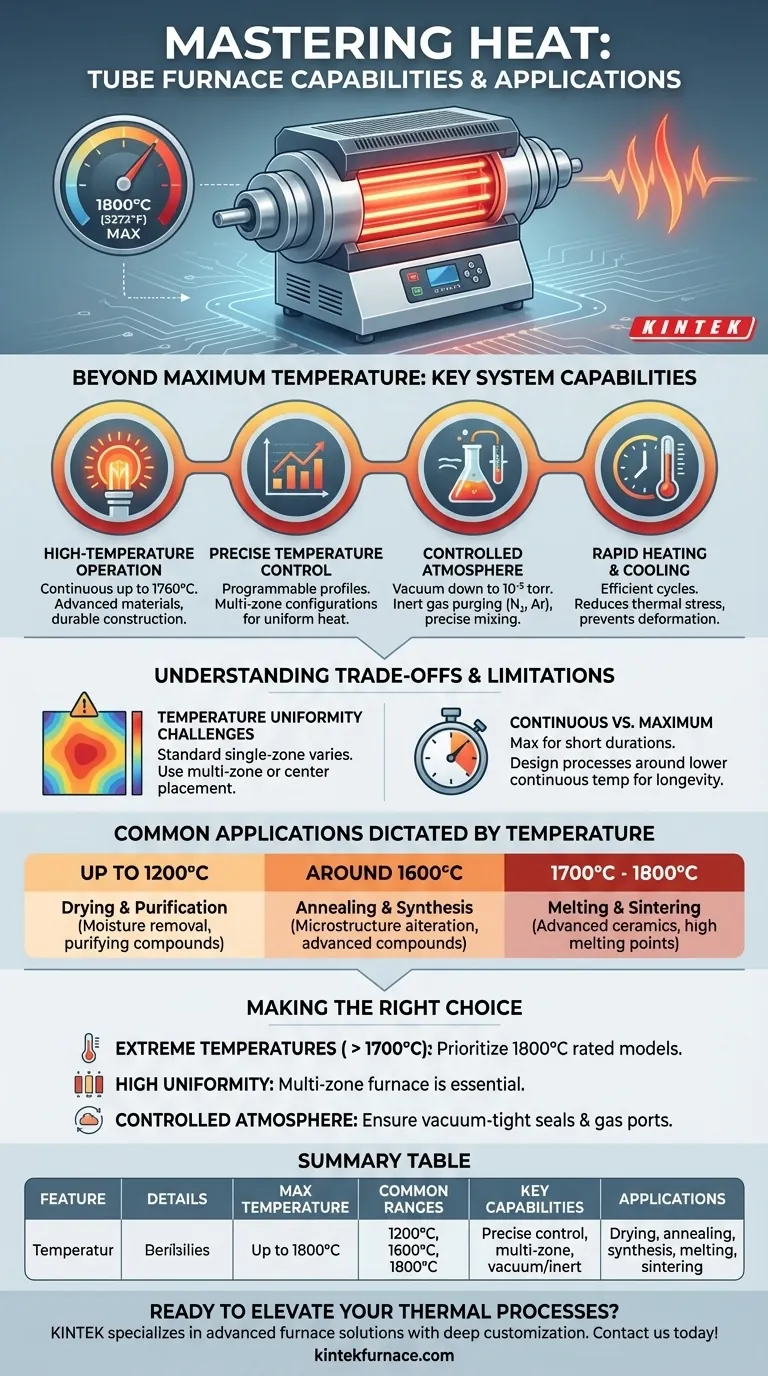
In short, modern tube furnaces can achieve operating temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F), with some specialized models capable of even higher thermal conditions. These furnaces are typically categorized by their maximum temperature capabilities, most commonly falling into ranges of 1200°C, 1600°C, and 1800°C, making them suitable for a wide array of advanced material processing and research applications.
The maximum temperature of a tube furnace is only one part of the equation. True process control comes from a combination of high-temperature capability, precise temperature uniformity, and the ability to manage the atmospheric environment within the tube.
