, the environment and the operator must be ready.
The Critical Role of the Environment
A furnace's location directly impacts its safety and performance. The equipment must be placed on a stable, vibration-free surface.
Ensure the area has good air circulation to dissipate heat and prevent the buildup of any potential process gases. Keep the space completely free of flammable or explosive materials, dust, and corrosive gases.
Ensuring Electrical Integrity
High-wattage heating elements pose a significant electrical risk. Effective grounding is the most critical defense against electric shock and is non-negotiable.
Before use, visually inspect the power supply cord and connections for any signs of wear or damage. Any suspected electrical issues must be addressed by a qualified professional before operation.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The extreme temperatures of a tube furnace demand respect. Always wear heat-resistant gloves when handling materials near the furnace opening and safety glasses to protect from thermal radiation and potential projectiles.
During Operation: Maintaining Control
Vigilance during the heating and insulation stages is essential for preventing equipment failure and ensuring a successful process.
Adhering to Temperature Limits
Never program the furnace to exceed its maximum rated temperature. Pushing the equipment beyond its design limits can cause catastrophic failure of the heating elements and insulation, creating a severe safety hazard.
Managing Gas and Vacuum Systems
If using process gases, ensure all connections are secure and monitor flow rates to prevent dangerous leaks. Be aware of the properties of the gases you are using, especially if they are flammable or toxic.
The Importance of Active Monitoring
Stay aware of the furnace's status throughout its operation. Familiarize yourself with the machine's normal sounds and indicators.
Crucially, every operator must know the emergency shutdown procedure and be able to execute it without hesitation.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Even with the best equipment, human error and neglect are the most common sources of incidents. Understanding these pitfalls is key to avoiding them.
Complacency in Maintenance
A furnace is not a "set and forget" appliance. Regular inspection of heating elements, power circuits, and gas lines is vital.
Allowing dust and debris to accumulate on or around the unit can impede ventilation and create a fire hazard. Keep the equipment and the surrounding area clean.
Inadequate Operator Training
No one should operate a furnace without being properly trained. This training must include not only standard operation but also a thorough understanding of the specific safety features and emergency protocols for that model.
Ignoring Built-in Safety Features
Modern furnaces often include over-temperature and over-pressure protection. These are critical safety interlocks, not inconveniences. Never attempt to bypass or disable them. If a safety feature triggers, it is a signal that an unsafe condition has occurred that must be investigated.
How to Apply This to Your Role
Your specific responsibilities dictate where your safety focus should be concentrated.
- If your primary focus is daily operation: Prioritize mastering the specific startup, shutdown, and emergency procedures for your machine.
- If your primary focus is lab management: Ensure comprehensive operator training is documented and that a regular maintenance and inspection schedule is strictly followed.
- If your primary focus is purchasing new equipment: Specify furnaces with modern, certified safety features like over-temperature protection, interlocks, and integrated leak detection.
A systematic and vigilant approach transforms this powerful tool from a potential hazard into a reliable asset for your work.
Summary Table:
| Safety Aspect | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Environment | Ensure good ventilation, keep area free of flammables, stable surface |
| Electrical | Proper grounding, inspect cords, address issues with professionals |
| PPE | Wear heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses |
| Operation | Adhere to max temperature, monitor gases, know emergency shutdown |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections, keep clean, avoid bypassing safety features |
| Training | Provide comprehensive operator training and documentation |
Upgrade your lab's safety and performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures they meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Don't compromise on safety—contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















