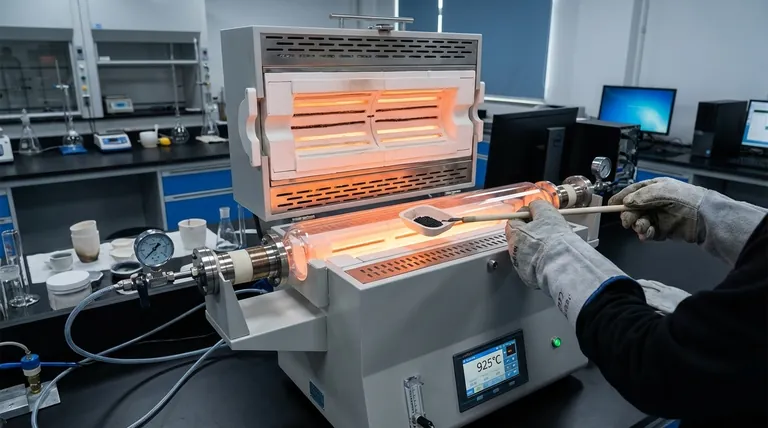
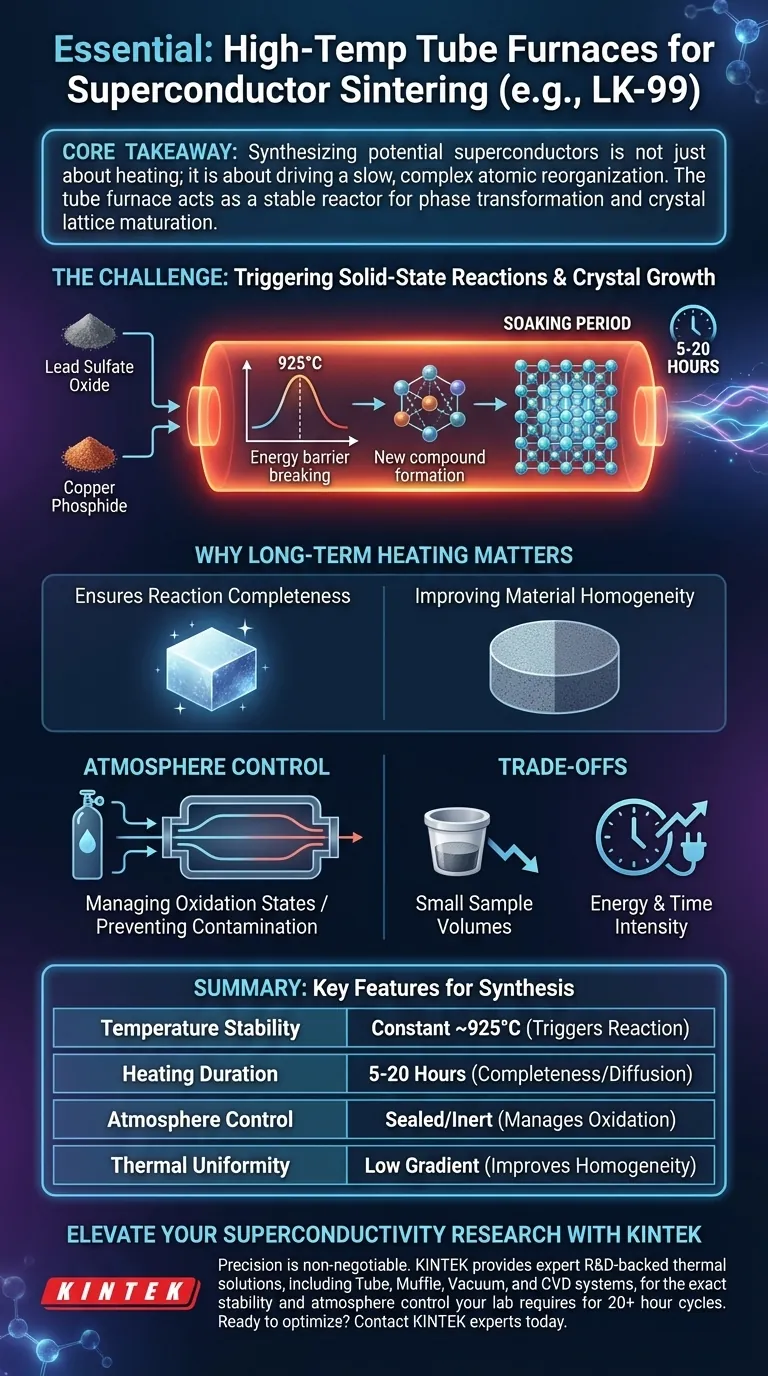
A high-temperature tube furnace is essential because it provides the precise, sustained thermal environment—specifically around 925°C—necessary to induce solid-state chemical reactions between complex precursors. This equipment maintains a stable temperature profile for extended periods (5 to 20 hours), ensuring that the reaction between components like lead sulfate oxide and copper phosphide proceeds to completion.