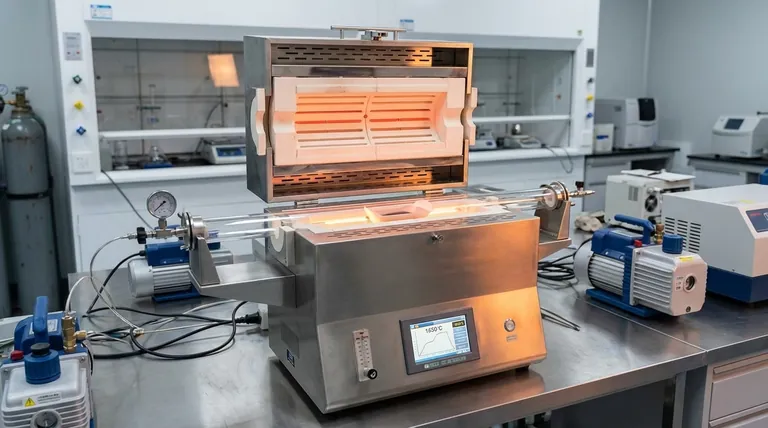

Beyond Maximum Temperature: Key System Capabilities
A tube furnace is more than a simple heater; it's a precision instrument. Understanding its core features is essential to leveraging its full potential for your specific thermal process.
High-Temperature Operation
The primary feature of a tube furnace is its ability to reach extreme temperatures. Most models are designed for continuous operation at temperatures just below their absolute maximum, such as a continuous temperature of 1760°C for a furnace with an 1800°C peak.
This capability is enabled by durable construction and advanced, heat-resistant materials for the heating elements and insulation.
Precise Temperature Control
Reaching a high temperature is not enough; it must be stable and uniform. Tube furnaces utilize fully programmable control panels that allow for precise management of heating rates, dwell times, and cooling profiles.
To ensure uniform heat distribution along the length of a sample, many furnaces are available in multi-zone configurations. Each zone has its own thermocouple and controller, allowing you to create a highly consistent temperature profile or even a specific thermal gradient.
Controlled Atmosphere Environments
Many advanced processes cannot be performed in ambient air. Tube furnaces excel at providing controlled atmospheres.
With the proper end caps and seals, these systems can maintain a high-quality vacuum, often down to 10⁻⁵ torr. They can also be purged with inert gases like nitrogen or argon or used with precise gas mixing systems to create a specific reactive environment.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
Process efficiency is critical. Modern tube furnaces often feature rapid heating rates to reach the target temperature quickly.
Equally important are fast cooling capabilities, which can be crucial for reducing thermal stress and preventing unwanted phase changes or deformation in the material as it cools.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, tube furnaces have operational considerations that must be understood to ensure successful and repeatable results.
Temperature Uniformity Challenges
In a standard single-zone horizontal furnace, you may observe slight temperature variations along the length of the processing tube. The ends will naturally be cooler than the absolute center.
This is a known physical constraint. It is mitigated by either placing the sample directly in the center of the "hot zone" or, for more demanding applications, by using a multi-zone furnace to actively compensate for heat loss.
Continuous vs. Maximum Temperature
It is critical to distinguish between the maximum temperature and the continuous operating temperature. The maximum temperature is a peak rating that can be reached for short durations.
For longevity of the heating elements and furnace components, processes should be designed around the continuous operating temperature, which is typically slightly lower than the maximum.
Common Applications Dictated by Temperature
The required temperature directly informs the furnace's application. Different thermal processes have vastly different requirements.
- Drying and Purification: Lower-temperature processes (up to 1200°C) are often sufficient for removing moisture or purifying certain organic and inorganic compounds.
- Annealing and Synthesis: Altering the microstructure of metals (annealing) or synthesizing advanced compounds often requires mid-range temperatures (around 1600°C).
- Melting and Sintering: Processing advanced ceramics or melting materials with high melting points necessitates furnaces capable of reaching 1700°C to 1800°C.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct equipment, you must match the furnace's full feature set to your primary experimental or production goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (>1700°C): Prioritize a furnace explicitly rated for 1800°C operation, which will include specialized heating elements and robust insulation.
- If your primary focus is high temperature uniformity: A multi-zone furnace is non-negotiable, as it is the only way to ensure a consistent thermal profile across a longer sample.
- If your primary focus is processing in a controlled atmosphere: Ensure the model you choose supports vacuum-tight end caps and has ports for gas inlet/outlet and vacuum pumps.
Ultimately, choosing the right tube furnace means looking beyond the maximum temperature and selecting a complete system that provides the control your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) |
| Common Ranges | 1200°C, 1600°C, 1800°C |
| Key Capabilities | Precise control, multi-zone uniformity, vacuum/inert atmospheres |
| Applications | Drying, annealing, synthesis, melting, sintering |
Ready to elevate your thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring precise temperature control, uniformity, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















