High-temperature tube furnaces optimize ceramic performance by providing a rigorously controlled environment specifically designed for stress relief and microstructural refinement. Through the application of precise temperature curves and stable soaking phases, these furnaces eliminate the residual thermal stresses inherent in the initial sintering process while actively reorganizing grain boundaries. This controlled post-processing is the defining factor in transforming a sintered shape into a mechanically reliable and thermally stable component.
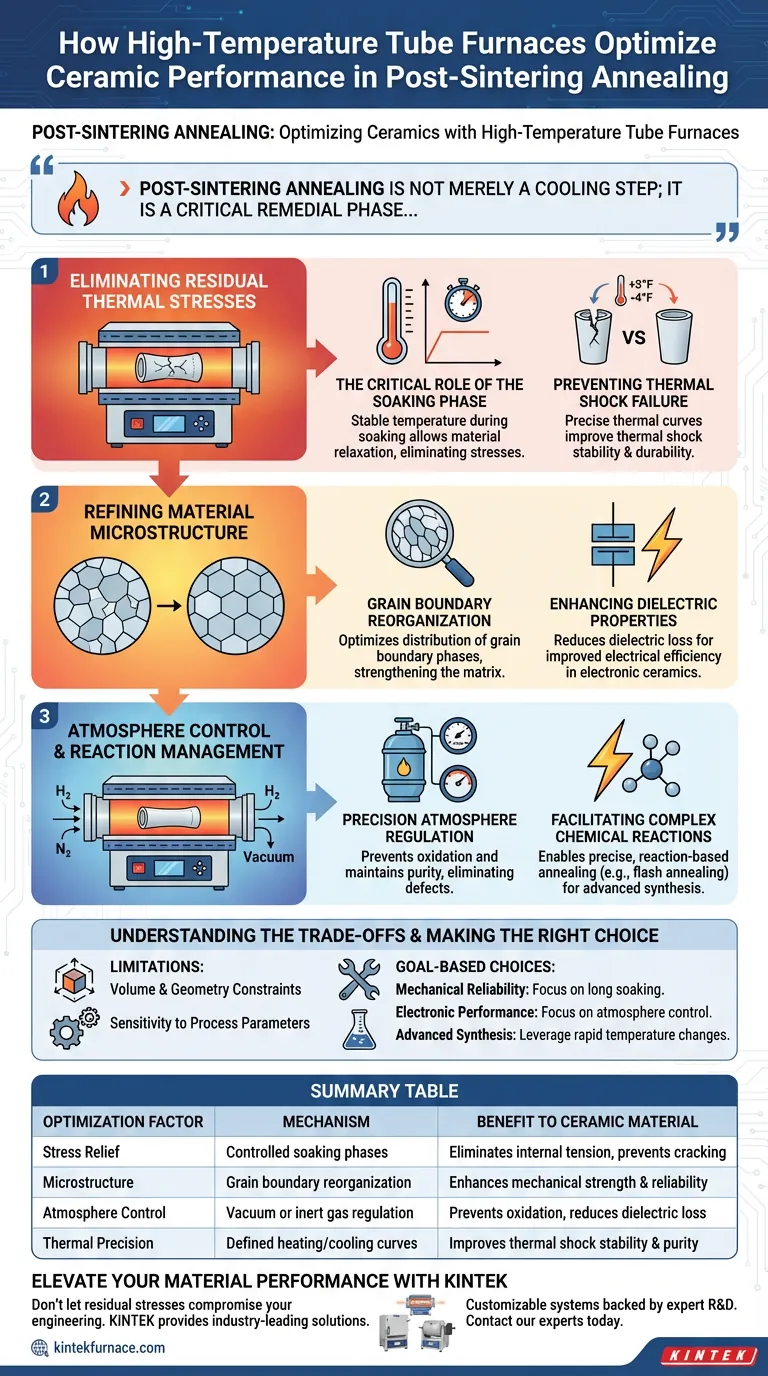
Post-sintering annealing is not merely a cooling step; it is a critical remedial phase. By maintaining precise thermal and atmospheric conditions, tube furnaces correct internal instabilities to enhance the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of the final product.
Eliminating Residual Thermal Stresses
The Critical Role of the Soaking Phase
Sintering often leaves ceramic materials with significant internal tension due to rapid heating or cooling. High-temperature tube furnaces address this by maintaining a highly stable temperature during the soaking phase. This dwell time allows the material to relax, effectively eliminating residual thermal stresses that could lead to cracking or failure.
