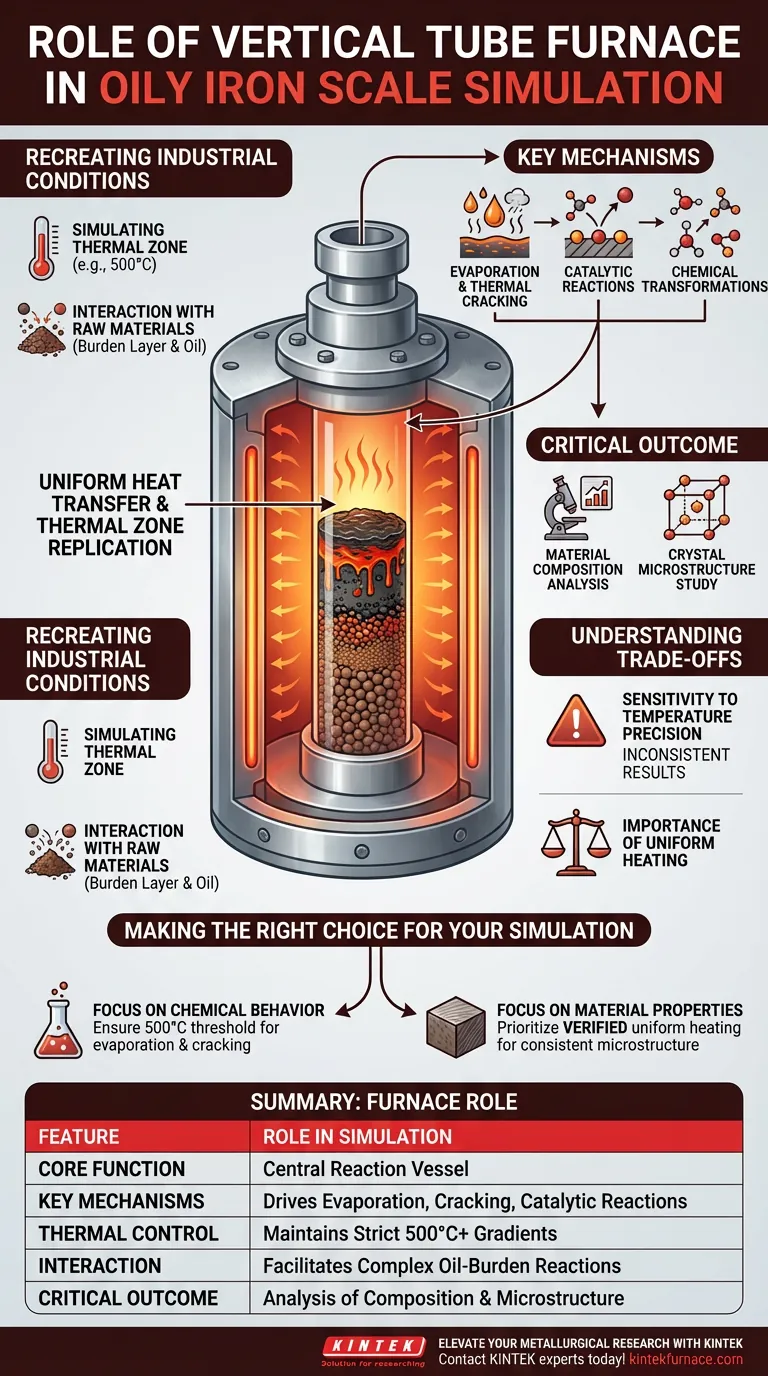
A vertical tube furnace acts as the central reaction vessel for physically simulating the behavior and distribution of oily iron scale components. It replicates the thermal zones of a blast furnace by heating iron ore raw materials, such as mixtures of pellets and sinter, to precise temperatures (e.g., 500°C).
The furnace's controlled environment is essential for triggering and observing specific chemical behaviors—namely evaporation, thermal cracking, and catalytic reactions—between the oil components and the burden layer under a strict temperature gradient.