Core Takeaway Synthesizing potential superconductors like LK-99 is not just about heating materials; it is about driving a slow, complex atomic reorganization. The tube furnace acts as a stable reactor that supplies the exact activation energy needed for phase transformation while allowing sufficient time for crystal lattice structures to mature and stabilize.

The Critical Role of Thermal Precision
Triggering Solid-State Reactions
In the synthesis of materials like LK-99, the precursor components—specifically lead sulfate oxide and copper phosphide—are stable solids at room temperature.
To force these materials to interact and recombine, you must overcome a significant energy barrier.
The tube furnace provides the requisite high-thermal environment (approximately 925°C) to break existing chemical bonds and drive the formation of new compounds.
Facilitating Crystal Growth
Achieving the correct chemical formula is only half the battle; the material must also achieve a specific geometric arrangement of atoms.
This structural alignment, or crystal growth, does not happen instantly.
The furnace allows for a "soaking" period, maintaining the target temperature to allow crystals to grow and microscopic structures to align properly.
Why "Long-Term" Heating Matters
Ensuring Reaction Completeness
The synthesis process described involves a timeframe ranging from 5 to 20 hours.
If the heating cycle is too short, the precursors may not fully react, leaving impurities in the final sample.
Continuous, long-term heating ensures that the diffusion of atoms between the solid components is thorough and uniform.
Improving Material Homogeneity
Superconductivity is often a bulk property that requires the entire sample to be uniform.
Fluctuations in temperature or interruptions in heating can lead to inconsistencies in the material's microstructure.
A tube furnace is designed to minimize thermal gradients, ensuring the core of the sample experiences the same conditions as the surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Throughput Limitations
While tube furnaces offer exceptional control, they are generally limited by small sample volumes.
The physical geometry of the tube restricts the amount of material that can be processed at one time, making this method ideal for research but challenging for industrial-scale mass production.
Energy and Time Intensity
The requirement for long-term sintering at temperatures near 1000°C demands significant energy consumption.
Furthermore, the 5 to 20-hour cycle restricts the speed of iteration; researchers must wait a full day to test a single hypothesis or recipe adjustment.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
Managing Oxidation States
While the primary focus for LK-99 is thermal input, tube furnaces are also selected for their ability to control the gaseous environment.
For many superconductors, such as YBCO, the oxygen content is the critical variable that defines performance.
Preventing Contamination
A tube furnace allows researchers to seal the reaction chamber or introduce specific gas flows.
This capability is vital for optimizing oxygen stoichiometry or preventing unwanted oxidation from ambient air during the long sintering and annealing stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is synthesizing LK-99 types: Prioritize a furnace capable of maintaining 925°C with high stability over 20-hour cycles to drive the reaction between lead sulfate oxide and copper phosphide.
- If your primary focus is optimizing oxide superconductors (like YBCO): Ensure your furnace features precise gas flow controls to regulate oxygen stoichiometry during annealing.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the fundamental vessel that allows precise thermodynamic theory to be translated into physical reality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for LK-99/Superconductors | Purpose in Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | Constant ~925°C | Triggers solid-state reaction between precursors |
| Heating Duration | 5 to 20 Hours | Ensures reaction completeness and atom diffusion |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed or Gas-Inert | Manages oxidation states and prevents contamination |
| Thermal Uniformity | Low Gradient | Improves material homogeneity and crystal alignment |
Elevate Your Superconductivity Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing complex materials like LK-99. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our high-temperature Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems are engineered to deliver the exact thermal stability and atmosphere control your lab requires. Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable furnace for unique sintering protocols, we deliver the reliability needed for 20-hour cycles and beyond.
Ready to optimize your material synthesis? Contact KINTEK experts today and let us build the perfect furnace for your breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Yong‐Jihn Kim. Superconductor Exclusion Principle for Identifying a Room Temperature Ambient Pressure Superconductor. DOI: 10.33425/2690-8077.1209
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum tube furnace function in Ti6Al4V post-processing? Optimize Additive Manufacturing Outcomes
- What are common applications of Tube Furnaces? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
- What are the specific requirements for quartz tubes used in fixed-bed reactors? Optimize Your CeAlOx/Ni-Foam Performance
- Why is a mixture of hydrogen and argon gas used during the annealing phase in a high-temperature tube furnace?
- What role does a vertical tube furnace play in oily iron scale simulation? Master Blast Furnace Component Distribution
- How is a vertical alumina tube resistance furnace applied in the hydrogen reduction of bauxite residue particles?
- How does a High Temperature Tube Furnace maintain the desired temperature? Discover Precision Control for Your Lab
- How does a benchtop fixed-bed quartz reactor simulate industrial conditions? Evaluate Pt-Ni Catalyst Stability



