Preventing Thermal Shock Failure
When internal stresses are removed, the material's resistance to rapid temperature changes improves. The precise heating and cooling curves provided by the tube furnace ensure that the ceramic develops superior thermal shock stability. This makes the final product far more durable during actual service conditions.
Refining Material Microstructure
Grain Boundary Reorganization
Beyond simple stress relief, these furnaces facilitate the physical reorganization of the material's internal structure. The process optimizes the distribution of grain boundary phases, which are often the weak points in a ceramic matrix. Strengthening these boundaries directly enhances the mechanical reliability of the product.
Enhancing Dielectric Properties
For electronic ceramics, microstructural flaws can lead to poor performance. By optimizing the grain boundary phases, post-sintering annealing significantly reduces dielectric loss. This results in a material that is not only mechanically stronger but also electrically more efficient.
Atmosphere Control and Reaction Management
Precision Atmosphere Regulation
A distinct advantage of tube furnaces is the ability to control the annealing atmosphere. Whether utilizing a vacuum or specific gases, this control prevents unwanted oxidation and maintains material purity. This is essential for eliminating defects like oxygen vacancies, which can degrade optical transparency or mechanical strength.
Facilitating Complex Chemical Reactions
In advanced applications, these furnaces allow for precise, reaction-based annealing. For example, in flash annealing processes, the furnace can maintain instantaneous high temperatures (such as 1100°C) to induce specific chemical changes. This capability is used to synthesize complex matrices, such as regulating the modulus of micron-sized SiOx anode materials through rapid disproportionation reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Volume and Geometry Limitations
While tube furnaces offer exceptional precision, they are constrained by their physical geometry. The diameter of the tube limits the size and volume of the ceramic components that can be processed. They are less suitable for high-volume mass production of large, bulky items compared to continuous tunnel kilns.
Sensitivity to Process Parameters
The effectiveness of the annealing process relies entirely on the accuracy of the programmed thermal curves. Incorrect soaking times or cooling rates can fail to relieve stress or, conversely, induce new grain growth that weakens the material. The precision of the tool requires an equally precise understanding of the material's thermal properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a high-temperature tube furnace for your specific application, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Reliability: Prioritize long soaking phases to ensure complete relaxation of residual thermal stresses and optimization of grain boundaries.
- If your primary focus is Electronic Performance: Focus on atmosphere control and precise cooling curves to minimize dielectric loss and eliminate oxygen vacancies.
- If your primary focus is Advanced Material Synthesis: Leverage the furnace's ability to handle rapid temperature changes for flash annealing to induce specific chemical reactions within the matrix.
The ultimate value of a high-temperature tube furnace lies in its ability to turn a formed part into a finished, engineering-grade component through precise thermal management.
Summary Table:
| Optimization Factor | Mechanism | Benefit to Ceramic Material |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Relief | Controlled soaking phases | Eliminates internal tension and prevents cracking |
| Microstructure | Grain boundary reorganization | Enhances mechanical strength and reliability |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum or inert gas regulation | Prevents oxidation and reduces dielectric loss |
| Thermal Precision | Defined heating/cooling curves | Improves thermal shock stability and purity |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Don't let residual stresses compromise your ceramic engineering. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of post-sintering annealing.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to your unique microstructural requirements, ensuring your components achieve peak mechanical and electrical efficiency.
Ready to refine your thermal processing? Contact our experts today to discover how KINTEK’s precision furnaces can transform your laboratory results.
Visual Guide
References
- Muthukumaran Ramasamy, Hamad A. Al‐Lohedan. Characterization on properties of Al7050/TiC/BN hybrid metal matrix composite. DOI: 10.1063/5.0204280
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do the heating elements in a tube furnace function? Uncover Key Insights for Precise Heating
- How are horizontal furnaces used in materials science? Unlock Precision in Heat Treatment
- What role do tubular furnaces play in heat treatment processes? Precision Control for Material Properties
- How does a vacuum tube furnace serve as the core equipment in the consolidation of Ti-xCr-2Ge alloys?
- Why is the encapsulation of raw materials in a vacuum-sealed quartz tube necessary for crystal growth? Key to Purity
- What critical physical environment does a tube furnace provide for iron ore? Master Precision Reduction Control
- Can a quartz tube furnace be used for melting materials? Unlock Precise Melting with Visual Control
- What is the primary function of a Drop Tube Furnace (DTF)? Simulating Industrial Combustion for Research



