Recreating Industrial Conditions
Simulating the Thermal Zone
The primary function of the vertical tube furnace in this context is to create a high-fidelity thermal simulation environment. By surrounding the sample tube with a heating element, the furnace facilitates efficient heat transfer.
This setup ensures uniform temperature distribution along the length of the sample. This uniformity is critical for mimicking the specific thermal zones found within an industrial blast furnace.
Interaction with Raw Materials
Inside the vertically oriented heating chamber, researchers place the iron ore raw materials. The furnace is designed to handle the complex interactions between these solids and the oily components being studied.
Mechanisms of Component Distribution
Driving Chemical Transformations
Once the precise temperature (such as 500°C) is reached, the furnace drives the transformation of the oil components. The heat forces the oil to undergo evaporation and thermal cracking, breaking down heavier molecules into lighter ones.
Facilitating Catalytic Reactions
Beyond simple heating, the furnace enables catalytic reactions between the oil derivatives and the burden layer (the iron ore mixture). The precise temperature gradient maintained by the furnace ensures these reactions occur under controlled, observable conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Temperature Precision
While these furnaces allow for the manipulation of material composition and microstructure, the validity of the simulation relies entirely on precise temperature control.
Fluctuations or lack of uniformity in the heating element can lead to inconsistent crystal structures or microstructures in the sample. If the temperature gradient is not maintained perfectly, the resulting properties will not accurately reflect the target industrial scenario.
How to Apply This to Your Research
## Making the Right Choice for Your Simulation
To effectively utilize a vertical tube furnace for oily iron scale simulation, align your setup with your specific research goals:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Behavior: Ensure the furnace can maintain the specific 500°C threshold required to trigger evaporation and thermal cracking of oil components.
- If your primary focus is Material Properties: Prioritize a furnace with verified uniform heating capabilities to ensure the burden layer's microstructure and crystal structure are processed consistently.
Reliable simulation data depends on the furnace's ability to maintain an unwavering thermal environment for complex catalytic interactions.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Oily Iron Scale Simulation |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Central reaction vessel for thermal zone replication |
| Key Mechanisms | Drives evaporation, thermal cracking, and catalytic reactions |
| Thermal Control | Maintains strict 500°C+ gradients for uniform heat transfer |
| Interaction | Facilitates complex reactions between oil and burden layers |
| Critical Outcome | Analysis of material composition and crystal microstructure |
Elevate Your Metallurgical Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of reliable physical simulations. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vertical Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces designed to meet the rigorous demands of iron and steel research.
Whether you are studying oily iron scale distribution or advanced material transformations, our systems offer the uniform heating and precise control necessary for high-fidelity results. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable for your unique laboratory needs.
Ready to optimize your simulation environment? Contact KINTEK experts today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- А. С. Харченко, E. O. Kharchenko. Modeling the distribution of components emitted from oiled scale between water, gas, and dust media in blast furnace dedusting plant. DOI: 10.17073/0368-0797-2025-4-332-338
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Reducing Gas in Tube Furnace Thermal Treatment? Unlock Pure Metallic Phases and Defects
- What is the primary use of a laboratory tube furnace in biomass carbonization processes? Precision Biochar Engineering
- How do high-temperature tube furnaces optimize the performance of ceramic materials during post-sintering annealing?
- What specific environmental conditions does a horizontal quartz tube furnace provide during boron diffusion? - KINTEK
- How are horizontal furnaces utilized in the automotive sector? Boost Component Durability and Efficiency
- Why are near alpha-titanium alloy ingots often sealed in quartz tubes? Unlock Superior Purity and Microstructure
- What features enable precise temperature control in a vertical tube furnace? Unlock Superior Thermal Accuracy for Your Lab
- Why must the final sintering of NiTiNb alloys be conducted in a high-vacuum tube furnace? Ensure Pure Shape Memory Performance



















